Resource utilization efficiency during hand-off in mobile communication systems
a mobile communication system and resource utilization efficiency technology, applied in the field of wireless communication systems, can solve the problems of data packet loss, data throughput drop, missing or delayed acknowledgment signals, etc., and achieve the effect of avoiding disadvantages and maintaining data throughpu
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
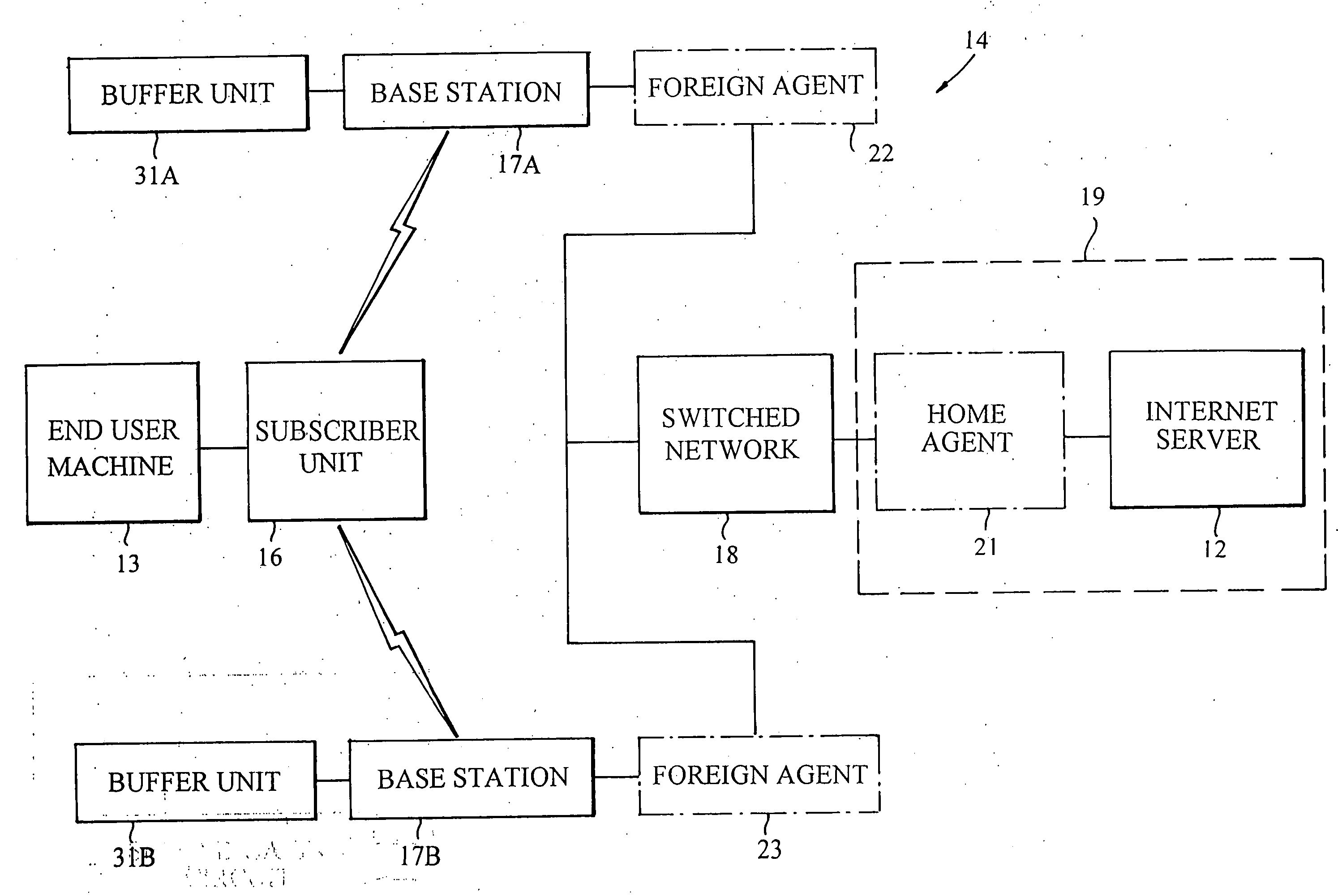
