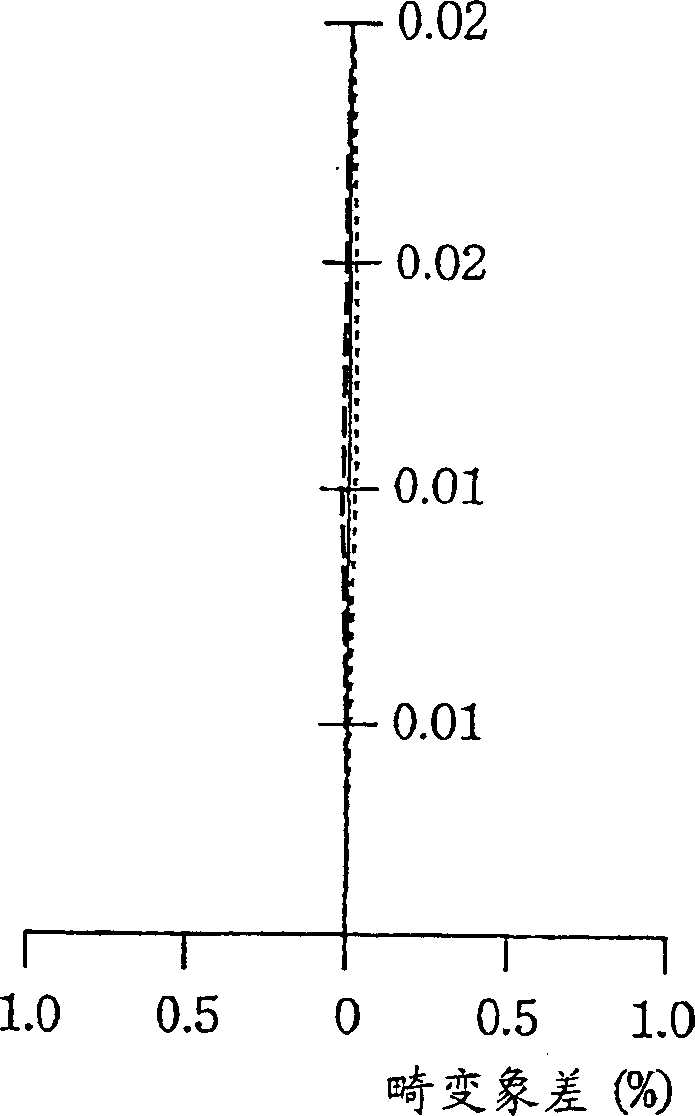Optical pickup-use object lens, optical pickup and optical disk unit
A technology of optical disc device and pick-up, which is applied in the direction of beam guiding device, optics, optical elements, etc., can solve the problems of focusing diffraction limit, difficult laser, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the number of parts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
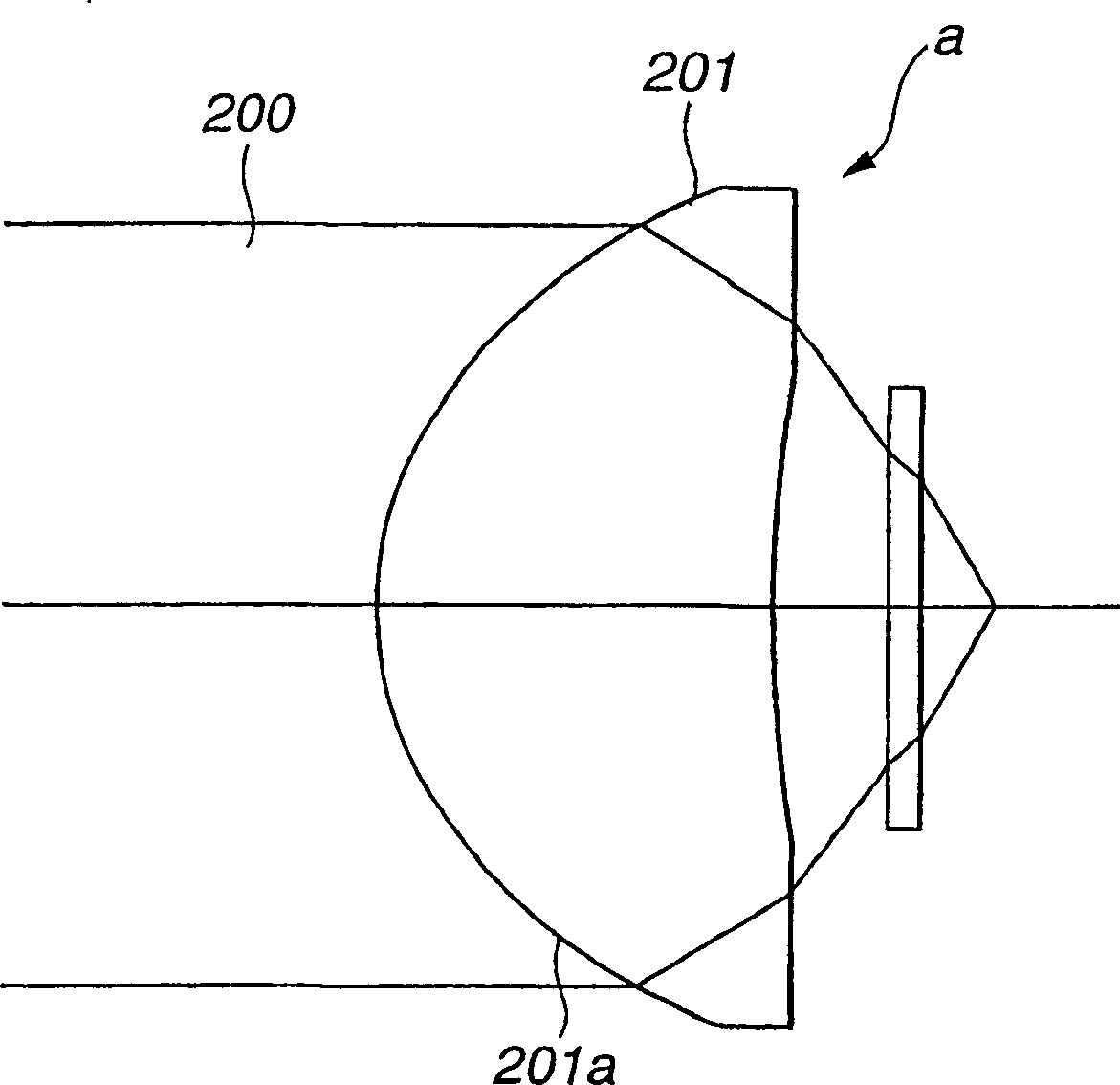
[0184] The objective lens 15 of embodiment 2 has the 1st lens group GR1 that is made up of the 1st lens L1 and the 2nd lens group GR2 that is made up of the 2nd lens L2, and this 1st lens L1, by having the refractive surface S 2r is the base plane and forms the diffraction plane S 2d and the composite surface S 2 The second lens L2 is a single-piece aspheric glass molded lens with large magnification. A protective layer 30 made of polycarbonate is disposed between the second lens L2 and the image surface (recording layer of the optical disc 100).
