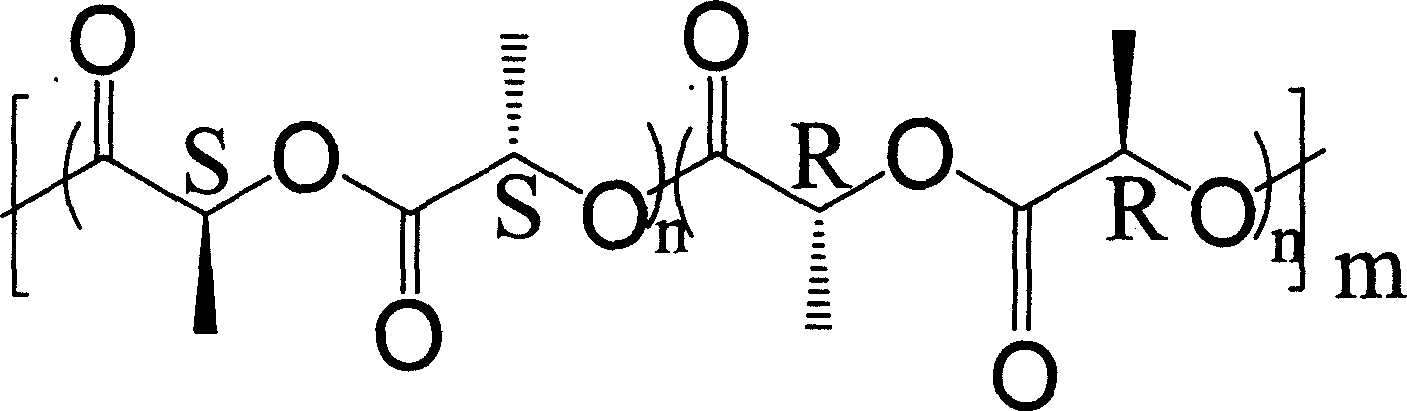
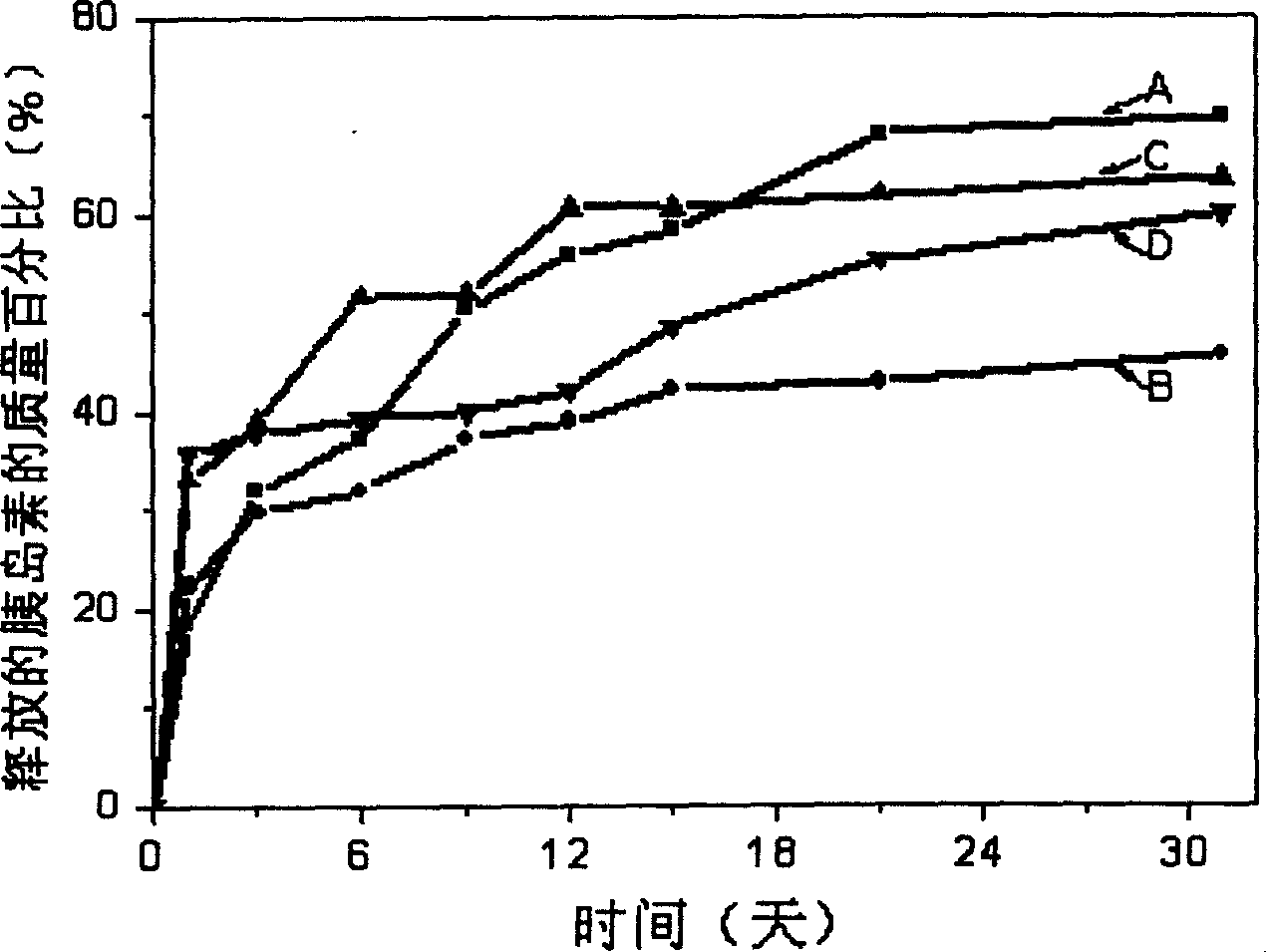
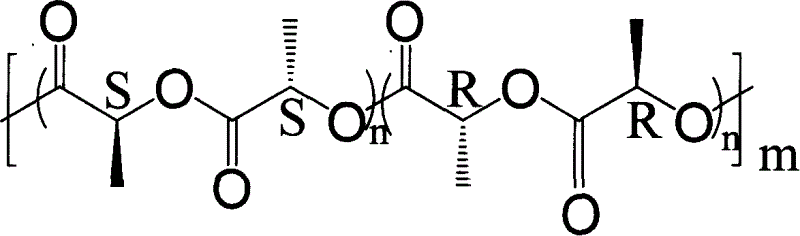
Biological degradable polyester micropartical and its preparation process and application
A technology for degrading polyester and microparticles, which is applied in the field of biodegradable polyester microparticles or microspheres and its preparation, which can solve the problems of high material cost and cumbersome polymerization process, and achieve uniform particle size, simple process and good application prospects Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1: Using stereoactive multi-block polylactide (n=8.2) with different molecular weights and high stereoregularity as materials, microparticles or microspheres were prepared by adopting the cooling method included in the method of the present invention.
[0034] Divided into four steps:
[0035] 1) Weigh 50 mg of stereo-optical multi-block polylactide (n=8.2) with number-average molecular weights of 2800, 8700, 13600, 23200, and 79800 Da, respectively, and dissolve them in dichloromethane solvent, and the solution reaches 50 mL;
[0036] 2) Move the polymer solution to a 250mL round bottom flask, and slowly add absolute ethanol dropwise to each of them until the solution starts to become slightly cloudy;
[0037] 3) Store the mixed solvent system of the above polymers at -20°C for 24 hours to precipitate the polymers;
[0038] 4) The suspension was centrifuged at -20°C for 10 min, the supernatant was discarded, and the precipitate was vacuum-dried at room tempera...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2: Using stereoactive multi-block polylactide (n=8.2) with different molecular weights and high stereoregularity as materials, microparticles or microspheres were prepared by the solvent evaporation method included in the method of the present invention.