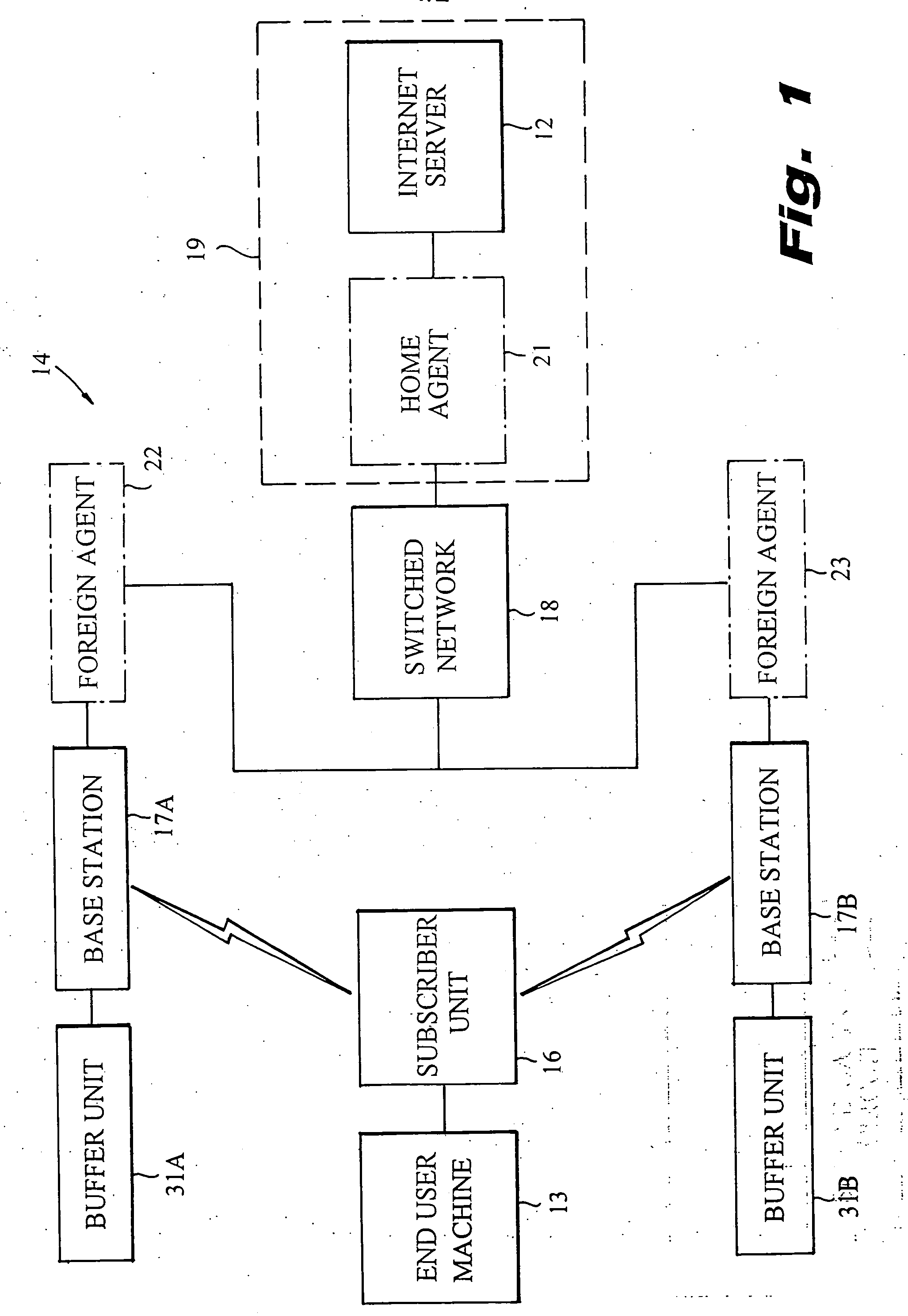
[0012] Referring to FIG. 1, there is depicted a wireless communication system 11, such as a cellular packet network, which illustratively operates according to the Mobile IP protocol. The system 11 is adapted for the two-way transmission of digital data packets between an Internet server 12 and an end user machine 13. The end user machine 13 may be a laptop computer, a portable computer, a personal digital assistant (PDA), or the like, which may be moved from place to place.
