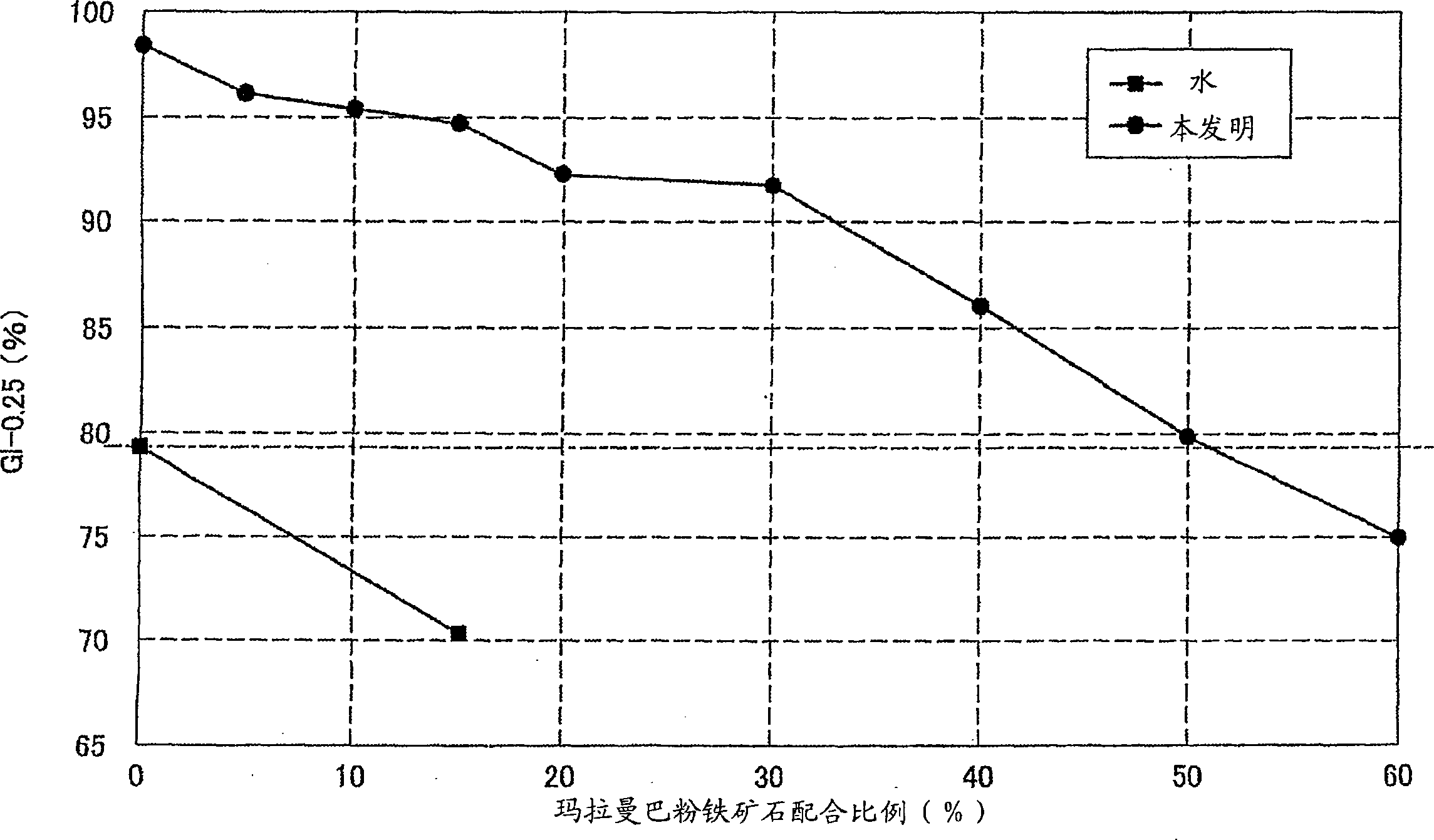
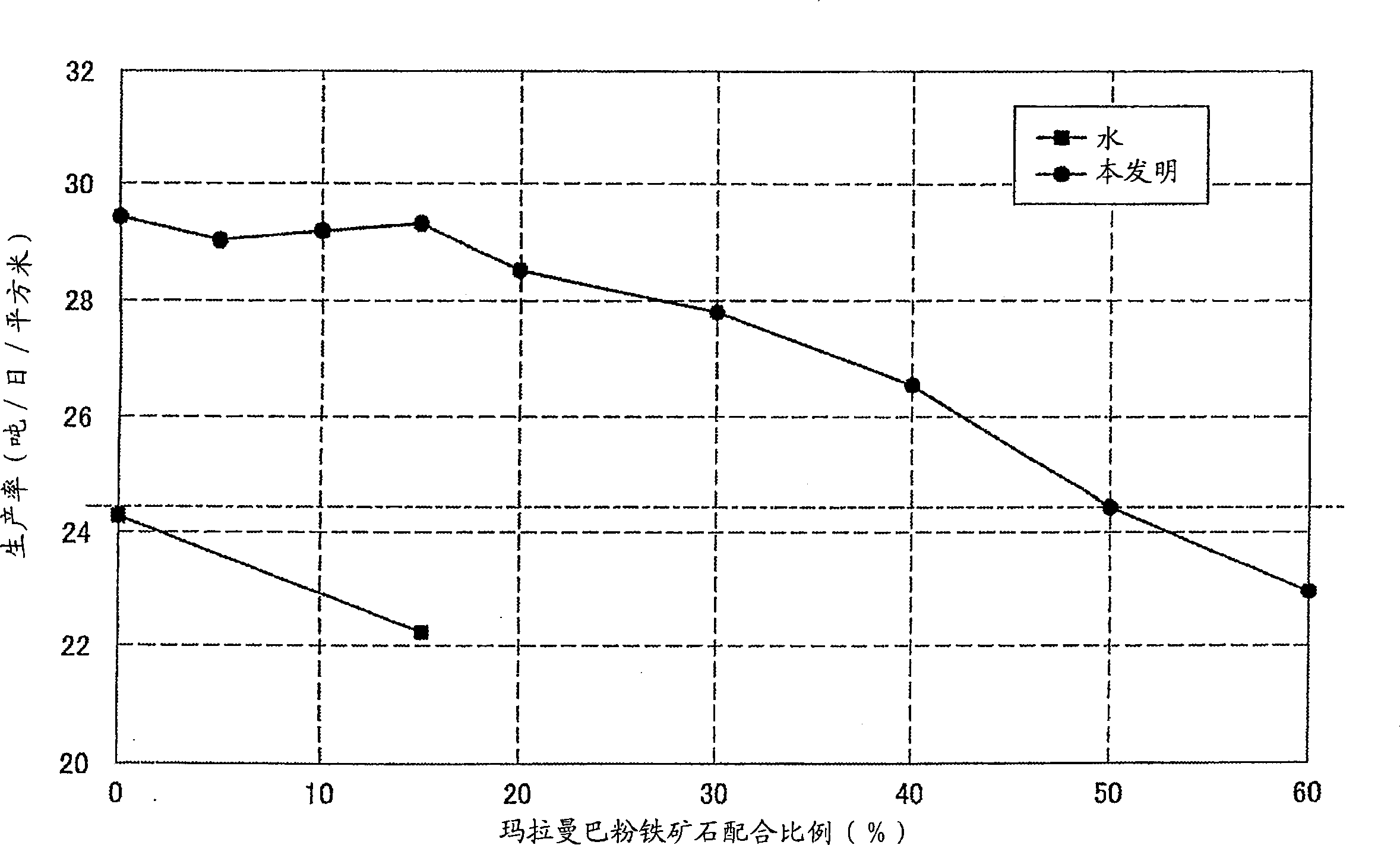
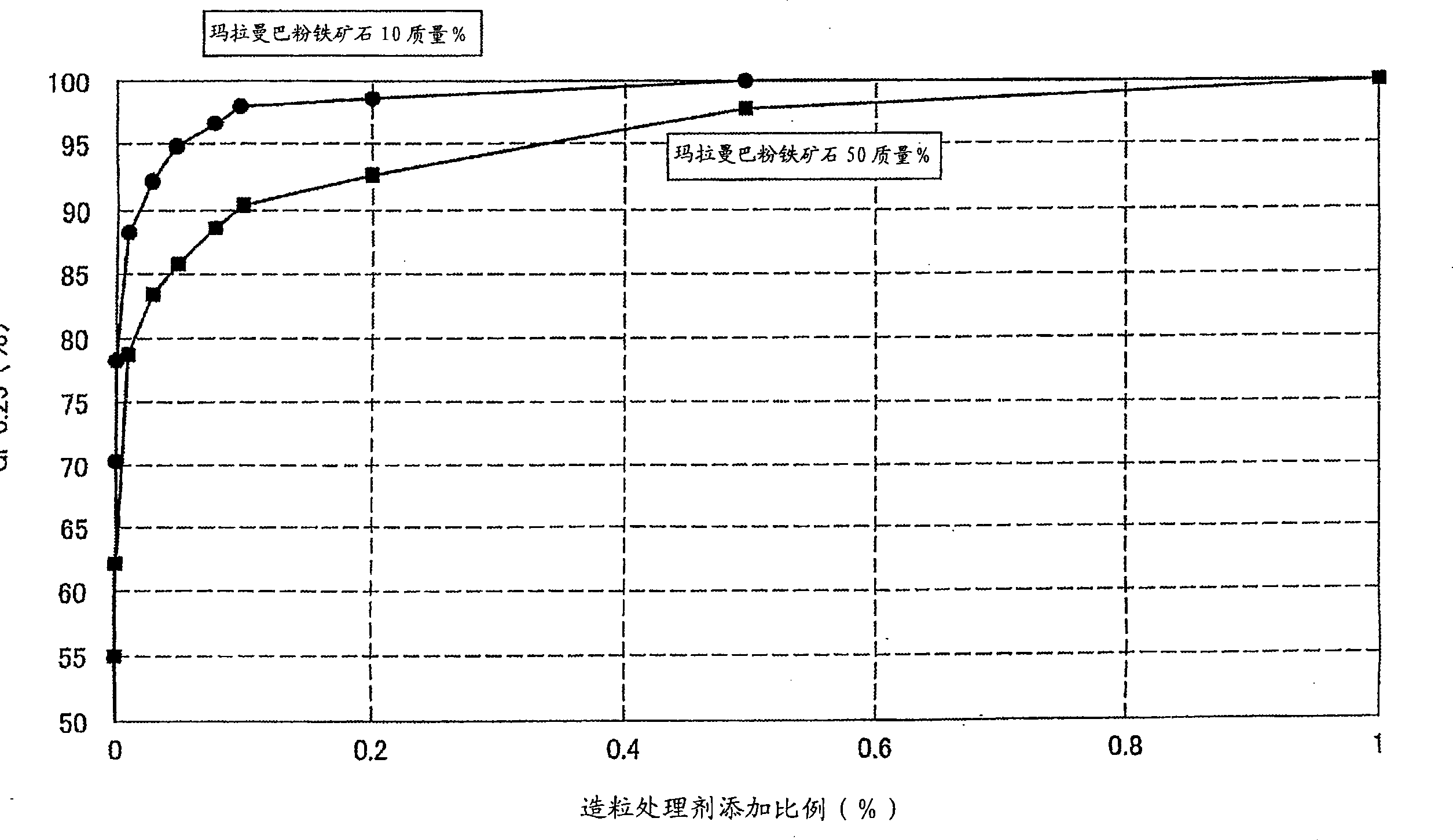
Method of granulating sintering material for iron manufacturing
A processing method and raw material technology, applied in the direction of special binder granulation, etc., can solve the problems of decreased air permeability of sintering machine and decreased productivity of sintering process, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0243] Charge 805.5 parts of ion-exchanged water and 40.1 parts of 45% sodium hypophosphite monohydrate aqueous solution as a chain transfer agent into a 5L separable flask (made by SUS316) equipped with a stirrer and a condenser. The temperature is raised to the system under stirring. Boiling point (100°C). Next, into the above-mentioned separable flask, 2126.1 parts of 80% acrylic acid aqueous solution as a carboxyl group-containing monomer, 112.4 parts of 15% sodium persulfate aqueous solution and 160.2 parts of 45% sodium hypophosphite as a polymerization initiator were added dropwise. Aqueous hydrate solution. The above-mentioned 80% acrylic acid aqueous solution, 15% sodium persulfate aqueous