Pumped fluid cooling system and method
a pumped fluid and cooling system technology, applied in the field of cooling systems, can solve the problems of low heat capacity and high viscosity, inefficient pumped fluid system, and large values of rsub>convection/sub>, and achieve the effect of efficient cooling a device, decreasing a spread resistance and reducing a convection resistan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
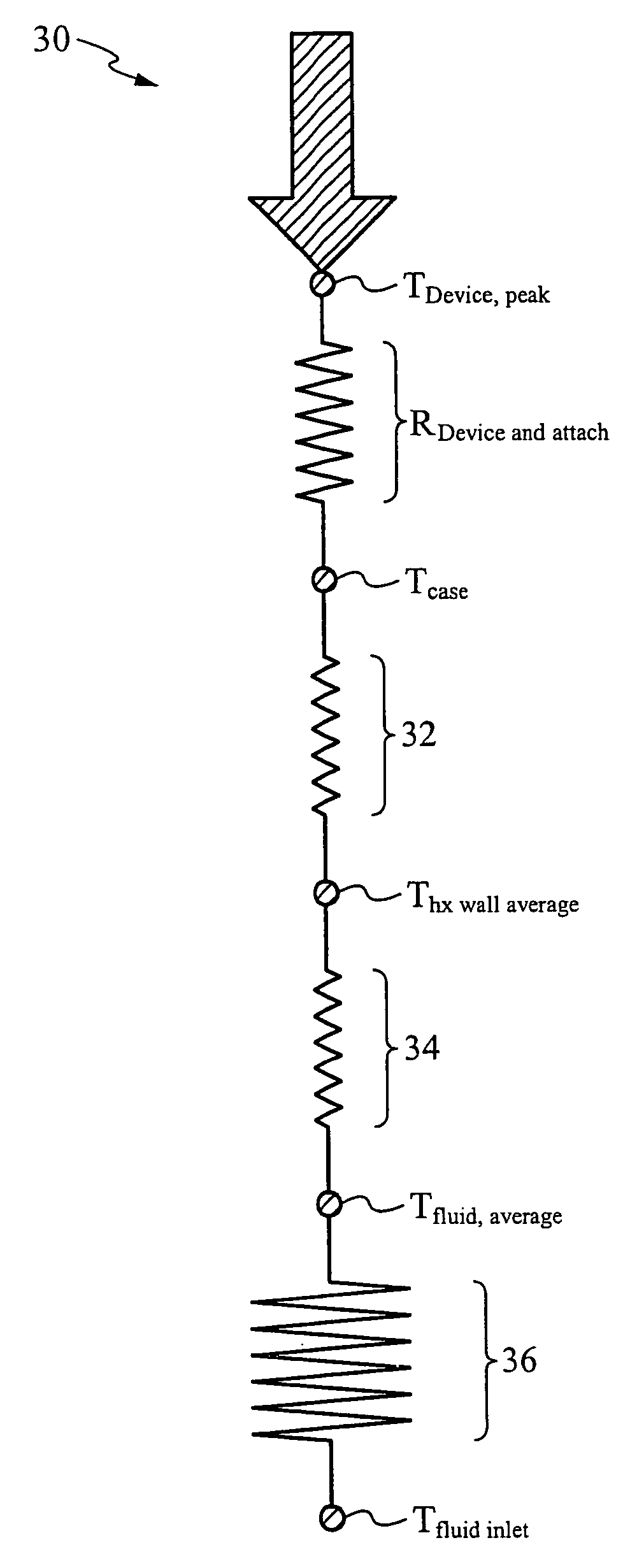
[0028]FIG. 3 is a graphical representation of the preferred embodiment of the present invention. The preferred embodiment of the present invention includes new relative magnitudes of the advection 36, convection 34, and spreading 32 components of the resistance for a pumped fluidic system (PFS) 30, which enable lower pump flowrates and, consequently, pumps that are smaller and consume less power. The new relative magnitudes of these resistances are enabled by a micro hx as described below with feature sizes in the range of 15-300 microns. Still referring to FIG. 3, this micro hx of the PFS 30 of the preferred embodiment of the present invention allows for a smaller spread resistance 32 and smaller convection resistance 34, thereby conserving the temperature budget. This conservation allows for a higher advection 36 component.
[0029] Referring back to the advection formula once again, C / mc where m is the flowrate, reducing the flowrate m will cause the advection 36 component to incre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com