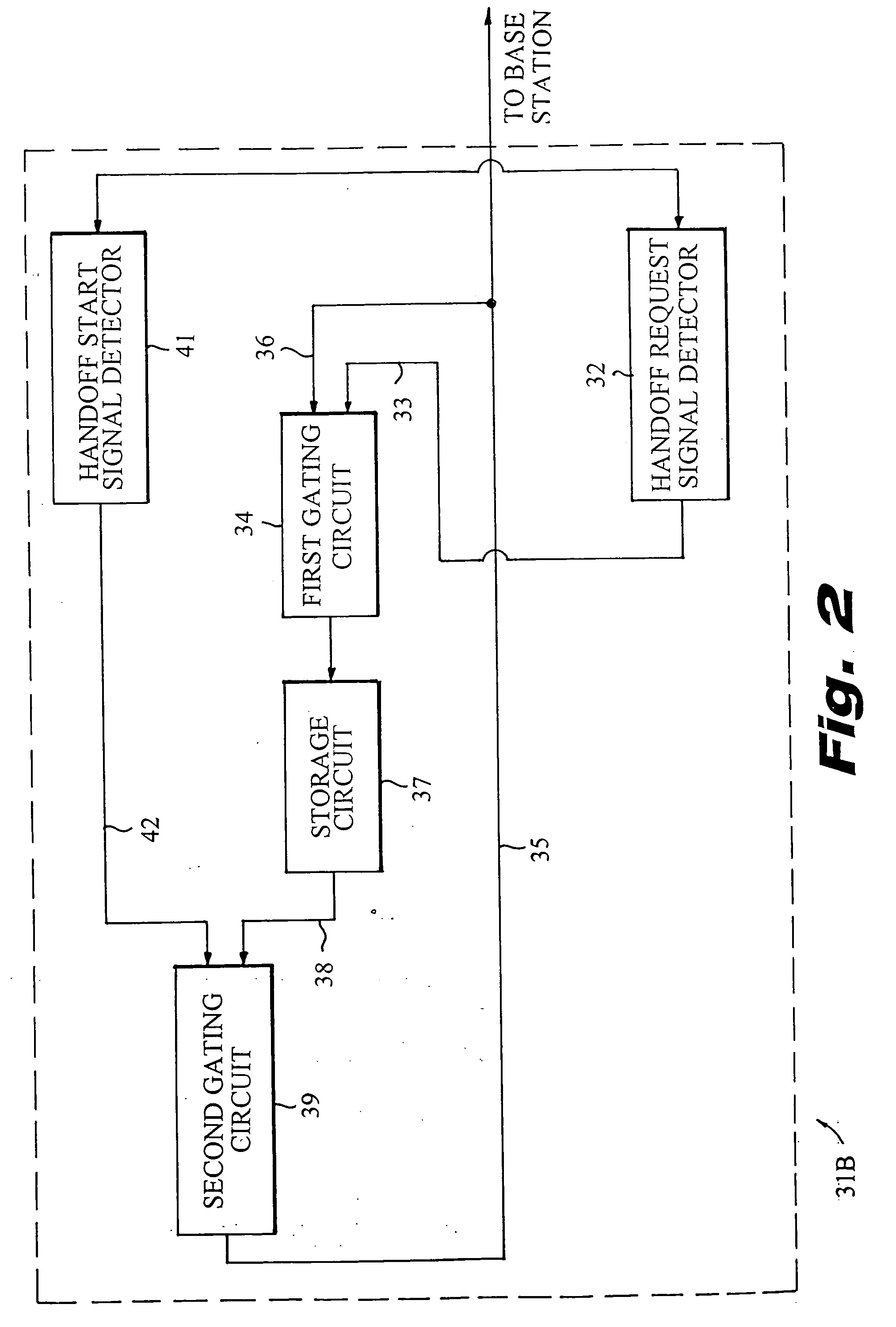
[0013] The system 11 has a wireless link 14 that includes a mobile subscriber unit 16 and a multiplicity of base stations 17, two of which (identified as 17A and 17B) are illustrated. The subscriber unit 16 is coupled to the end user machine 13. The base stations 17A and 17B are connected to the server 12 through a switched network 18, illustratively the Internet. Data packets transmitted from the server 12 to the end user machine 13 are routed through the switched network 18, a selected one of the base stations...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com