In situ organism restoring method for copper contaminated soil
An in-situ remediation and copper-polluted technology, applied in the field of copper-contaminated soil, can solve the problems of ineffective remediation and treatment of heavy metal-contaminated soil, and achieve the goals of improving cultivation measures and farming conditions, promoting root growth, accelerating absorption and enrichment Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
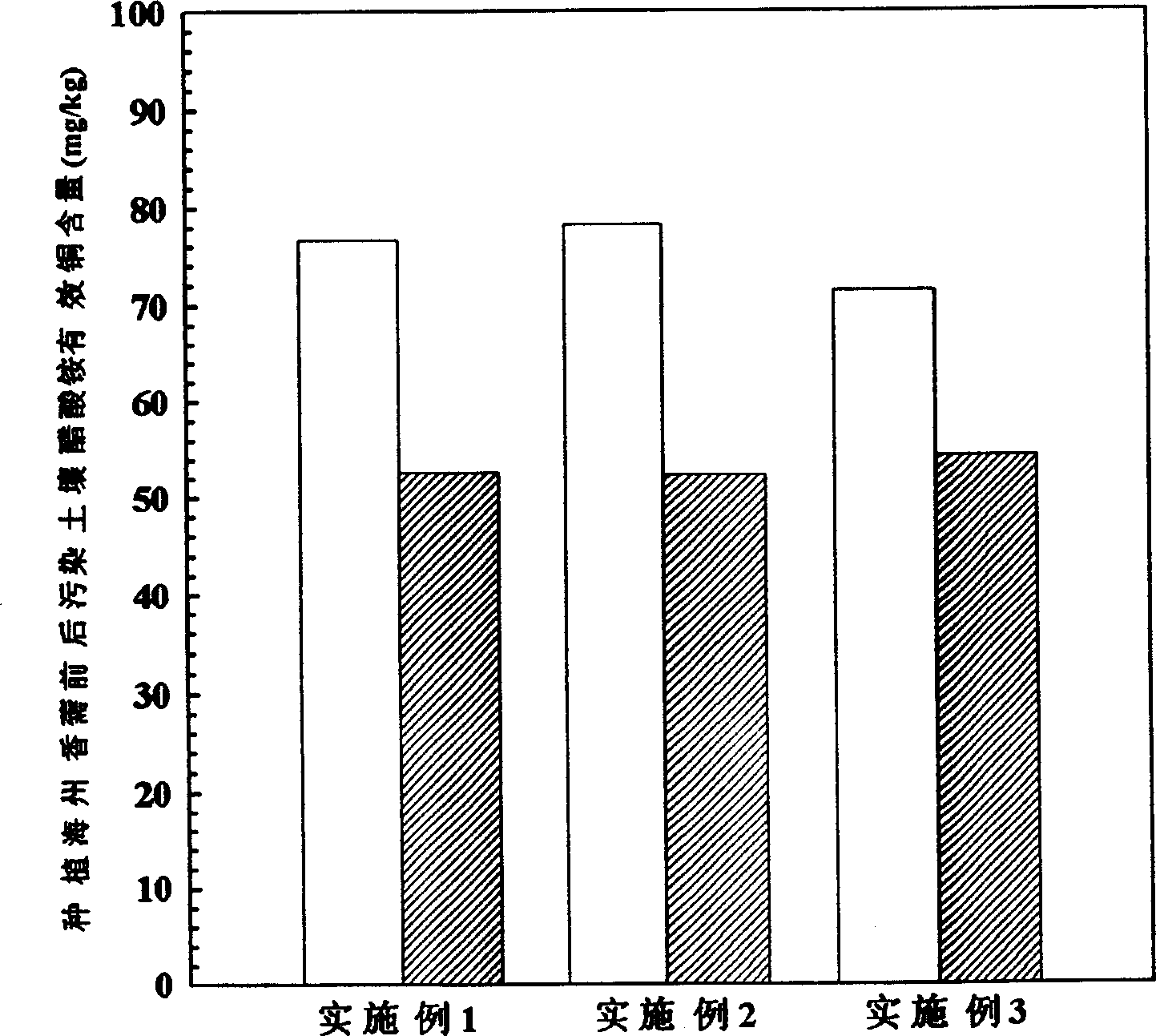
[0023] In the soil environment with a copper content of 1435mg / kg, if only the traditional method is used to apply nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers, the effective copper content of ammonium acetate on the soil surface is 76.7mg / kg. Plant the Herba chinensis and follow the management methods of common crops, and harvest the aboveground part after 10 months. It has been determined that after one season of planting A. haizhou, the effective copper content of ammonium acetate on the soil surface is 52.7mg / kg, a decrease of 24.0mg / kg; The effective copper content of ammonium nitrate increased by 5.68mg / kg, and the activation rate of heavy metals in the rhizosphere was 18.1%. After one season of planting, the biological yield of the aboveground part of Haizhou fenugreek can reach 9.2t / ha, the total amount of copper absorbed and enriched by the aboveground part from the copper-containing soil environment is 0.89kg / ha, and the copper content in the aboveground part remov...
Embodiment 2
[0027] In the soil environment with copper content of 1435mg / kg, if the method of applying organic fertilizer is adopted, the effective copper content of ammonium acetate on the soil surface is 78.2mg / kg. Plant the Herba chinensis and follow the management methods of common crops, and harvest the aboveground part after 10 months. It has been determined that after one season of planting A. haizhou, the effective copper content of ammonium acetate on the soil surface is 52.4mg / kg, a decrease of 25.8mg / kg; The effective copper content of ammonium nitrate and ammonium acetate in the rhizosphere of C. chinensis increased by 15.71mg / kg and 0.04mg / kg correspondingly, and the activation rates of heavy metals in the rhizosphere were 48.0% and 9.6%, respectively. After one season of planting, the biomass of the aboveground part of A. haizhouensis was 9.1t / ha, the total amount of copper absorbed and enriched by the aboveground part from the copper-containing soil environment was 0.82kg / h...
Embodiment 3
[0031] In the soil environment with a copper content of 1435mg / kg, if the method of applying organic fertilizer and fly ash at the same time is adopted, the effective copper content of ammonium acetate on the soil surface is 71.4mg / kg. Plant the Herba chinensis and follow the management methods of common crops, and harvest the aboveground part after 10 months. It has been determined that after one season of planting A. haizhou, the effective copper content of ammonium acetate is 54.4 mg / kg, which can be reduced by 20.9 mg / kg; the pH of the rhizosphere of A. haizhou decreases by 0.27, and the secretion of soluble organic matter in the rhizosphere increases by 0.16 mg / kg. The effective copper content of ammonium nitrate and ammonium acetate in the rhizosphere of C. chinensis increased by 8.66mg / kg and 2.27mg / kg correspondingly, and the activation rate of heavy metals in the rhizosphere was 25.0% and 4.4%, respectively. After one season of planting, the biomass of the aboveground...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com