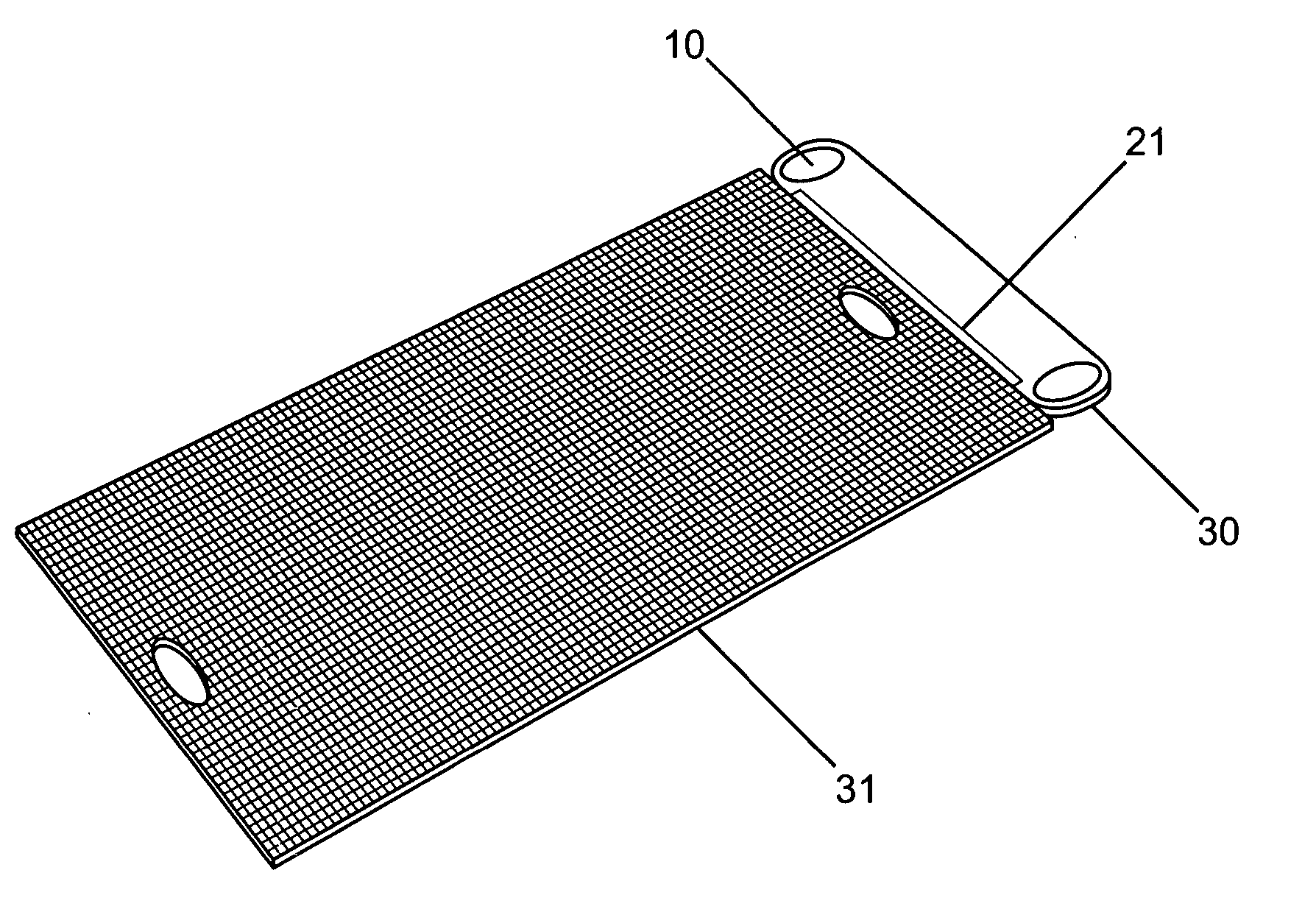
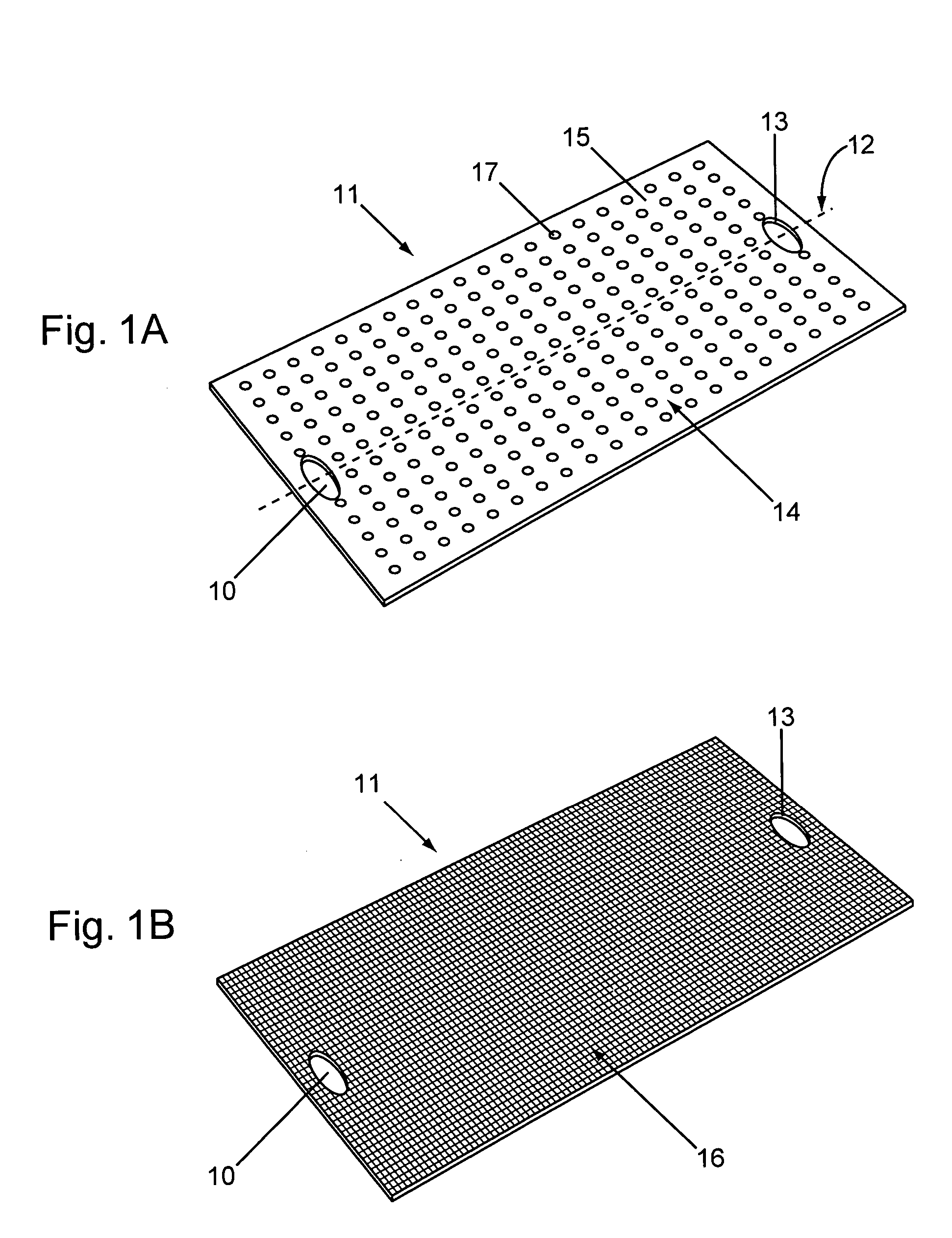
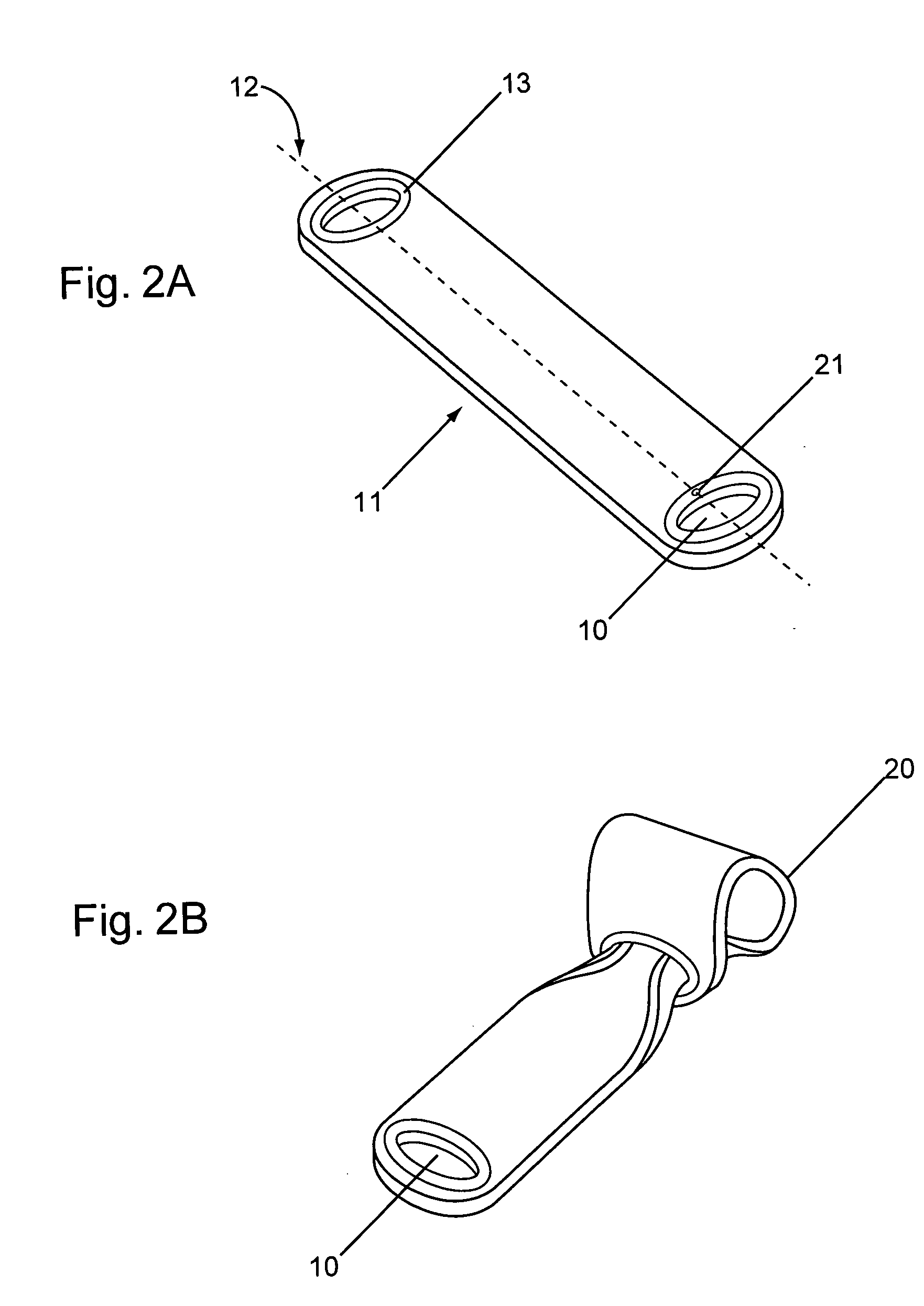
[0009] Composite yoga mats of the invention can provide unique combinations of practical functions not available from traditional yoga mats. Yoga mats of the invention can absorb
moisture,
control transfer of
moisture, provide
cushioning, insulate, provide stability, present functional information, be lightweight and portable, and / or the like. Yoga mats of the invention generally comprise, e.g., a moisture absorbent fabric sheet having a moisture absorbent first side surface, and a frictional material disposed on the fabric sheet second side to provide-
cushioning and a stable yoga practice surface.
