Composite wave absorbing material and production thereof
A composite wave-absorbing material and preparation technology, applied in radiation-absorbing coatings, etc., can solve problems such as poor temperature stability and high density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
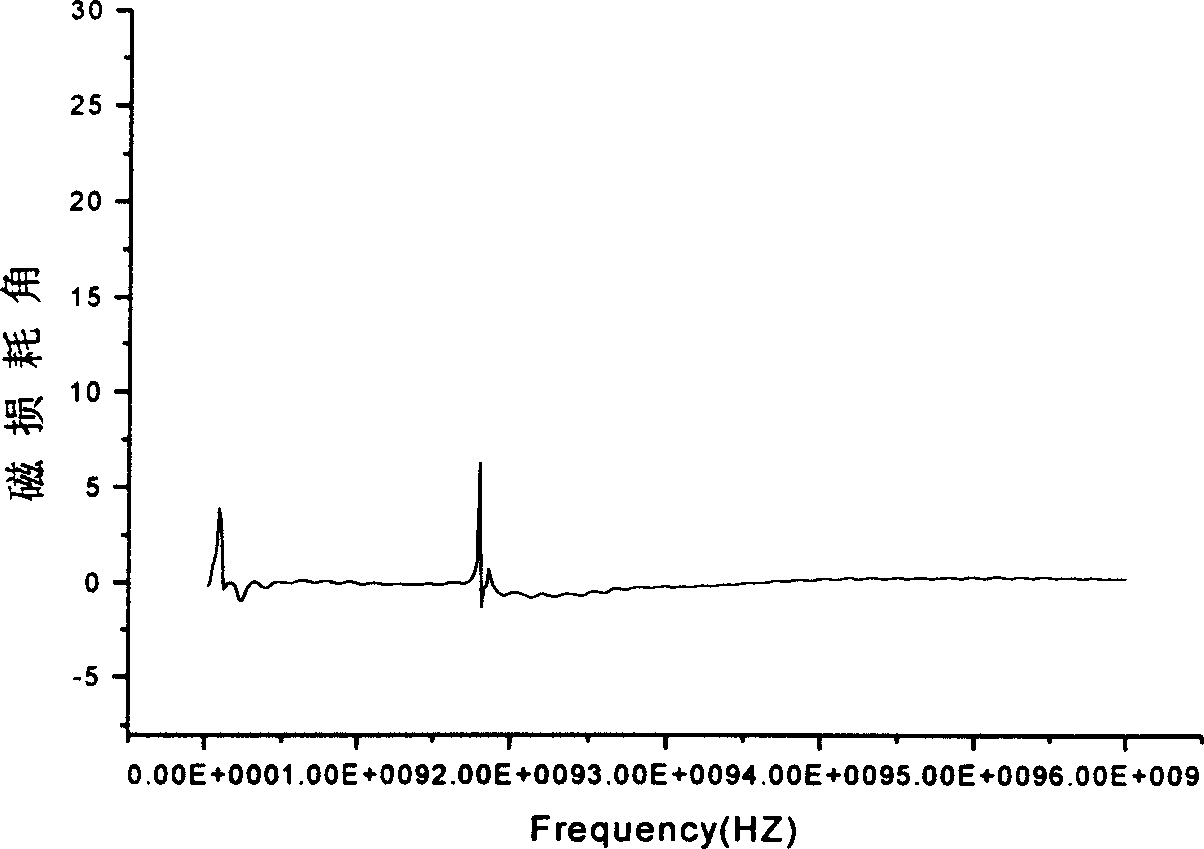
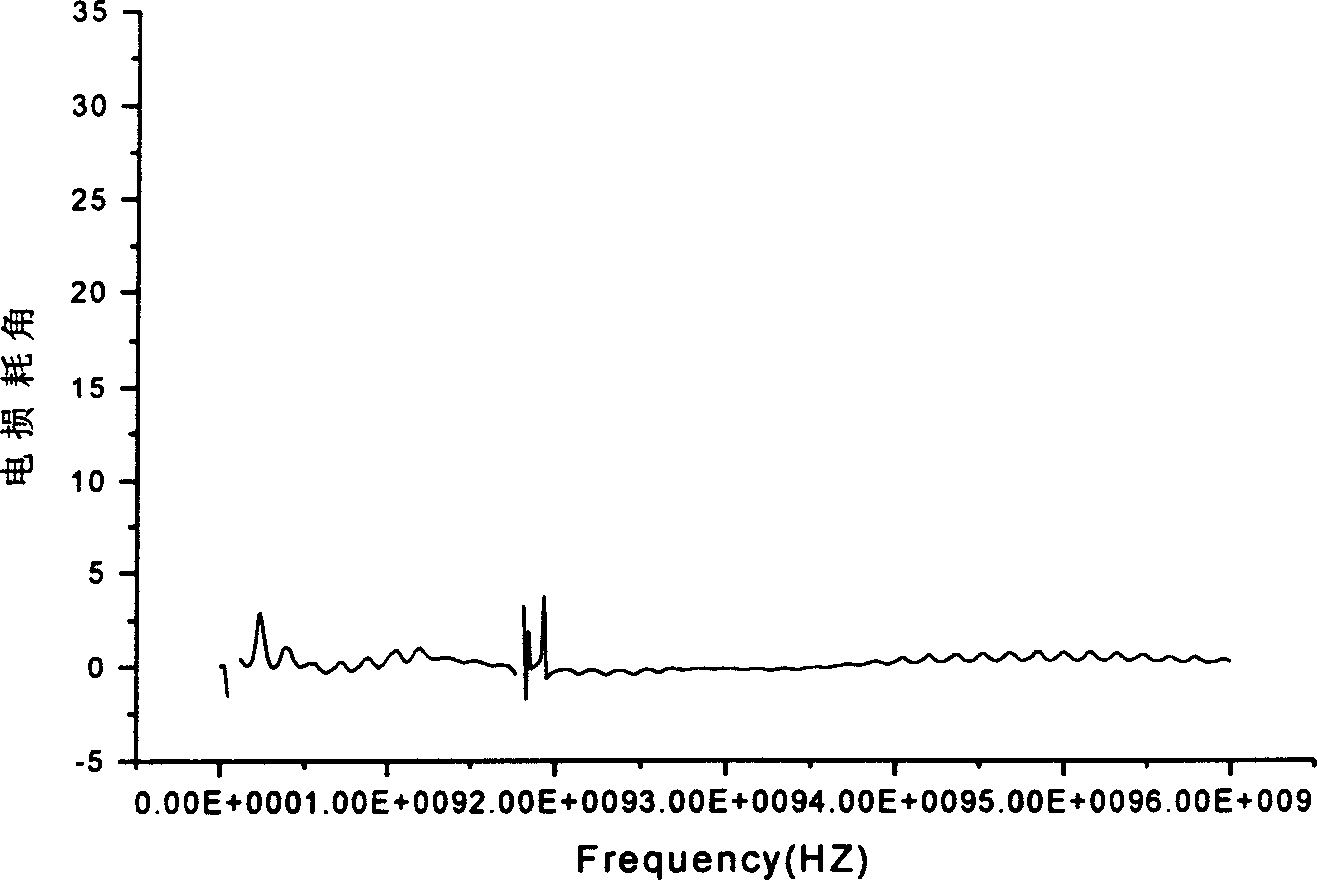
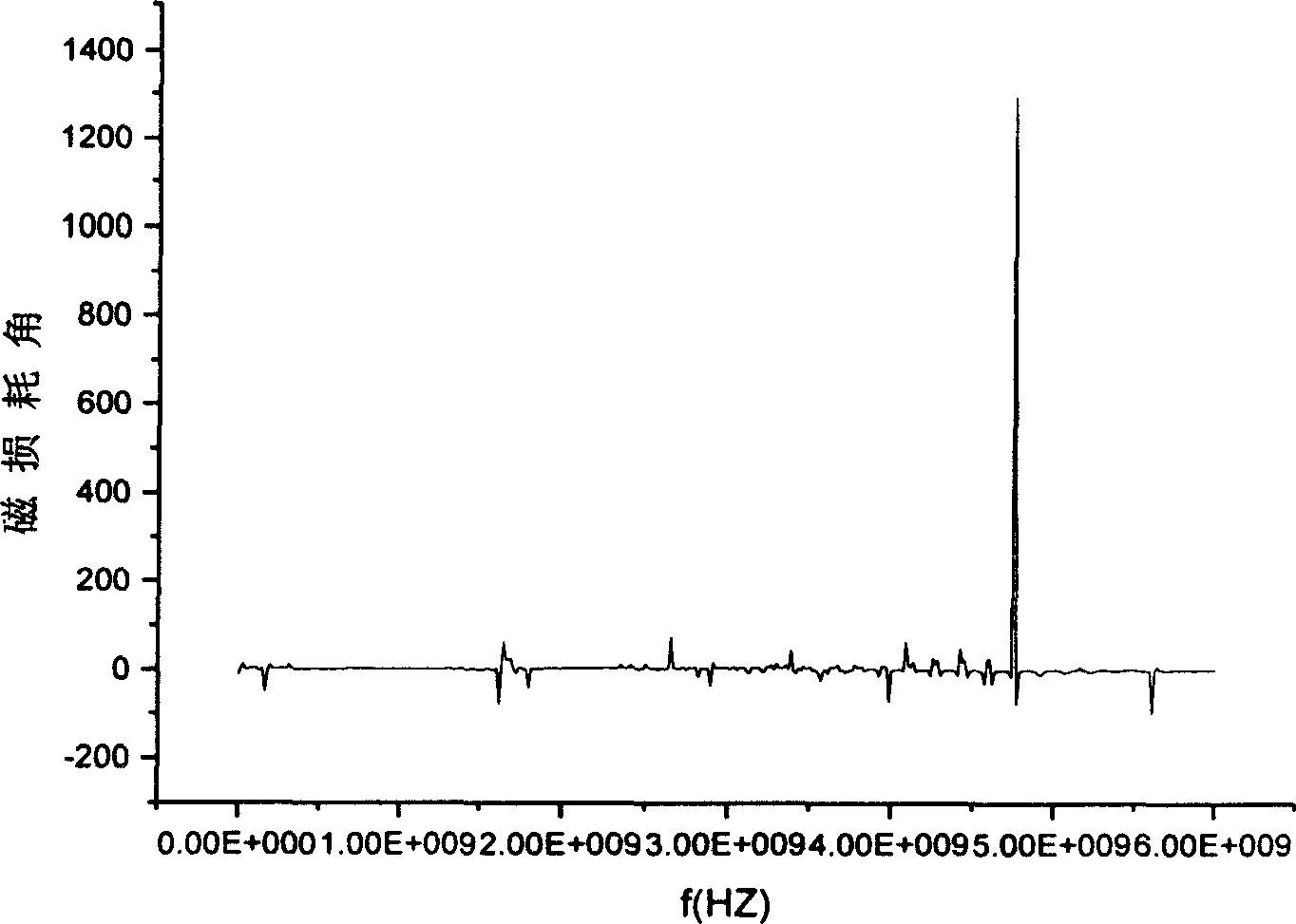
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] The precursor was prepared by complexing ferric nitrate and barium nitrate with citric acid. Stoichiometric ratio: Ba(NO 3 ) 2 : Fe(NO 3 ) 3 : citric acid = 1:12:19. A solution is prepared and the porous glass phase is added to the solution. The theoretical product mass ratio of porous glass phase to ferrite is 1:1. Ammonia water was added dropwise to adjust the pH value to 7. The solution was placed in a 90°C water bath and stirred for 4 