Method based on repetitive sequence recognition for splicing sequencing data of whole genome
A whole-genome sequencing and repeating sequence technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as splicing errors in large genome data of higher animals and plants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
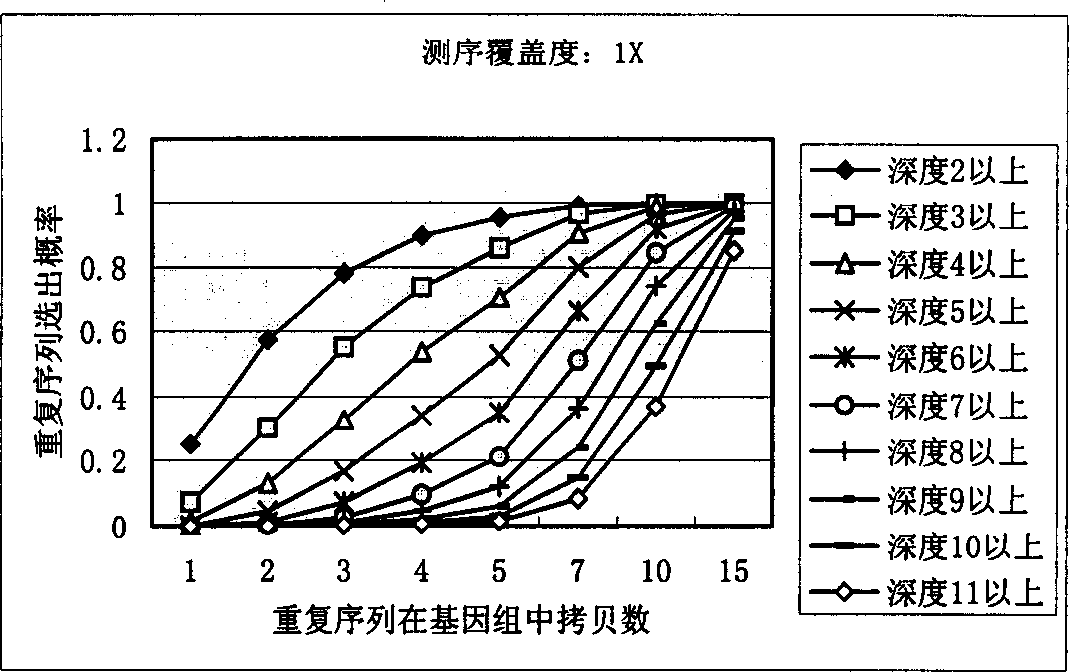
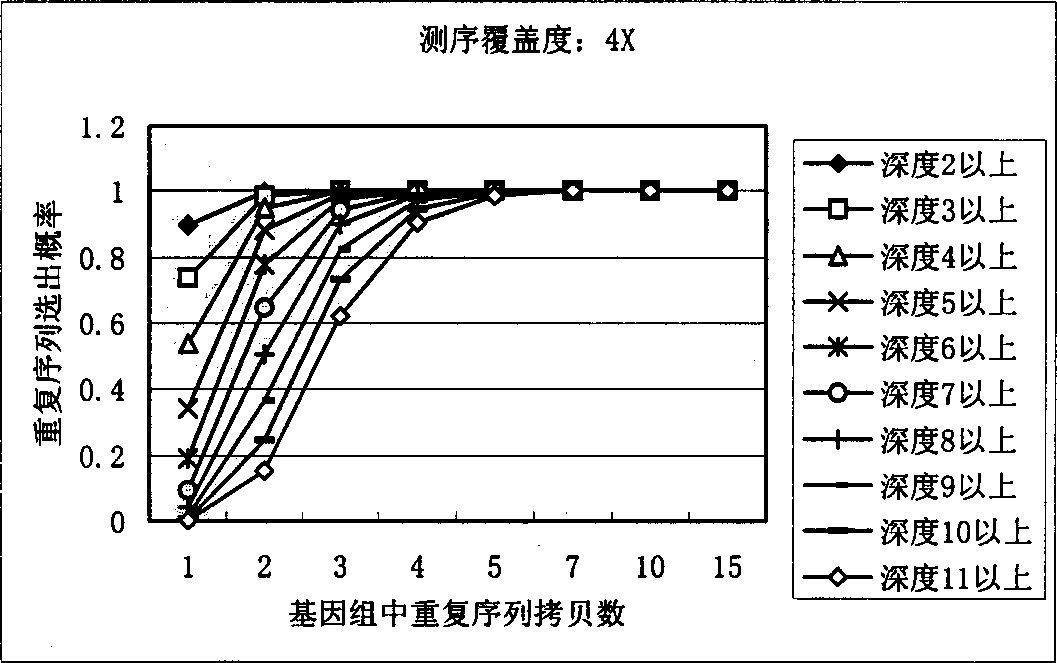
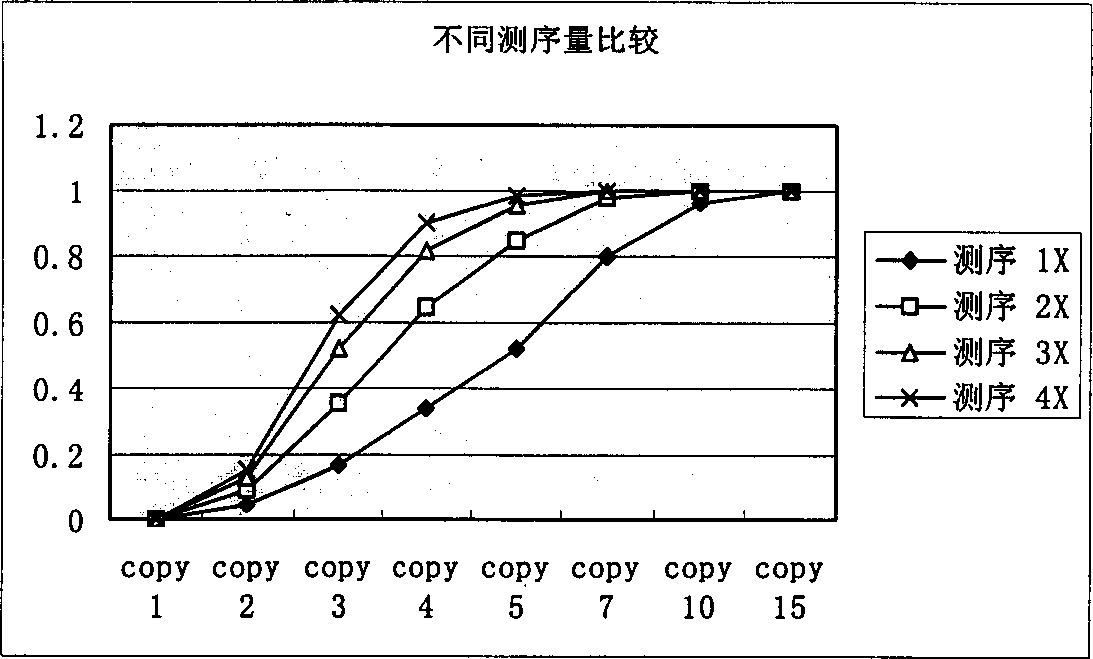
[0026] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, introduce each step of the inventive method in detail:
[0027] In order to identify repetitive sequences, the present invention first sets a minimum fragment length, generally set to 15bp-20bp, and repetitive sequences shorter than this length will not be considered. To simplify the model, it is assumed that all sequencing reads are equal in length, L.
[0028] The meaning of the parameters in the following formulas: G: total genome length, L: average effective read length of sequencing N: number of successful sequencing reactions, F: minimum fragment length for identification.
[0029] Count the occurrences of small non-repeated fragments in shotgun sequencing:
[0030] Define a random variable Y ik Describe the event that the above-mentioned DNA fragment of the specified length appears K times in the whole genome sequencing by the shotgun method:
[0031] If the number of occurrences of fragments starting from a ce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com