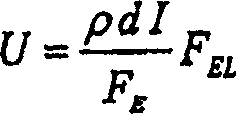Electroluminescent device with homogeneous brightness
An electroluminescence device and electroluminescence technology, which are applied to organic semiconductor devices, electric solid state devices, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of reduced visible transmission of electrodes, increased manufacturing cost, inability to obtain, etc., and achieve uniform light emission, Simple cost, effect of reducing layer resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
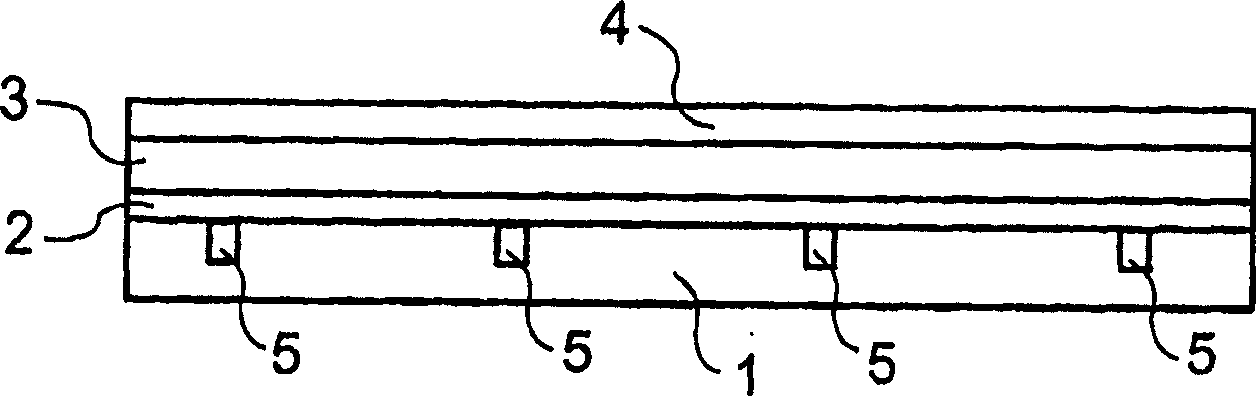
[0045] A glass substrate 1 of 356 mm x 356 mm was coated with a photosensitive layer of polyurethane. The polyurethane layer was exposed and polyurethane was removed in bands with a width of more than 200 μm at intervals of 20 mm.
[0046]Subsequently, the glass was removed by sandblasting in areas not covered by polyurethane. The depth of the groove was 350 μm.
[0047] Once the remaining areas of the polyurethane layer have been removed, the recesses in the substrate 1 comprising glass are filled with a conductive silver paste by several screen printing operations.
[0048] Multilayers of the layer assembly are then applied using known methods, for example a first electrode 2 comprising ITO, a hole transport layer comprising polyethylenedioxythiophene (PDOT) and poly(styrenesulfonate), a field comprising PPV Luminescent layer 3 and a second unstructured electrode 4 comprising a 5 nm thick first layer with barium and a 200 nm thick second layer with aluminum.
[0049] An e...
Embodiment 2
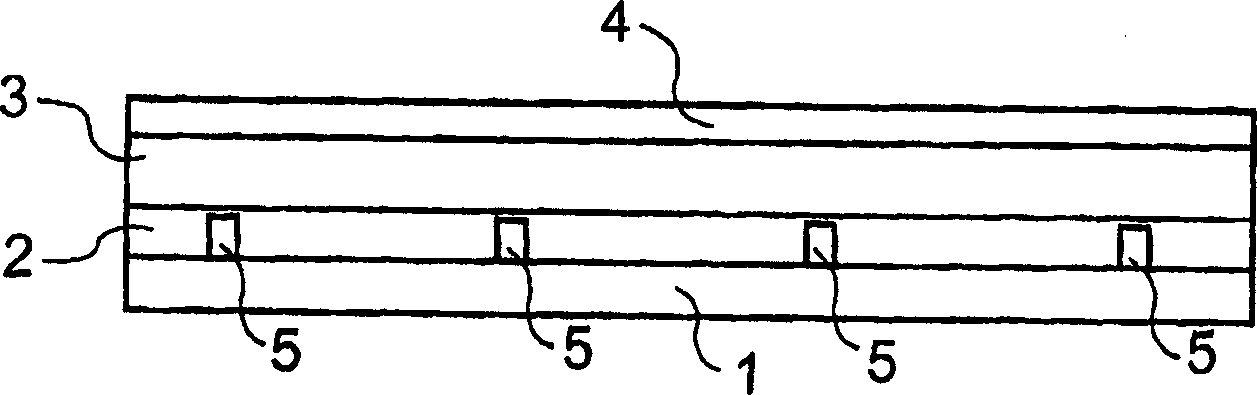
[0051] A Cu wire grid of individual wires with layers 400 μm thick and 200 μm wide rolled into a stationary liquid glass substrate. The distance between the individual lines is 25 mm.
[0052] After cooling and curing the glass substrate 1 , further layers are applied in a manner analogous to Example 1.
[0053] An electroluminescent device with improved uniformity of emission is obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com