Optical connection structure and optical connection method
A technology for optical connection and connecting components, which is applied in the field of optical connection structures, can solve problems such as low production efficiency, high cost, difficult state, etc., and achieve the effects of good adhesion, good heat resistance and retention, and excellent water resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
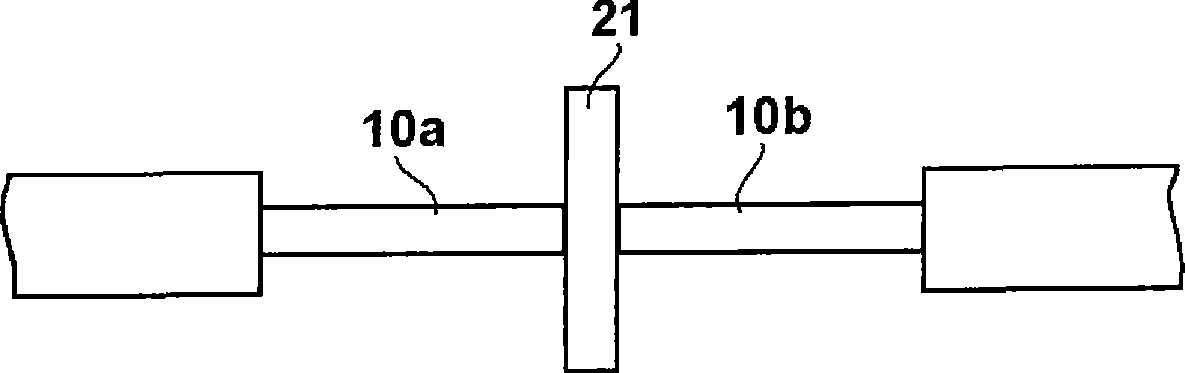
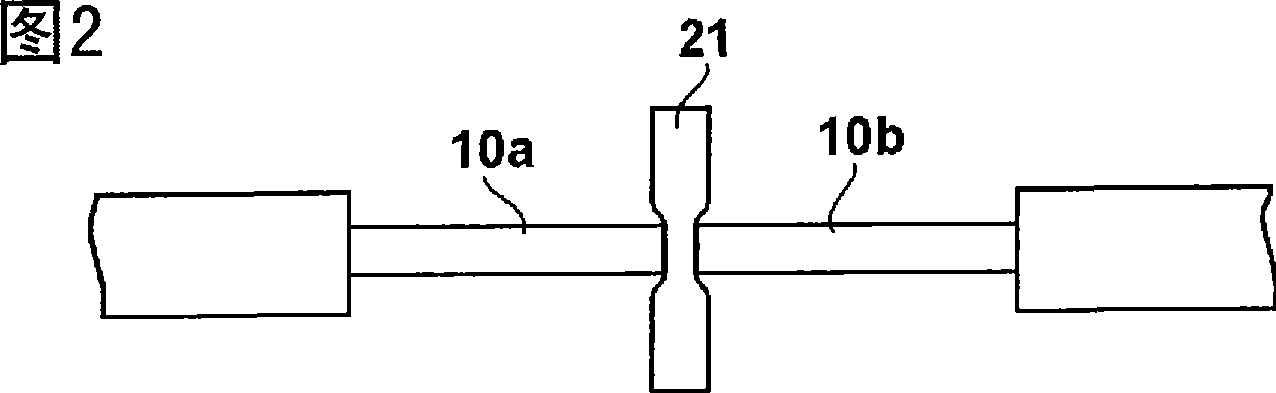
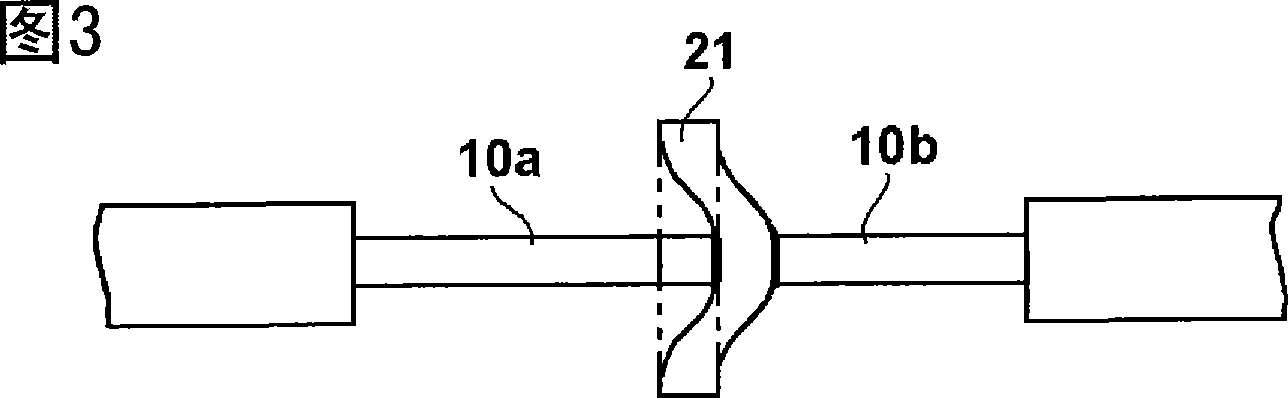
[0156] Use the flake-shaped adhesive connection member (1) obtained by the above method, such as Figure 33 The optical connection structure is formed as shown. First, use an optical microscope to align the cross-section of the V-groove (with a size of 5 mm × 10 mm) with two alignment members 43a, 43b, and then at a position 0.2 mm away from the 0.05 mm notch 801 provided on the glass substrate 80, The V-shaped end faces are positioned, and the alignment member is fixed on the glass substrate 80 with an adhesive. Then, the sheet-like connecting member 21 is inserted into the cutout of the glass substrate and arranged vertically on the glass substrate. After that, the optical fibers 10a, 10b are arranged in the V-shaped grooves of the both array members 43a, 43b. As the optical fiber, a silica fiber core wire (made by Furukawa Electric, 250μm in diameter, single mode) was used, and the coating was removed approximately 25mm from the end with a fiber stripper, and the bare fiber of ...
Embodiment 2
[0160] Using the sheet-like viscous connection member (2) obtained by the above method, an optical connection structure was formed as in Example 1. As a result of measuring the connection loss of the connected optical fiber, it was 0.4dB or less, showing good optical characteristics. In addition, the above-mentioned optical connecting structure was subjected to a heat resistance test (according to JIS C 0021) in an environment of 125±2°C and a temperature cycle test in the range of -40°C to 75°C. The result was The light loss variation was 0.4dB or less, and the adhesive connection member was observed after the optical connection was disconnected. As a result, no curing or yellowing was observed, indicating that the optical connection member can be fully reused.
Embodiment 3
[0162] Figure 34 It is a plan view showing an optical connection structure for connecting 4-core optical fiber ribbon core wires. In order to realize the optical connection of the four optical fibers to each other, in addition to the use of two 4-core optical fiber ribbon core wires 15a (the optical fibers in this ribbon core wire are 101-104) and 15b, and two V-grooves fixed on the glass substrate 80 Except for the arrangement members 43a and 43b, the connection operation was performed in the same manner as in Example 1, and the four optical fibers were simply optically connected by using a sheet-like viscous connection member 21. In addition, the length of the cleaved optical fiber was detected. As a result, there was a deviation of about ±10 μm between the four bare optical fibers. Since the sheet-like adhesive connecting member can be tightly bonded and fixed to each optical fiber through soft deformation, The variation of light loss between bare optical fibers is also small...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com