[0042] Be divided into four steps, wherein step 1) and 2) are the same as embodiment 1, also have the following steps:
[0043] 3) respectively place the mixed solvent system of the above-mentioned polymers at room temperature and stir for 12 hours to completely volatilize the dichloromethane and precipitate the polymers;
[0044] 4) The resulting suspension was centrifuged at room temperature for 10 min, the supernatant was discarded, and the precipitate was vacuum-dried at room temperature for 24 h.
[0045] The obtained microparticles were cake-shaped, and the particle diameters are shown in Table 2.
[0046] Number average molecular weight (M n )
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3: Using stereoactive multi-block polylactide (n=8.2) with different molecular weights and high stereoregularity as materials, microparticles or microspheres were prepared by using the non-solvent precipitation method included in the method of the present invention.
[0048] Be divided into four steps, wherein step 1) and 2) are the same as embodiment 1, also have the following steps:
[0049] 3) Slowly add a large amount of absolute ethanol (50-5000 mL) to the mixed solvent system of the above polymer to precipitate the polymer;
[0050] 4) The resulting suspension was centrifuged at room temperature for 10 min, the supernatant was discarded, and the precipitate was vacuum-dried at room temperature for 24 h.
[0051] The obtained microparticles were cake-shaped, and the particle diameters are shown in Table 3.
[0052] Number average molecular weight (M n )
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com