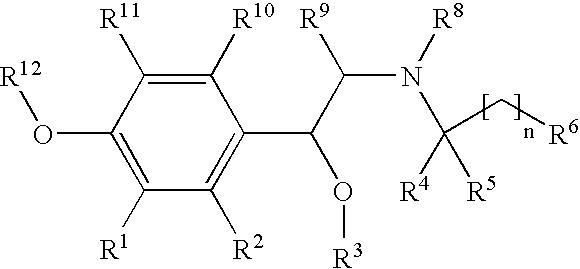
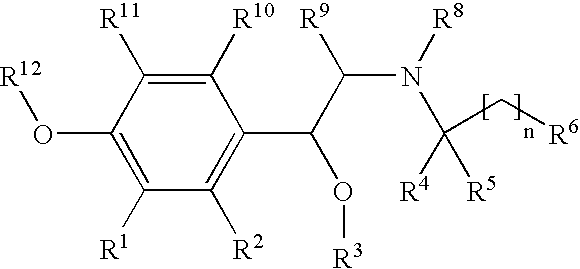
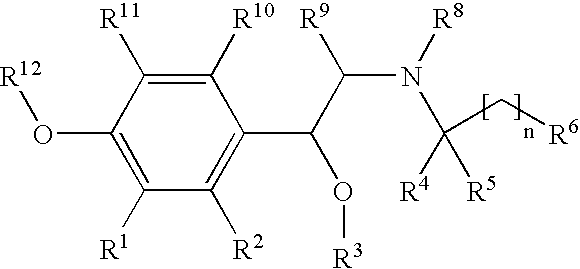
New beta-agonists, processes for preparing them and their use as pharmaceutical compositions
a technology of beta-agonists and processes, applied in the field of new beta-agonists, processes for preparing them and their use as pharmaceutical compositions, can solve the problem of rarely successful methods in the longer term
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 5
[0173] a) Enantiomerically Pure Synthesis of (R)-1-(4-benzyloxy-3-nitrophe-nyl)-2-[1,1-dimethyl-3-(4-phenylimidazol-1-yl)-propylamino]-ethanol
[0174] 0.90 g (3.1 mmol) of 3-chloro-1,1-dimethylpropylamine-hydrochloride were added to 10 mL sodium hydroxide solution (1 M) at 0.degree. C. with vigorous stirring. The reaction mixture was stirred for 30 min at 0.degree. C. and then combined with 20 mL methylene chloride. The phases were separated and the aqueous phase was extracted twice with 20 mL methylene chloride. The combined organic phases were dried over magnesium sulphate and the solvent was eliminated. The residue was dissolved in 5.0 mL methylene chloride and at ambient temperature combined with 0.70 g (2.6 mmol) (R)-2-(4-benzyloxy-3-nitrophenyl)-oxirane and 0.20 g (0.26 mmol) ytterbium (III) trifluoromethanesulphonate with stirring. The reaction mixture was stirred for 3 d at ambient temperature and then combined with 30 mL water / methylene chloride (1:1). The phases were separat...
example 12
[0193] a) Racemic Synthesis of N-(2-benzyloxy-5-{2-[1,1-dimethyl-3-(4-phen-yl-imidazol-1-yl)-propylamino]-1-hydroxy-ethyl}-phenyl)methanesulphonamide
[0194] 21.1 g (33.0 mmol) of N-[2-benzyloxy-5-(2-ethoxy-2-hydroxy-acetyl)--phenyl]-methanesulphonamide and 7.00 g (30.0 mmol) of 1,1-dimethyl-3-(4-phenyl-imidazol-1-yl)-propylamine in 150 mL ethanol were refluxed for 18 h. The reaction mixture was cooled to 0.degree. C. and then combined with 3 g (77.0 mmol) sodium borohydride. It was stirred for a further 3 h at ambient temperature and then combined with glacial acetic acid. The solvent was removed using the rotary evaporator and the residue was dissolved in 300 mL ethyl acetate / water (1:2). The aqueous phase was made alkaline with conc. ammonia and separated from the organic phase. The organic phase was washed twice with 200 mL water and once with 200 mL of saturated, aqueous sodium chloride solution, dried over sodium sulphate and freed from solvent using the rotary evaporator. The r...
example 27
[0199] a) Racemic Synthesis of N-(2-benzyloxy-5-{1-hydroxy-2-[3-(4-iodimid-azol-1-yl)-1,1-dimethyl-propylamino]-ethyl}-phenyl)-phenylsulphonamide
[0200] 2.1 g (7.7 mmol) of 3-(4-iodimidazol-1-yl)-1,1-dimethyl-propylamine and 3.4 g (7.7 mmol) of N-[2-benzyloxy-5-(2-ethoxy-1,2-dihydroxy-ethyl)-p-henyl]-phenylsulphonamide in 25 mL ethanol were refluxed for 18 h. The reaction mixture was cooled to 0.degree. C. and then combined with 0.3 g (7.7 mmol) sodium borohydride. The mixture was stirred for a further 3 h at ambient temperature and then combined with glacial acetic acid. The solvent was removed using the rotary evaporator and the residue was dissolved in 300 mL ethyl acetate / water (1:2). The aqueous phase was made alkaline with conc. ammonia and separated from the organic phase. The organic phase was washed twice with 100 mL water and once with 100 mL of saturated aqueous sodium chloride solution, dried over sodium sulphate and freed from solvent using the rotary evaporator. The res...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com