[0185] The numerical values of the constituent lenses of Example 2 are listed in Table 3 below.
[0186] r i
d i
r 1 =∞
d 1 =1.00
resin
r 2 =7.650
d 2 =0.20
r 3 =1.337
d 3 =1.60
LAH53
r 4 =6.486
d 4 =0.74
r 5 =∞
d 5 =0.1
Image plane = ∞
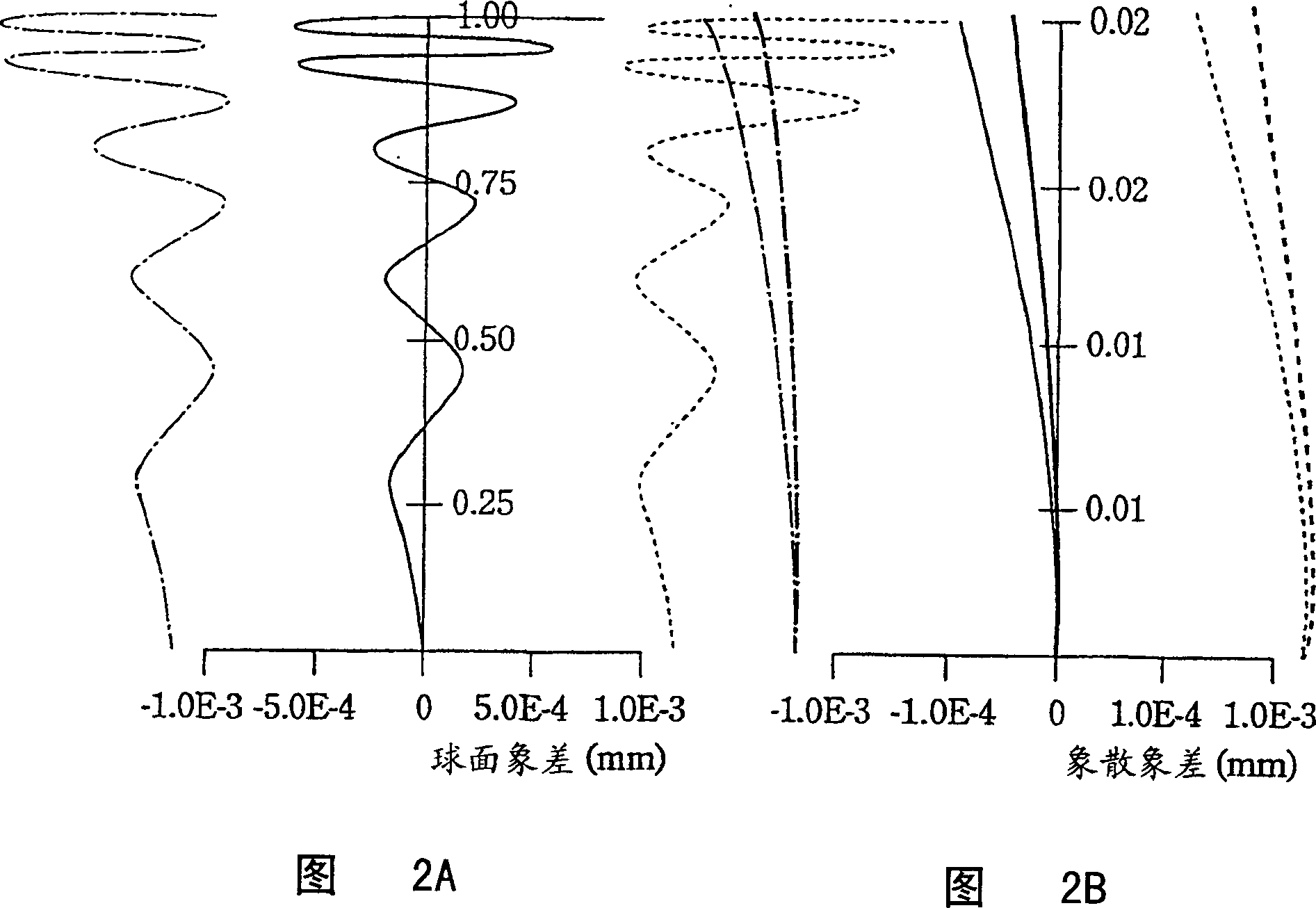
[0187] Embodiment 2, because the 1st lens L1 is f...
Embodiment 3
[0193] The objective lens 15 of embodiment 3 has the 1st lens group GR1 made up of the 1st lens L1 and the 2nd lens group GR2 made up of the 2nd lens L2, and this 1st lens L1, by having the refraction surface S 2r A synthetic resin layer 18 is laminated as a base surface, and a diffraction surface S is formed on the surface of the synthetic resin layer 18. 2d Composite surface S 2 The second lens L2 is a single piece of aspheric glass molded lens with large magnification. A protective layer 30 made of polycarbonate is disposed between the second lens L2 and the image surface (recording layer of the optical disc 100).
[0194] The numerical values of the constituent lenses of Example 3 are listed in Table 5 below.
[0195] r i
d i
r 1 =∞
d 1 =1.00
SBSL7
r 2r =7.750
d 2 =0.01
r 2d =7.750
d 3 =0.20
resin
r 3 =1.337
d 4 =1.60
LAH53
r 4 =6.486
d 5 =0.74
r 5 =∞ ...
Embodiment 5
[0212] The objective lens 15 of Example 5 has a first lens group GR1 composed of a first lens L1 having a refracting surface S with a second surface S, and a second lens group GR2 composed of a second lens L2. 2r is the basal plane and forms the diffractive surface S 2d while the composite surface S 2 The second lens L2 is a single-piece aspherical glass molded lens with large magnification. Between the second lens L2 and the image plane (the recording layer of the optical disc 100 ), the protective layer 30 made of polycarbonate is arranged.
[0213] The numerical value of each constituent lens of Example 5 is shown in the following Table 9.
[0214] r i
d i
r 1 =∞
d 1 =1.00
resin
r 2 =7.650
d 2 =3.00
r 3 =1.337
d 3 =1.60
LAH53
r 4 =6.486
d 4 =0.74
r 5 =∞
d 5 =0.1
polycarbonate
Image plane = ∞
[0215] In the objective lens 15 of the fifth embodiment, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com