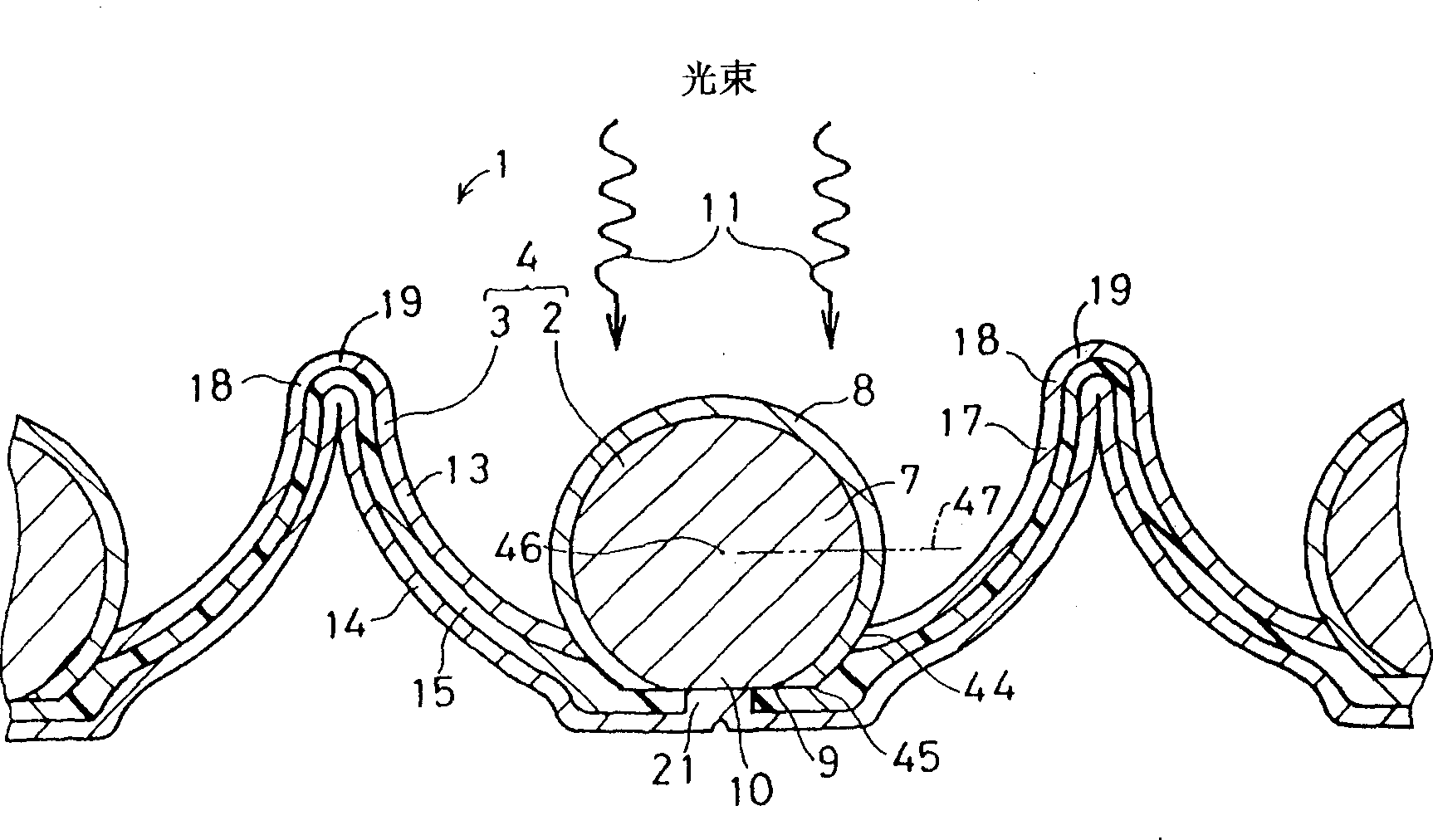
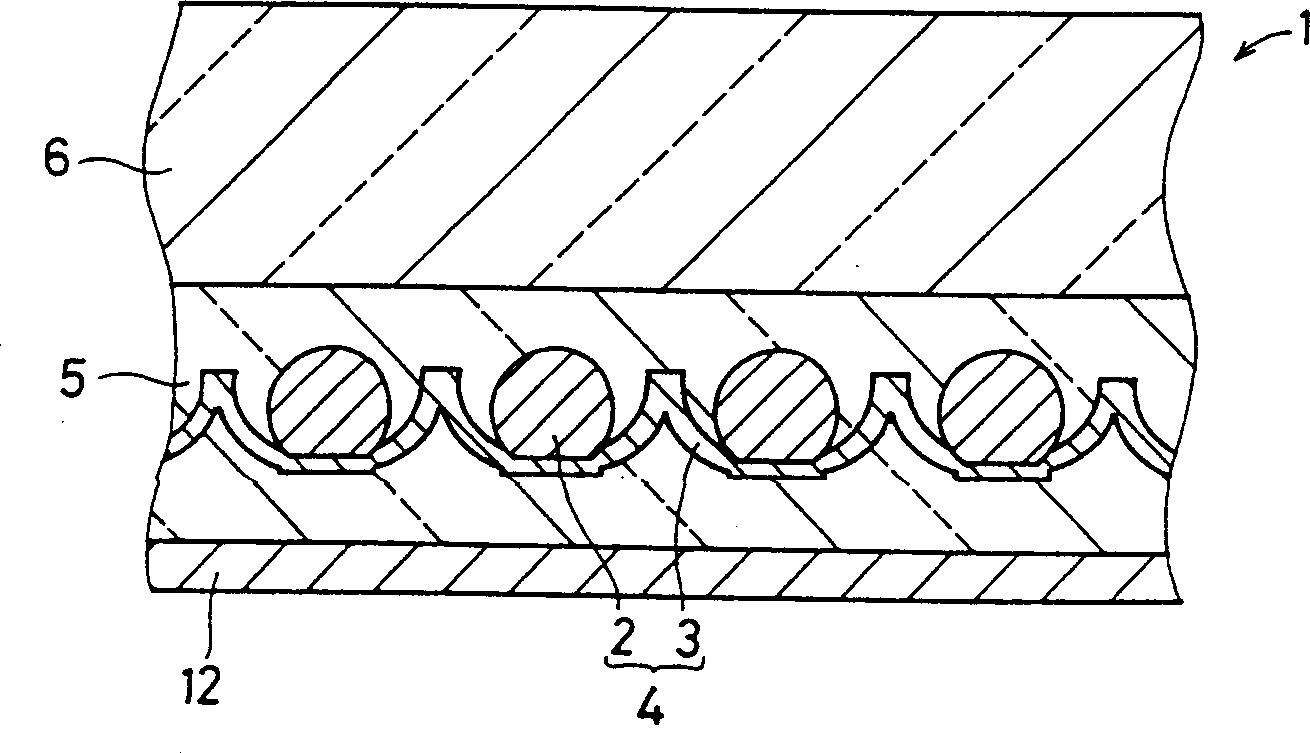
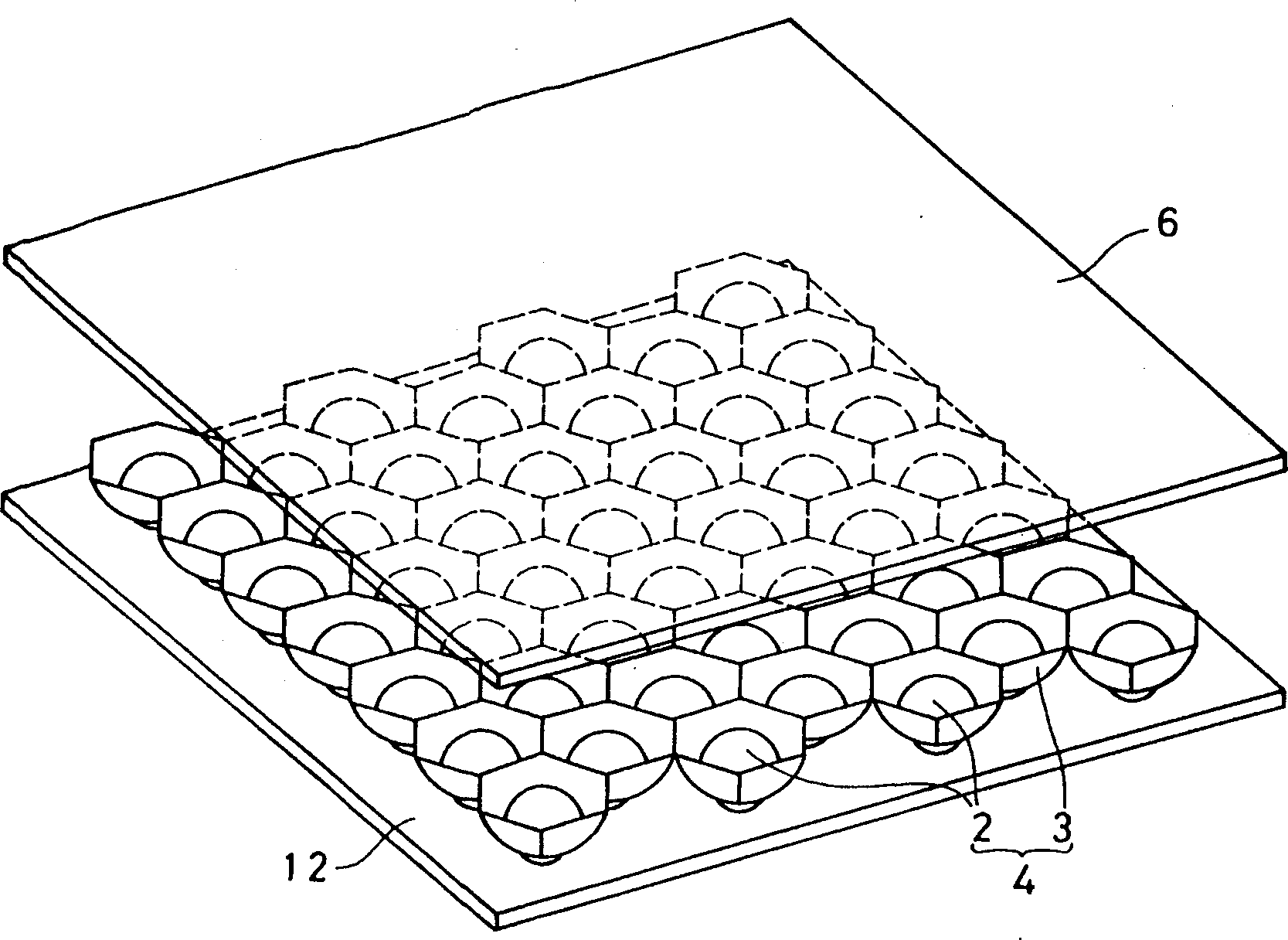
Photo-electric equipment and batch spherical semiconductor grain producing equipment
A technology of optoelectronic equipment and semiconductors, which is applied in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, crystal growth, etc., and can solve problems such as poor cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0213] About 1.5 ml of silicon material was added to a graphite crucible. The graphite crucible has an outer diameter of 20 mm, an outer length of 40 mm, its volume is represented by an inner diameter of 10 mm and a length of 35 mm, and is accommodated in a ceramic airtight and thermally insulated container with a nozzle at one end of the container having an inner diameter of 1 mm and a length of 5 mm. Immediately before particle production, 4.6kW of high-frequency induction power was applied for about 20 minutes to stabilize particle production conditions such as temperature. Particle formation was started by applying a nitrogen pressure of about 300 Pa, resulting in silicon spheres having an average diameter