Laser perimeter awareness system
a perimeter awareness and laser technology, applied in surveying and navigation, distance measurement, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient current perimeter security systems and processes, radar “clutter”, video cameras, night vision systems,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
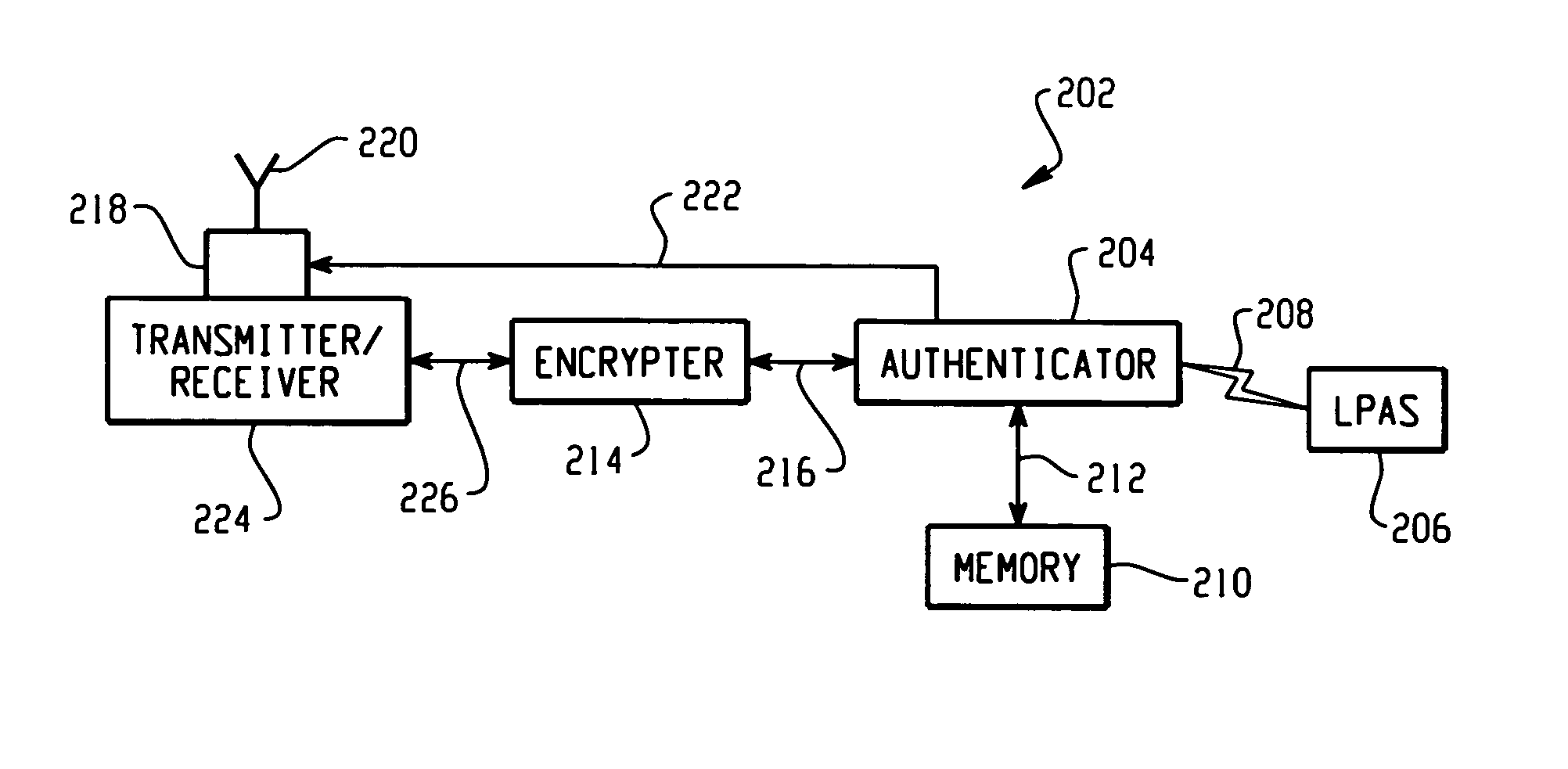
[0033] Developed initially for helicopters to avoid striking power lines and other ground obstacles, wide field scanning laser obstacle awareness systems such as the system disclosed in the U.S. Pat. No. 6,542,227, issued Apr. 1, 2003, for example, have been found applicable to monitoring objects within a perimeter around a vulnerable target for threat awareness and to search and rescue operations which will become more evident from the description found herein below. The aforementioned U.S. Pat. No. 6,542,227 which is assigned to the same assignee as the instant application is hereby incorporated by reference herein for providing greater detail of the structure and operation of an exemplary scanning laser obstacle awareness system (LOAS). In the development and testing of the LOAS over water several key phenomena were discovered. As noted in the aforementioned U.S. patent, the exemplary LOAS uses a 1550 nm near-infrared wavelength laser with variable fields of view, a distributed f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com