Method of multiplex fluorescence PCR ¿C improved molecule beacon for detecting pathogenesis bacterium stemmed from eating source
A technology for improving molecular beacons and food-borne pathogens, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc. Pathogenic bacteria and other problems, to achieve the effect of simple operation, high sensitivity, and intuitive and clear result observation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
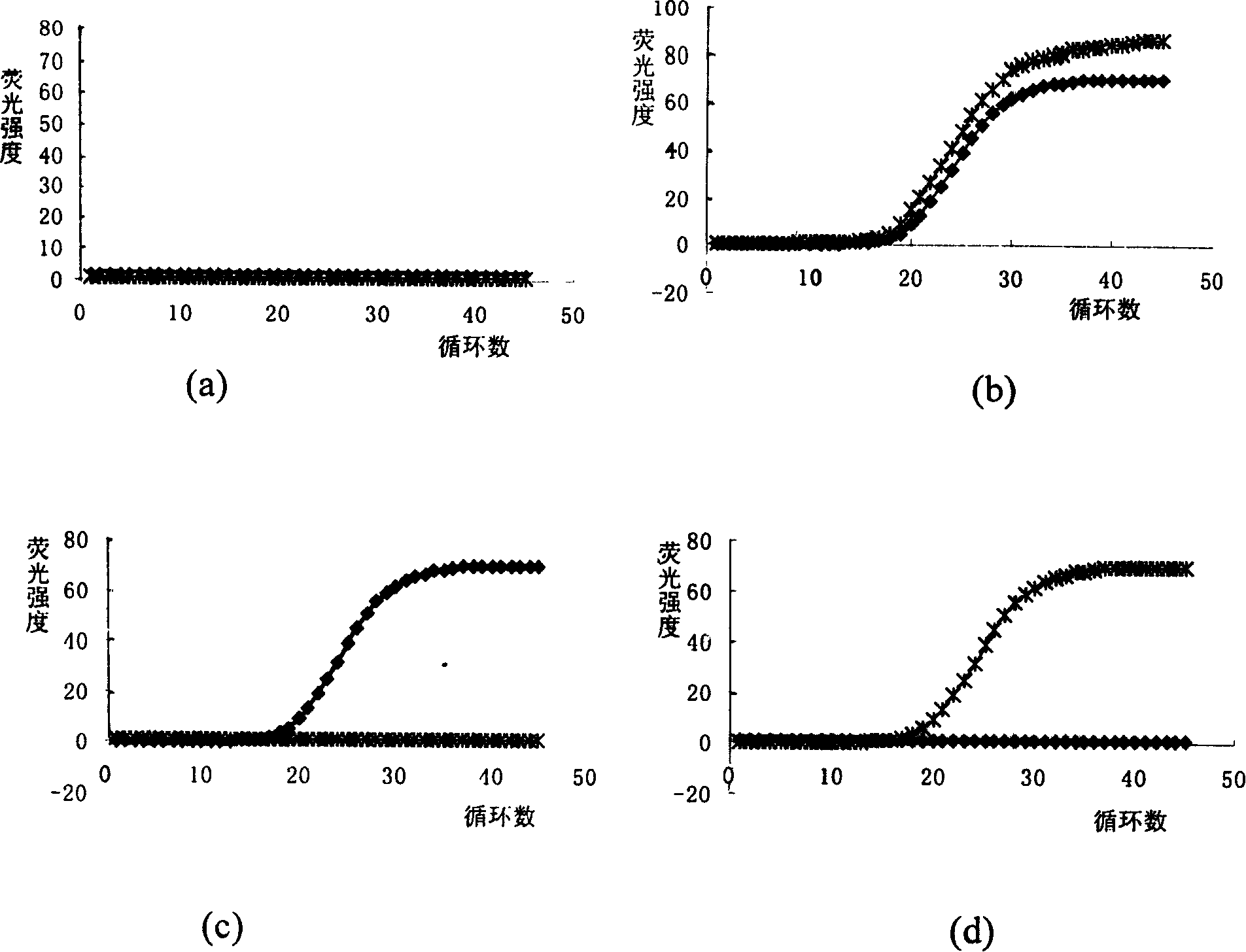
[0125] In this example, the detection of Salmonella and Shigella by dual fluorescent PCR-improved molecular beacons is taken as an example to analyze the method for the detection of foodborne pathogens by multiplex fluorescent PCR-improved molecular beacons. According to the sequences of Salmonella invasion gene (ivnA) and Shigella invasion plasmid antigen H gene (ipaH) published by GenBank and comparative analysis, a pair of primers and probes were designed respectively as described above.