of about 1 mm. In order to reduce the degree of reaction between silicon and graphite and the degree of combustion of graphite due to the presence of oxygen, a nitrogen pressure of about 100 Pa is maintained in the system where the flow rate becomes zero at the beginning...
example 2
[0215] About 1.5 ml of silicon material was added to a graphite crucible. The graphite crucible has an outer diameter of 20 mm, an outer length of 40 mm, its volume is represented by an inner diameter of 10 mm and a length of 30 mm, and is accommodated in a ceramic airtight and heat-insulated container with a nozzle of an inner diameter of 1 mm and a length of 10 mm at one end of the container. Immediately before particle production, 4.6kW of high-frequency induction power was applied for about 15 minutes to stabilize particle production conditions such as temperature. Particle formation was started by applying a nitrogen pressure of about 500 Pa, resulting in silicon spheres having an average diameter of about 1 mm. In order to reduce the degree of reaction between silicon and graphite and the degree of combustion of graphite due to the presence of oxygen, a nitrogen pressure of about 100 Pa is maintained in the system where the flow rate becomes zero at the beginning of appl...
example 3
[0217] About 1.2 ml of silicon material was added to a graphite crucible. The graphite crucible has an outer diameter of 20 mm, an outer length of 40 mm, its volume is represented by an inner diameter of 10 mm and a length of 25 mm, and is accommodated in a ceramic airtight and heat-insulated container with a nozzle of an inner diameter of 1 mm and a length of 10 mm at one end of the container. Immediately before particle production, a high-frequency induction power of 3.6kW was applied for about 20 minutes to stabilize particle production conditions such as temperature. Particle formation was started by applying a nitrogen pressure of about 300 Pa, resulting in silicon spheres having an average diameter of about 1 mm. In order to reduce the degree of reaction between silicon and graphite and the degree of combustion of graphite due to the presence of oxygen, a nitrogen pressure of about 100 Pa is maintained in the system where the flow rate becomes zero at the beginning of ap...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com