[0010] The moisture absorbent fabric sheet of the yoga mats can include shapes and materials suitable for particular intended uses within the field of yoga practice. The strength and absorbency of yoga mats can be influenced by the choice of materials. The yoga mats can be manufactured from, e.g., terry cloth, chamois, synthetic chamois, hydrophilic fibers, fibers with a
hydrophilic coating, a combination of absorbent and nonabsorbent fibers, microfibers, nanofibers, fibers embedded with a rubber,
plant fibers,
cellulose,
polyester, hemp, cotton, paper, and / or the like. More absorbent materials can be preferred in high moister yoga environments, while stronger or more cushioned materials can be preferred for more dynamic aerobic forms of yoga. Yoga mats of the invention can have a fabric sheet width, e.g., less than about 3 or 4 feet and a length less than about 6 or 7 feet; larger sizes can provide bigger practice surfaces, or narrower dimensions can be well suited for yoga mats focusing on strap / loop support utilities. The yoga mat fabric sheet can have a reinforced
peripheral edge to provide strength and
wear resistance. Yoga mats of the invention can have, e.g., fabric sheets with two or more opposing loop holes adjacent to the
peripheral edge with holes large enough to make a loop by
insertion of the other end of the mat, or large enough to insert fingers, hands, feet, etc., for support in particular yoga positions. The loop holes often have an internal circumference more than about 6 inches.
[0011] In one embodiment, yoga mats of the invention are configured to support yoga practitioners in strenuous or difficult positions. For example, a yoga mat can be provided with dimensions and loop holes well adapted for use in a functional yoga strap configuration. The fabric sheet can have, e.g., two or more opposing loop holes with an internal circumference of more than about 6 inches adjacent to a reinforced
peripheral edge so that yoga positions can be learned or practiced by
insertion of body appendages into the loop holes or constrictable loops formed with the mat. Loop holes can be made more strong and
wear resistant by reinforcing the internal circumference. Yoga mats configured for use as yoga straps typically have narrow dimensions with loop holes on the ends. For example, the yoga mats can have a length more than about 3 feet while the width is about 18 inches, 12 inches, 6 inches, or less. Intermediate loop holes can be included to provide a range of possible support locations on a mat or choice of constrictable loop sizes.
[0014] The present invention includes methods of practicing yoga using the composite yoga mats of the invention. The unique combination of features provided by the yoga mats of the invention allows, e.g., practice of yoga in an environment unavailable with traditional mats. Composite yoga mats provide a stable, dry location for yoga exercises, loop supports for difficult positions, and the ability to expand or thicken the practice surface. DEFINITIONS
[0017] The term “Composite yoga mat” or yoga mat of the invention, as used herein, refers to a yoga mat fabricated from two or more materials, or two or more structural elements, to provide functions adapted to the practice of yoga. For example, composite yoga mats can be fabricated with a combination of a moisture
absorbent material and a frictional material. A composite yoga mat can be fabricated to include various structural elements including combinations of loop holes for gripping and supporting, frictional surfaces to prevent slipping, reinforced edges to add strength and comfort, patterns and / or indicia to provide positioning references and an attractive appearance, connectors to maintain a compact roll or bind multiple mats together, long thin mats to function as pads and straps, large wide mats to provide an adequate defined yoga practice surface, and / or the like.
[0019] The term “frictional material”, as used herein, refers to materials disposed on fabric sheets of the invention to provide reduced slippage between the yoga mat and the yoga practitioner or the floor. Frictional materials can include, e.g., materials with a
coefficient of friction greater than that of the fabric sheet. Frictional materials can include, e.g., materials with a coefficient of static or
kinetic friction greater than about 0.6 in contact with typical surfaces encountered in yoga practice. Typical frictional materials of the invention include, e.g., rubber,
foam rubber, resilient polymers, polyvinyl foam,
sponge,
cork,
silicone rubber, and the like. Frictional materials can also contribute other characteristics to the composite mats of the invention, such as, e.g., cushioning, absorbency, ornamental designs,
toughness, and the like.
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More