to 5 hours until the liquid became a viscous colloid. The prepared sol was placed in an oven at 120° C. for 4 h to obtain a dry gel. The obtained gel was heated in a muffle furnace at a heating rate of 60 °C / h, and when the temperature was raised to 850 °C, it was kept for 1 h.
Embodiment 2
[0025] The precursor was prepared by complexing ferric nitrate and barium nitrate with citric acid. Stoichiometric ratio: Ba(NO 3 ) 2 : Fe(NO 3 ) 3 : citric acid = 1:12:13. A solution is prepared and the porous glass phase is added to the solution. The theoretical product mass ratio of porous glass phase to ferrite is 3:1. Ammonia water was added dropwise to adjust the pH value to 7. The solution was placed in a 90°C water bath and stirred for 4 to 5 hours until the liquid became a viscous colloid. The prepared sol was placed in an oven at 120° C. for 4 h to obtain a dry gel. The obtained gel was heated in a muffle furnace at a heating rate of 80 °C / h, and when the temperature was raised to 950 °C, it was kept for 1 h.
Embodiment 3
[0027] The precursor was prepared by complexing ferric nitrate and barium nitrate with citric acid. Stoichiometric ratio: Ba(NO 3 ) 2 : Fe(NO 3 ) 3 : citric acid == 1:12:15. A solution is prepared and the porous glass phase is added to the solution. The theoretical product mass ratio of porous glass phase to ferrite is 5:1. Ammonia water was added dropwise to adjust the pH value to 7. The solution was placed in a 90°C water bath and stirred for 4 to 5 hours until the liquid became a viscous colloid. The prepared sol was placed in an oven at 120° C. for 4 h to obtain a dry gel. The obtained gel was heated in a muffle furnace at a heating rate of 30°C / h, and when the temperature was raised to 650°C, it was kept for 5 hours.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com