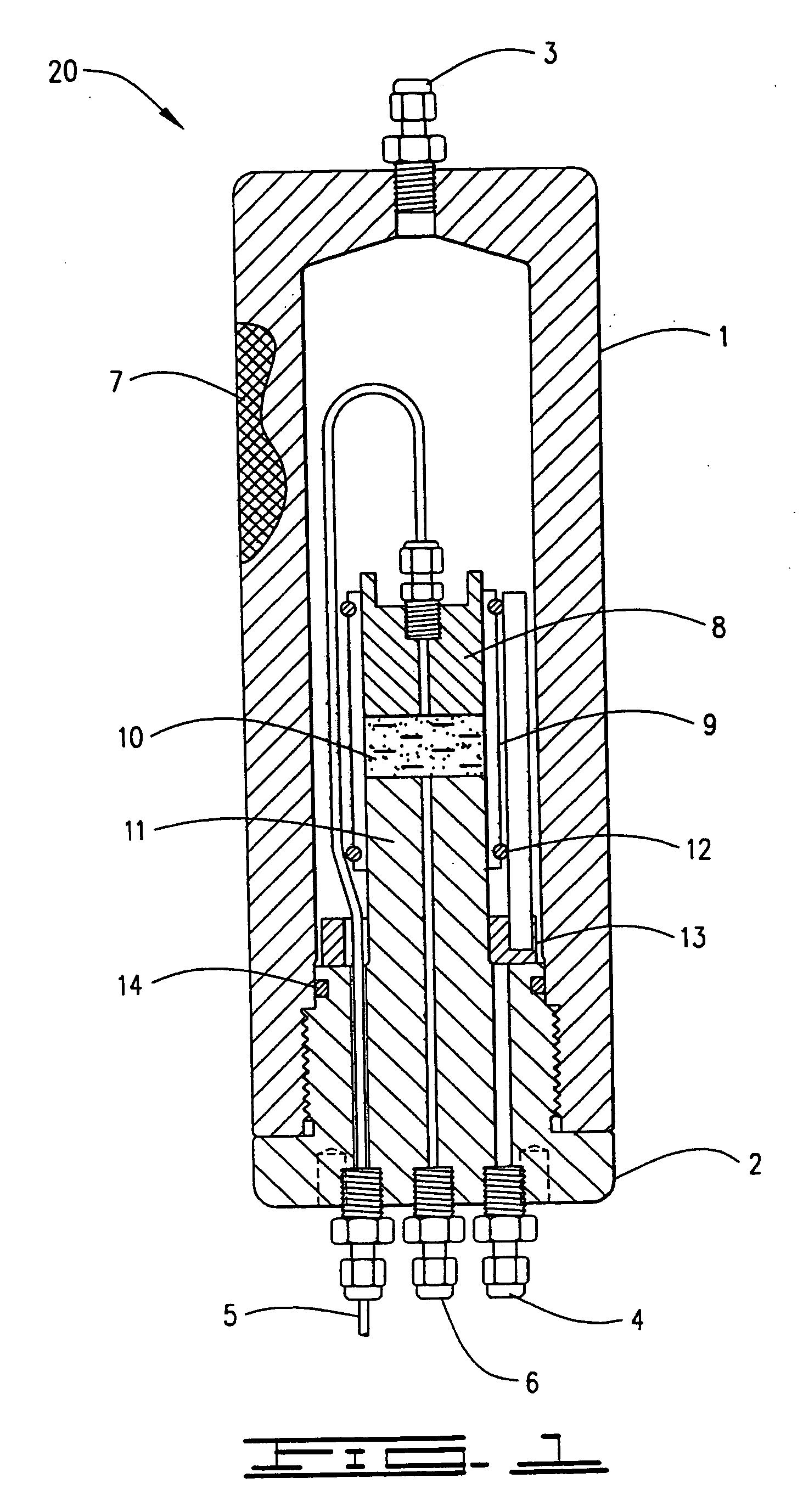
Cementing fluid for enhancing the stability of a water sensitive, reactive subterranean formation
a subterranean formation and cementing fluid technology, applied in the direction of sealing/packing, wellbore/well accessories, chemistry apparatus and processes, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the stability of wellbores, substantial annual expenditure of petroleum industry, and inconsistent use of salts in cement slurries, etc., to achieve the effect of enhancing the stability of a water sensitive, reactive formation, and low water activity levels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
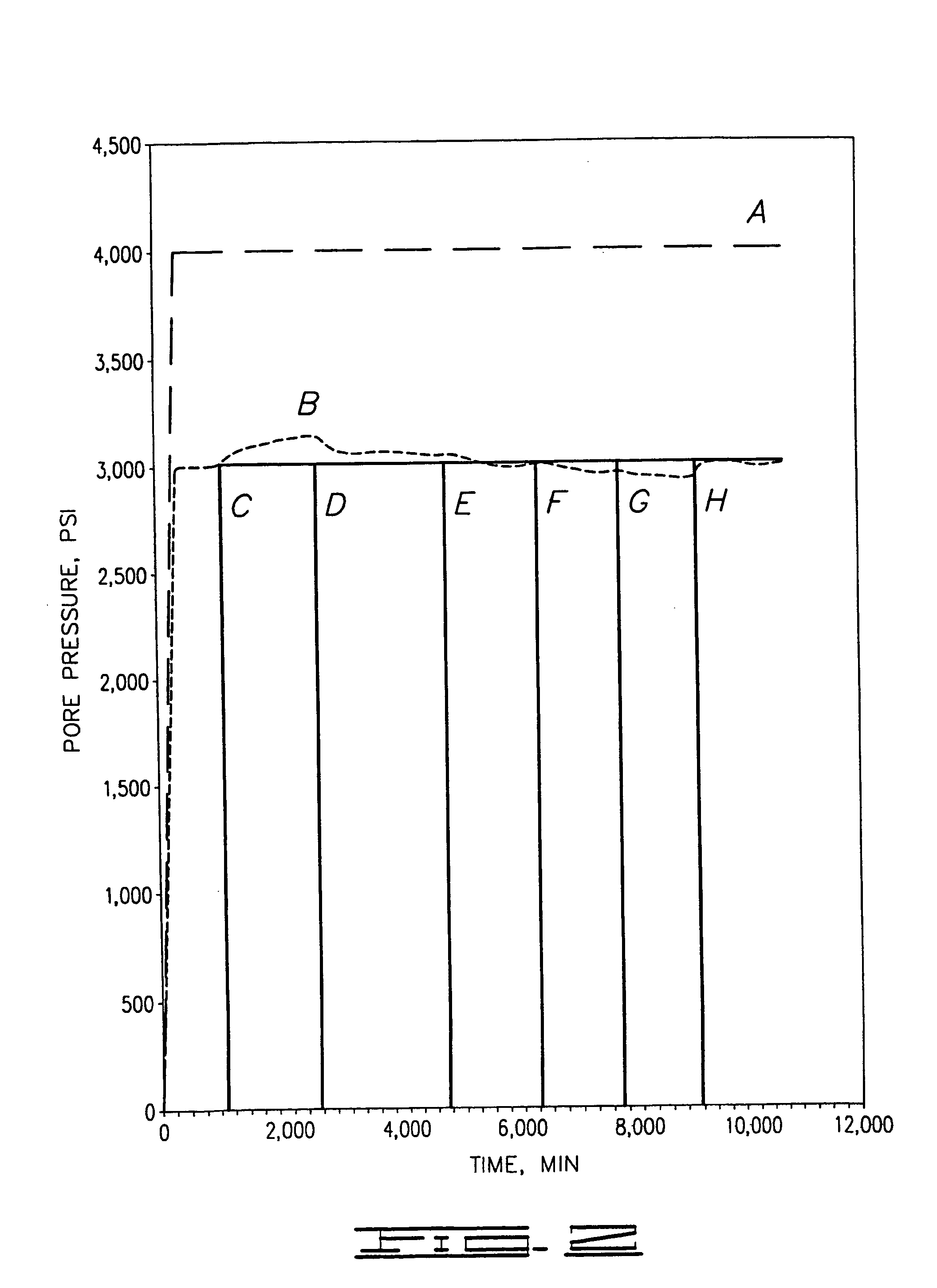
[0042] With reference to FIG. 2, Example 1 demonstrates how variations in salt content can influence pore pressure. In this example, a sample of shale was stabilized with a solution of 8% NaCl. The sample was placed under a confining pressure, represented by line A, of 27.6 MPa (4000 psi) and exposed to various concentrations of a KCl solution. The change in pore pressure was monitored and is represented in FIG. 2 as line B. The shale was exposed to the following concentrations of KCl solution as represented by lines C through G respectively: 1%, 4%, 8%, 15% and 20%. The final solution contained 8% NaCl and is represented by line H. As reflected by line B, the pore pressure within the shale increased when exposed to the 1% and 4% solutions of KCl due to the net imbalance in salinity. The 8% KCl solution resulted in a gradual reduction of pore pressure to approximately that of the shale prior to exposure to any upstream fluid. The 15% and 20% KCl solutions demonstrate a clear reducti...
