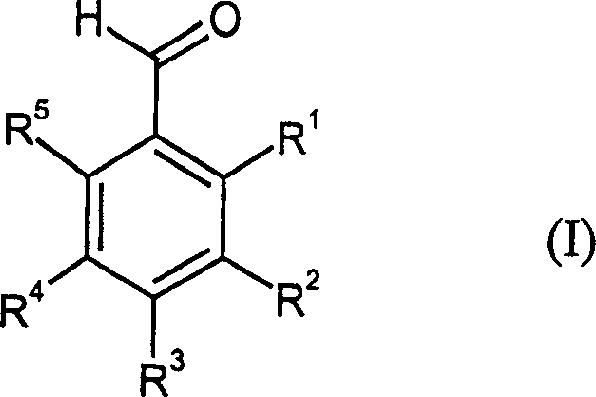
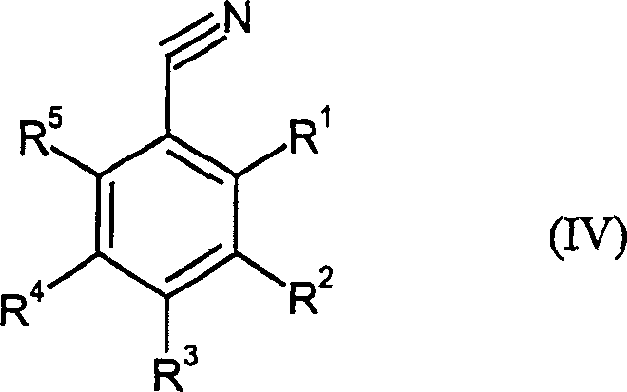
Catalytic reduction method of benzonitrile to benzoaldehyde
A technology of catalysts and compounds, applied in the fields of nitrile reduction and hydrolysis preparation, organic chemistry, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] 10.8 g of 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)-benzonitrile in 70 g of 80% formic acid and 0.9 g of Ni-Al-50 / 50 alloy were initially placed in the autoclave. The autoclave was pressurized with 15 bar nitrogen and heated to 70°C. Once the reaction temperature was reached, the hydrogen pressure was increased to 3 bar and kept constant for 10 hours. Subsequently, the mixture was cooled and filtered, and the solution was extracted with toluene, followed by fractional distillation under reduced pressure, yielding 8.8 g of 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)-benzaldehyde (80% of theory).
Embodiment 2
[0064] 7.7 grams of 3-trifluoromethylbenzonitrile in 70 grams of 70% formic acid and 0.9 grams of Ni-Al-50 / 50 alloy were first placed in the autoclave. The autoclave was pressurized with 15 bar nitrogen and heated to 80°C. Once the reaction temperature was reached, the hydrogen pressure was increased to 10 bar and kept constant for 7 hours. Subsequently, the mixture was cooled and filtered, and the solution was extracted with toluene, followed by fractional distillation under reduced pressure, yielding 6.5 g of 3-trifluoromethylbenzaldehyde (85% of theory).
Embodiment 3
[0066] 7.7 grams of 3-trifluoromethylbenzonitrile in 50 grams of 75% formic acid and 1 gram of NiFeCrAl prealloy were first placed in the autoclave. The autoclave was pressurized with 15 bar nitrogen and heated to 80°C. Once the reaction temperature was reached, the hydrogen pressure was increased to 6 bar and kept constant for 10 hours. Subsequently, the mixture was cooled and filtered, and the solution was extracted with toluene, followed by fractional distillation under reduced pressure, yielding 7.0 g of 3-trifluoromethylbenzaldehyde (89% of theory).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com