[0126] Test strains: 132 strains of 14 kinds of bacteria. Including 1 strain of enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC), 1 strain of invasive E. coli (EIEC), 1 strain of O157: H7 E. coli (O157: H7), 1 strain of pathogenic E. coli Enteropathogenic E.coli (EPEC), 1 strain of Citrobacter, 1 strain of Escherichia coli, 1 strain of Vibrio parahaemolyticus (V.parahaemolyticus), 1 strain of cholera (V.cholera ) Vibrio, 1 strain of Staphylococcus aureus (S.aureus), 1 strain of Listeria monocytogenes (Lis...
example 2
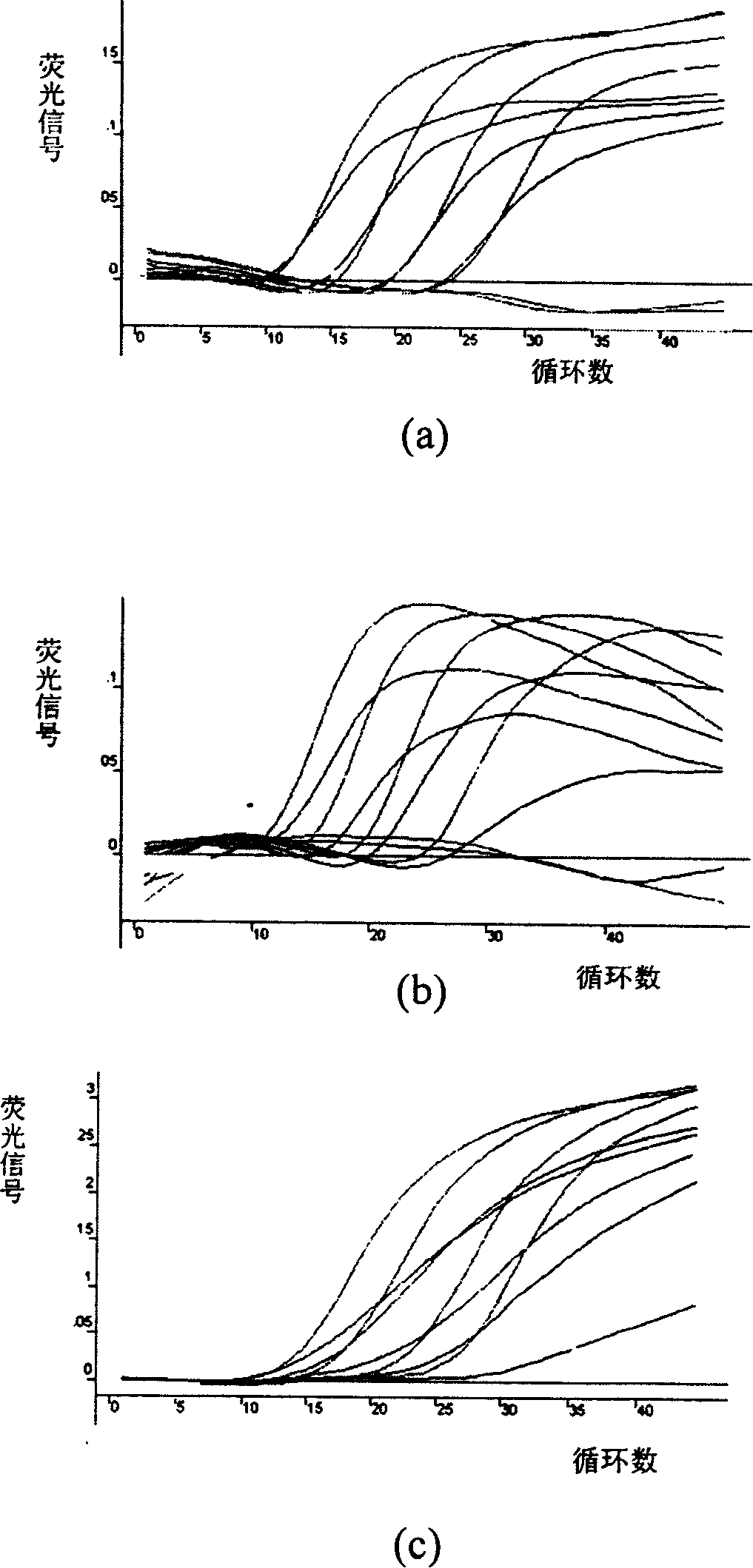
[0152] In this example, the detection of Shigella, O157:H7 Escherichia coli and Listeria monocytogenes by triple fluorescent PCR-improved molecular beacon is taken as an example. According to GenBank, the sequence of the coding invasion plasmid antigen H gene (ipaH) of Shigella, the sequence of the hemolysin gene rfbE of Escherichia coli O157:H7, and the sequence of the hemolysin gene (hly) of Listeria monocytogenes were published, respectively The designed pair of primers and probes and their amplified fragments are the same as those described above.
[0153] Test strains: O157: H7 Escherichia coli (O157: H7), Listeria monocytogenes, Shigella (various serotypes). All strains were isolated and identified in accordance with the National Inspection Standard of "Food Microbiology" promulgated by the People's Republic of China.