solution, and 45% sodium hypophosphite monohydrate aqueous solution were dropped from their respective drip openings. The 80% acrylic acid aqueous solution was added dropwise for 180 minutes. The 15% sodium persulfate aqueous solution was added dropwise for 185 minutes. The 45% sodium h...
Embodiment 2
[0250]The polymer aqueous solution (A) obtained in Example 1 was taken so that the solid content conversion amount was 70 parts, and it was diluted to 2460 parts with ion-exchanged water. Next, the polymer aqueous solution was stirred at a speed of 2000 rpm using a homomixer, and 2800 parts of "Alfa coat" (produced by ECC international incorporated) as fine particles (adhesive for granulation) were mixed into the polymer aqueous solution in about 30 minutes. The average particle size of kaolin is 2.7 μm), and the mixture is further maintained at a speed of 3000 rpm for 5 minutes to obtain the slurry (2) of the granulation treatment agent for ironmaking of the present invention. The viscosity of the slurry (2) is 4400×10 -3 Pa·s(4400cP).
[0251] Thereafter, the slurry (1) in Example 1 was replaced with the above slurry (2), and the same granulation operation as in Example 1 was performed to measure the moisture content of the obtained pseudo particles. At the same time, the pseudo...
Embodiment 3
[0253] A 5 L-capacity separable flask (made by SUS316) equipped with a stirrer and a condenser was charged with 805.5 parts of ion-exchange water, and the temperature was raised to the boiling point (100°C) of the system. Next, 2126.1 parts of 80% acrylic acid aqueous solution as a carboxyl group-containing monomer, 112.4 parts of 15% sodium persulfate aqueous solution as a polymerization initiator, and 88.5 parts of 45% hypophosphorous acid as a chain transfer agent were added dropwise to the above-mentioned separate flask Sodium monohydrate aqueous solution. The above-mentioned 80% acrylic acid aqueous solution, 15% sodium persulfate aqueous solution, and 45% sodium hypophosphite monohydrate aqueous solution were dropped from their respective drip openings. The 80% acrylic acid aqueous solution was added dropwise for 180 minutes. The 15% sodium persulfate aqueous solution was added dropwise for 185 minutes. The 45% sodium hypophosphite monohydrate aqueous solution was added drop...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com