System and method for detecting errors in a network
a network error and network technology, applied in the field of communication networks, can solve the problems of insufficient efficiency, increased difficulty in isolating network errors, and decreased efficiency, and achieve the effects of efficiently and accurately detecting network errors, network errors, and efficient detection and reporting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Introduction
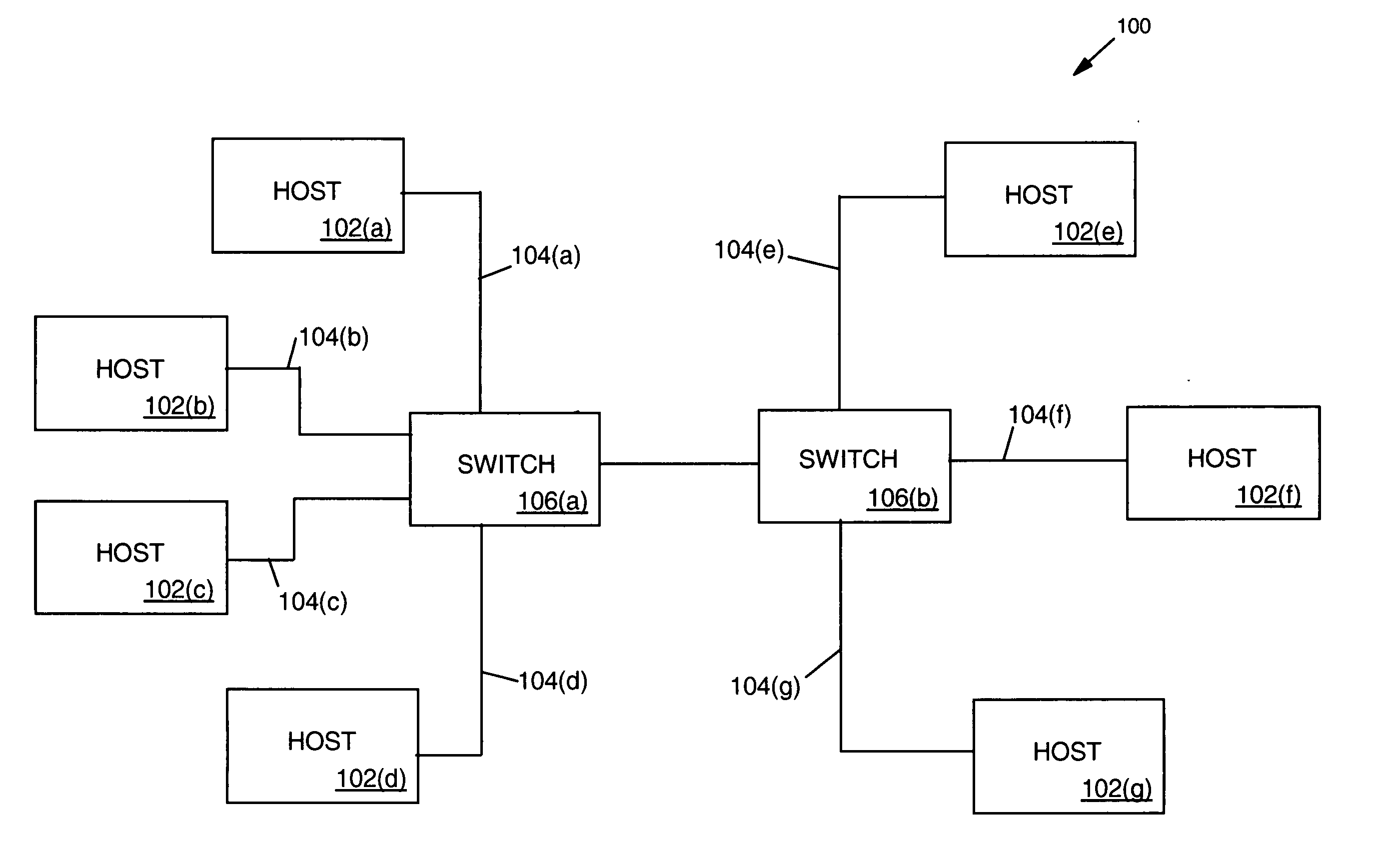
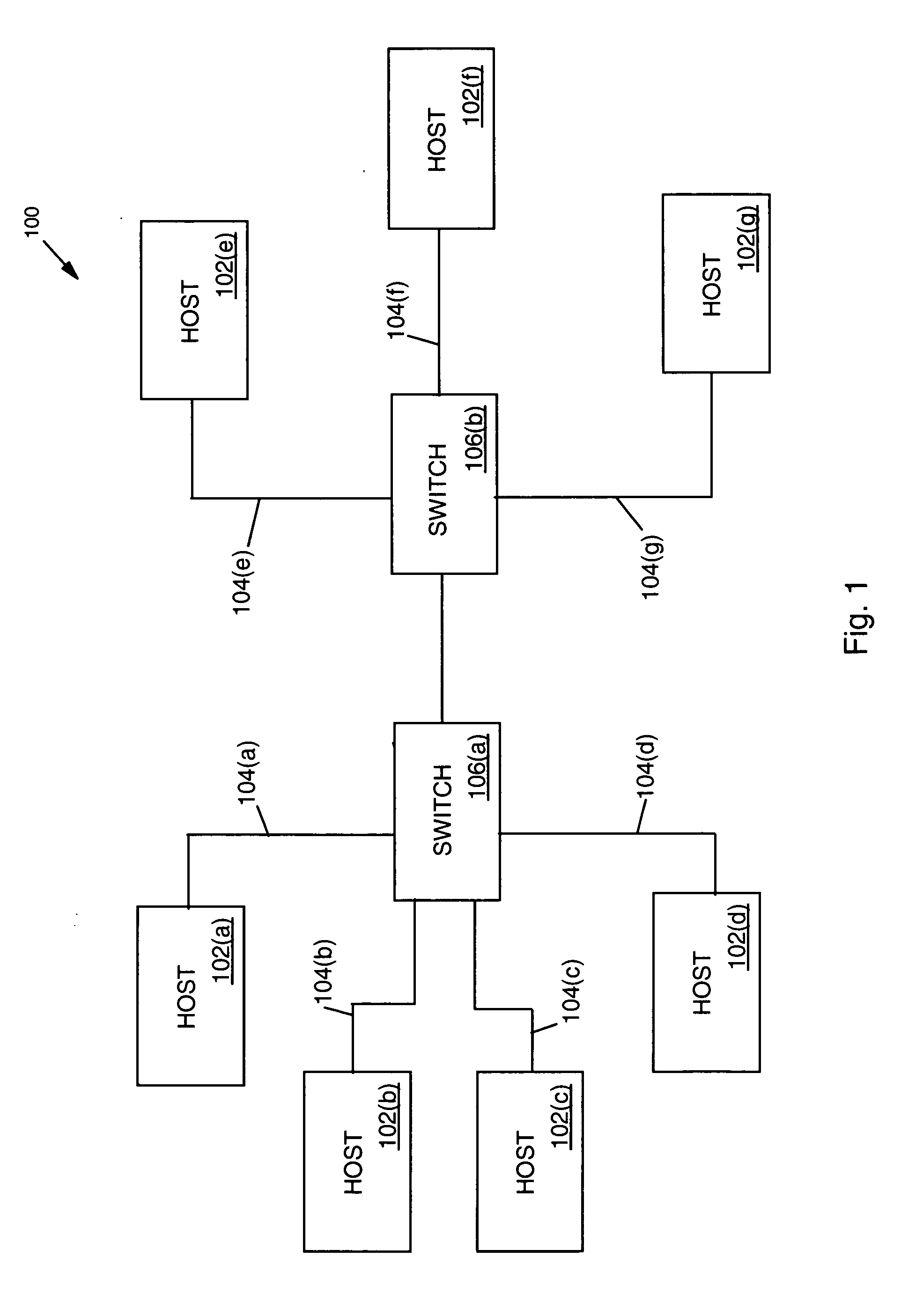
[0019] The detection and isolation of errors in a communication network is crucial to the successful operation of the network. Accordingly, the present invention provides a system and method for efficiently and accurately detecting errors in a network. Explained in greater detail below and in accordance with the present invention, devices coupled to a network are configured to determine their local network status and transmit their local network status to a network analyzer. The network analyzer is configured to receive the local network status from each device and provide network status for the entire network in accordance with the present invention. The network analyzer is also configured to analyze the collective network status information and report any network errors and / or present the information in a format that allows a user of the network to quickly determine the configuration and status of the network (such as a computer generated graphical representation of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com