[0154] The method for simultaneously detecting Shigella, O157:H7 Escherichia coli, and Listeria monocytogenes by utilizing the above-mentioned fluoresce...
example 3
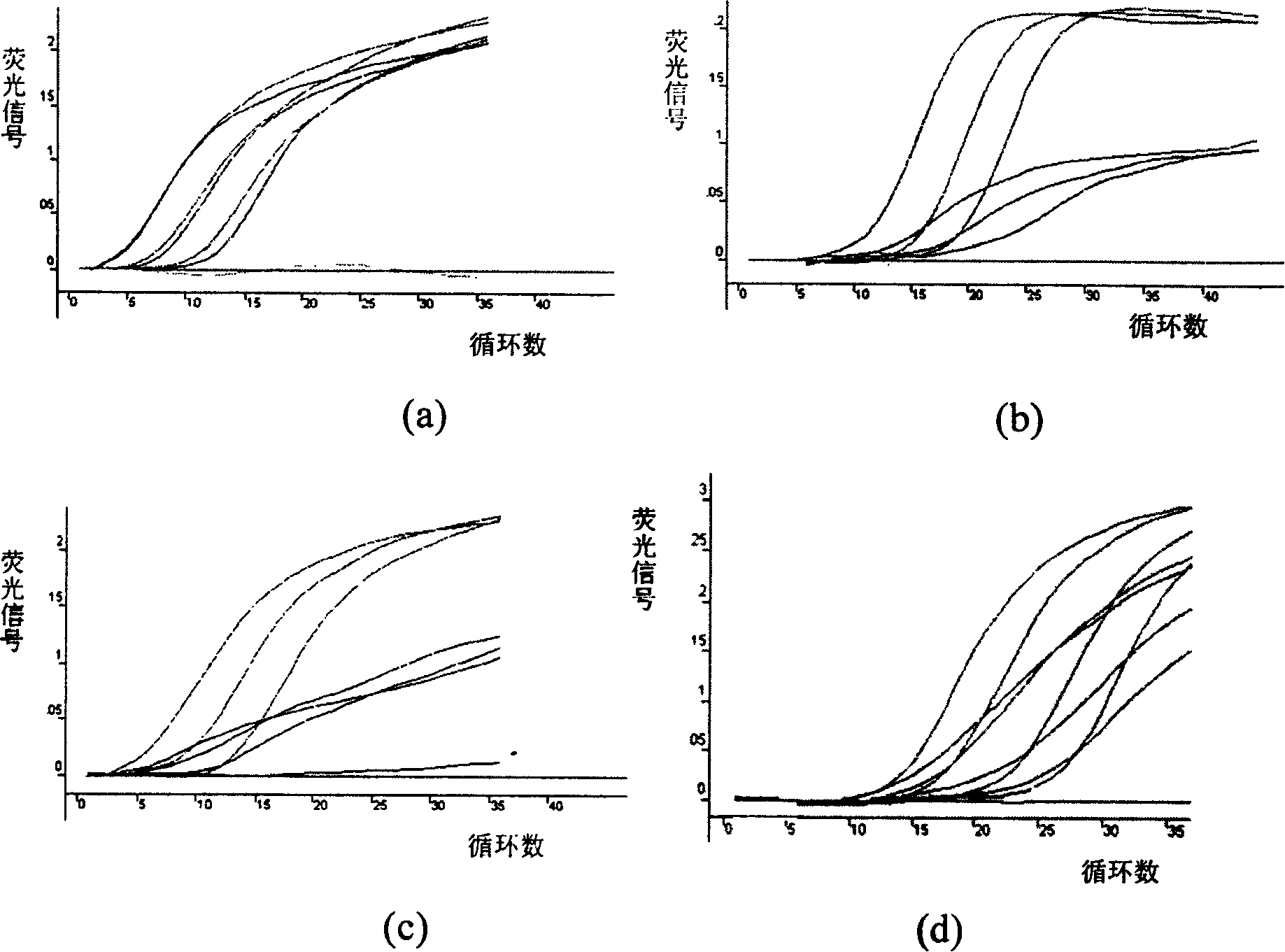
[0174] This example illustrates a method for the simultaneous detection of Shigella, Vibrio cholerae, Staphylococcus aureus, and Escherichia coli O157:H7 by quadruple fluorescent PCR-modified molecular beacons. According to GenBank, the sequence of the coding invasion plasmid antigen H gene (ipaH) of Shigella, the sequence of the enterotoxin gene ctxA of Vibrio cholerae, the sequence of the thermostable nuclease gene NUC of Staphylococcus aureus, and the sequence of Escherichia coli O157:H7 were released according to GenBank. The rfbE sequence of the hemolysin gene, a pair of primers and probes and amplified fragments designed respectively are the same as those described above.
[0175] Test strains: Shigella, Vibrio cholerae, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli O157:H7. All strains were isolated and identified in accordance with the National Inspection Standard of "Food Microbiology" promulgated by the People's Republic of China.
[0176] The method for simultaneously de...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com