examples 2-5
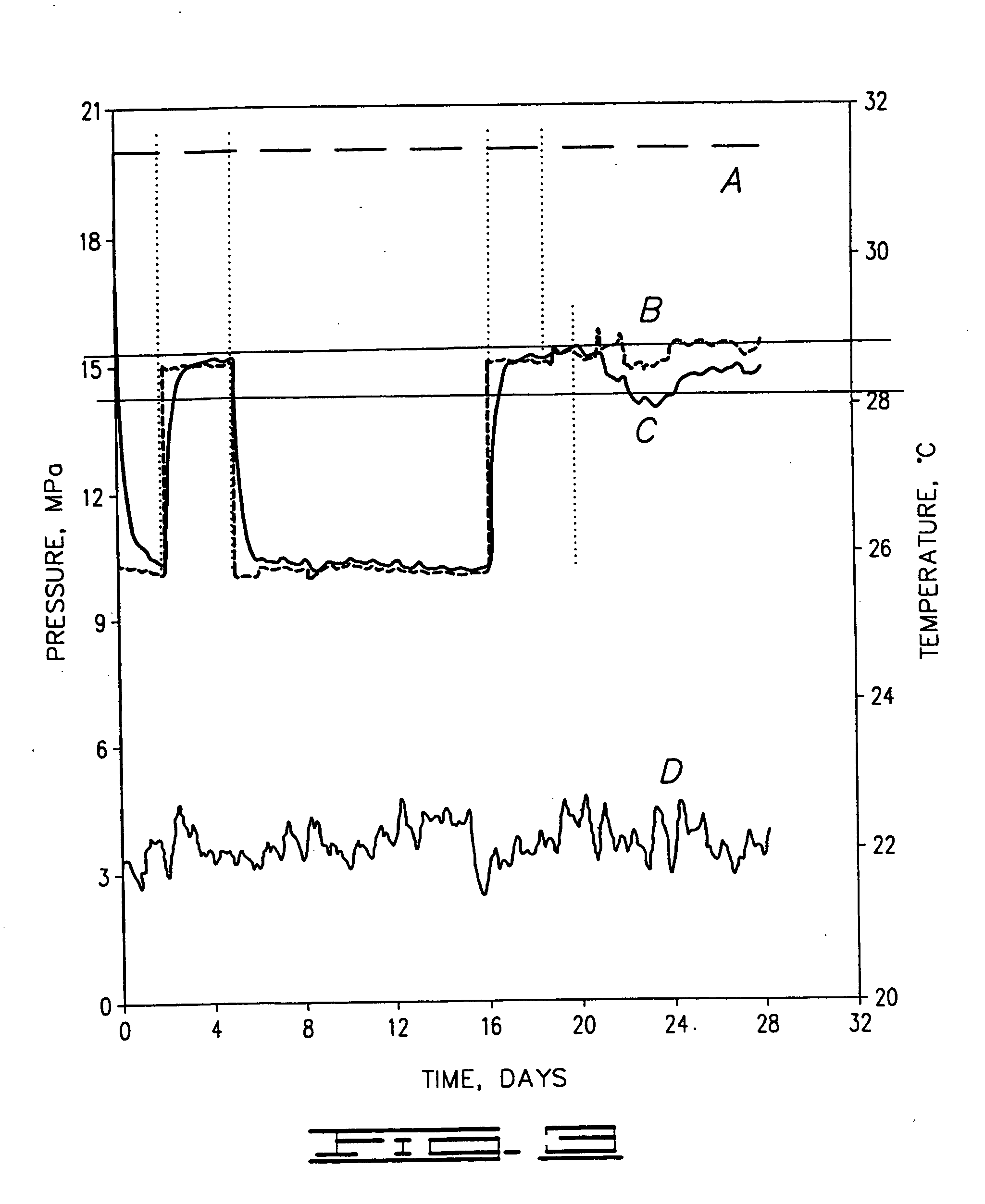
[0043] For Examples 2-5, FIGS. 3-6 depict the variation in both upstream and downstream pressures, as represented by lines B and C respectively, during performance of the testing method described above. The confining pressure applied to the shale sample is represented by line A. The temperature of the test cell is represented by line D.
[0044] The initial increase in downstream pressure reflects the performance of the Back-pressure Saturation step. The drop in pressure represents the subsequent Consolidation step. Thereafter, changes in downstream pressure are influenced by the application of upstream pressure to the shale sample. On about day 2 of each test, upstream pressure (Pore Fluid Pressure Transmission) is applied to the sample. This increase in upstream pressure reflects the expected pressure to be applied by the cementing fluid in the downhole environment. This pressure is removed and the sample allowed to re-consolidate as reflected by the drop in pressured depicted by bo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore pressure capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore pressure capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com