System and method for delivering a left atrial appendage containment device
a technology of containment device and left atrial appendage, which is applied in the field of system and method for delivering a left atrial appendage containment device, can solve the problems of irregular and turbulent blood flow in the vascular system, rapid and chaotic heartbeat that produces lower cardiac output, and patients with atrial fibrillation typically have a significantly decreased quality of life, and fail to contract with any vigor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
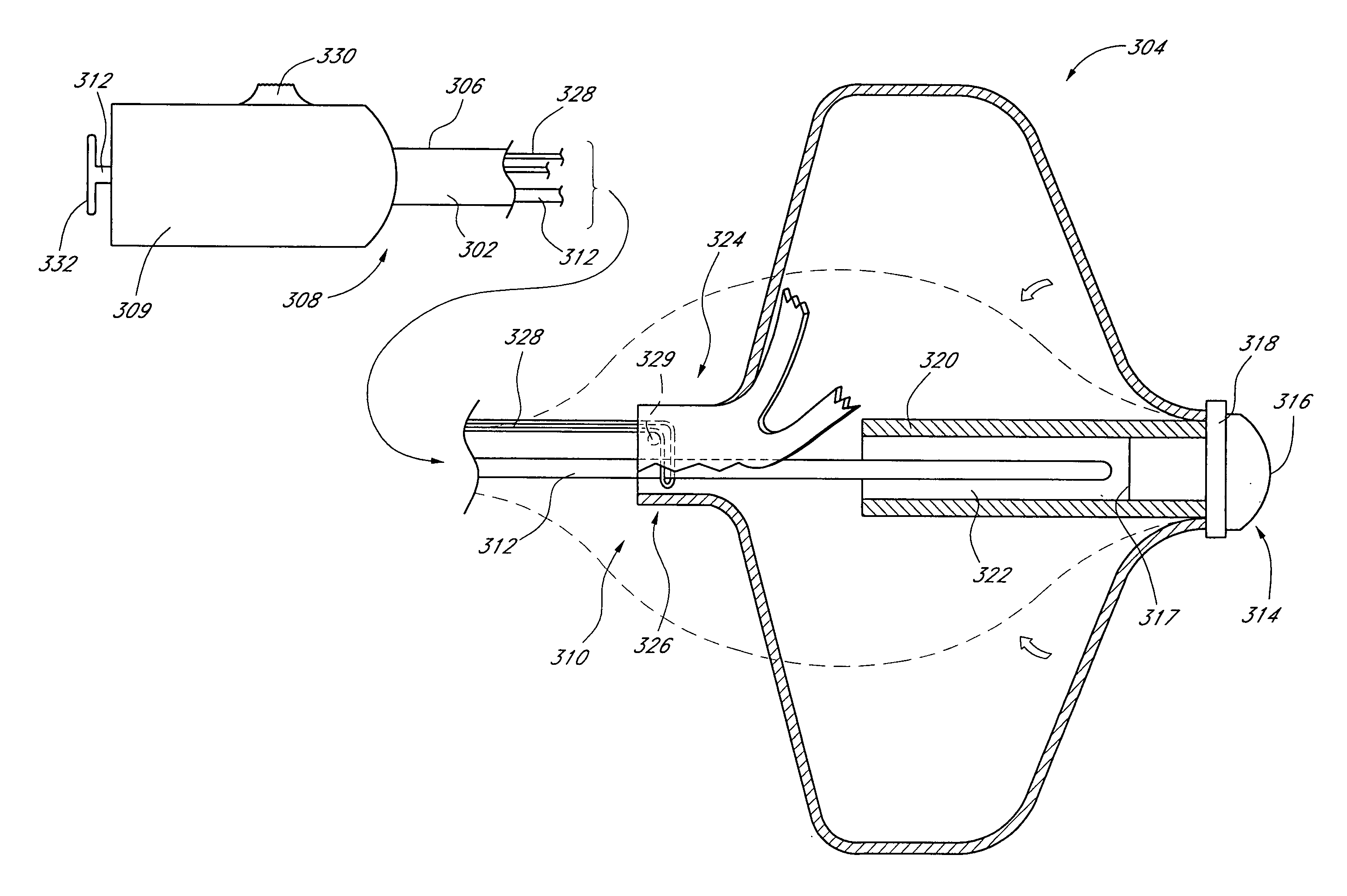
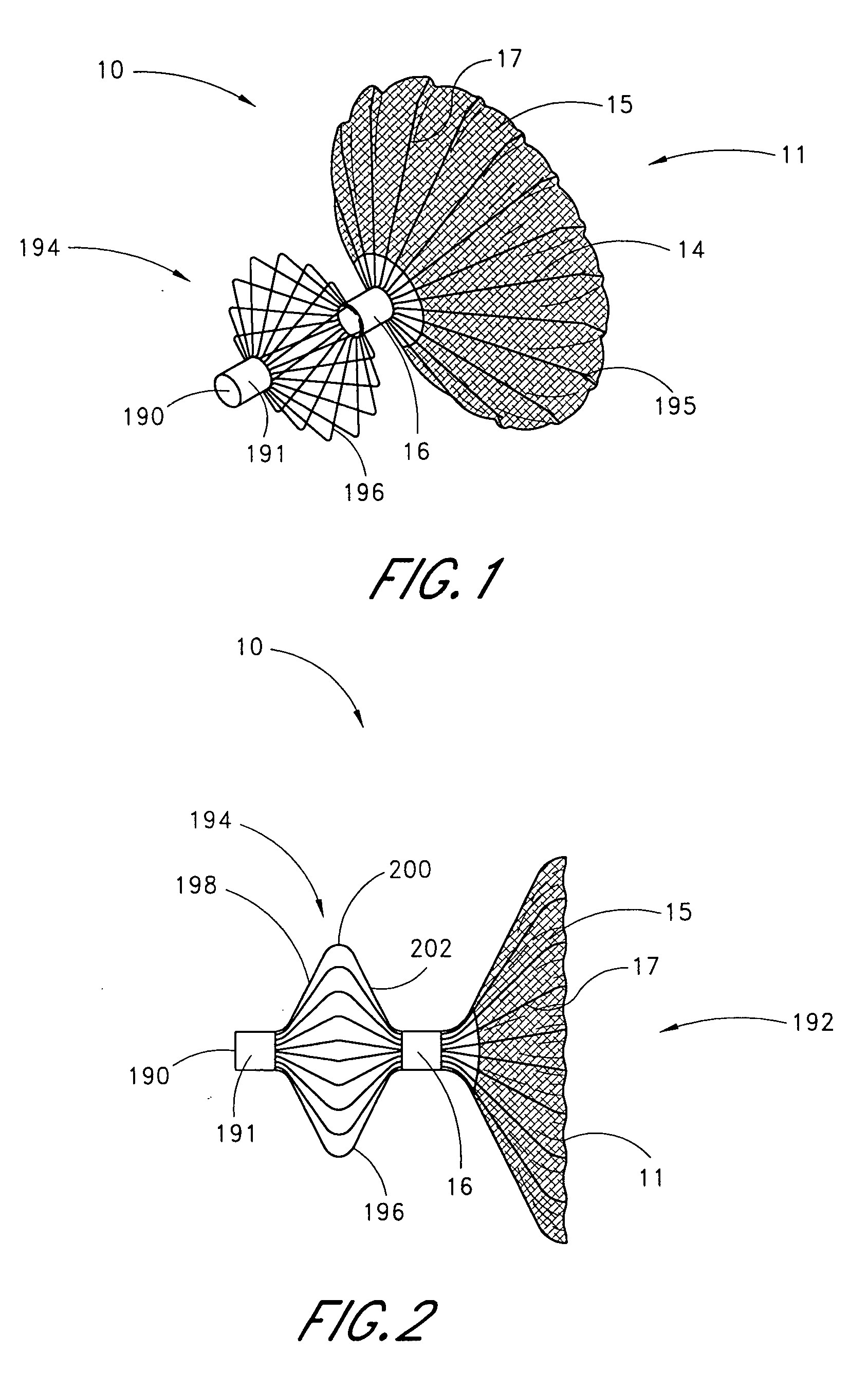
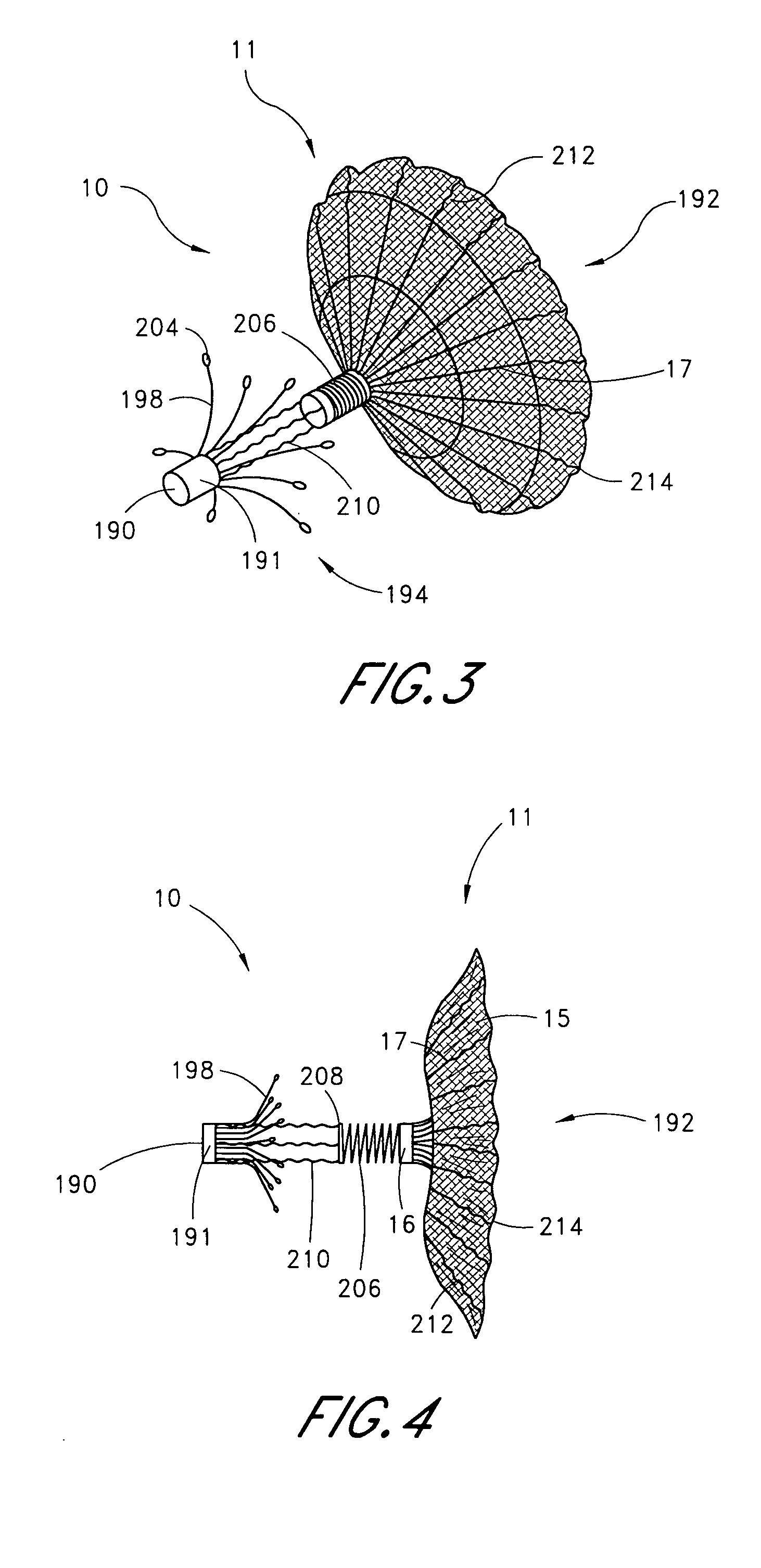
[0103] Referring to FIGS. 1 and 2, there is illustrated one embodiment of an occlusion or containment device 10 in accordance with the present invention. Although the present invention will be described primarily in the context of an occlusion device, the present inventors also contemplate omitting the fabric cover or enlarging the pore size to produce implantable filters or other devices which are enlargeable at a remote implantation site. The terms “occlusion device” or “containment device” are intended to encompass all such devices.
[0104] The occlusion device 10 comprises an occluding member 11 comprising a frame 14 and a barrier 15. In the illustrated embodiment, the frame 14 comprises a plurality of radially outwardly extending spokes 17 each having a length within the range of from about 0.5 cm to about 2 cm from a hub 16. In one embodiment, the spokes have an axial length of about 1.5 cm. Depending upon the desired introduction crossing profile of the collapsed occlusion dev...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com