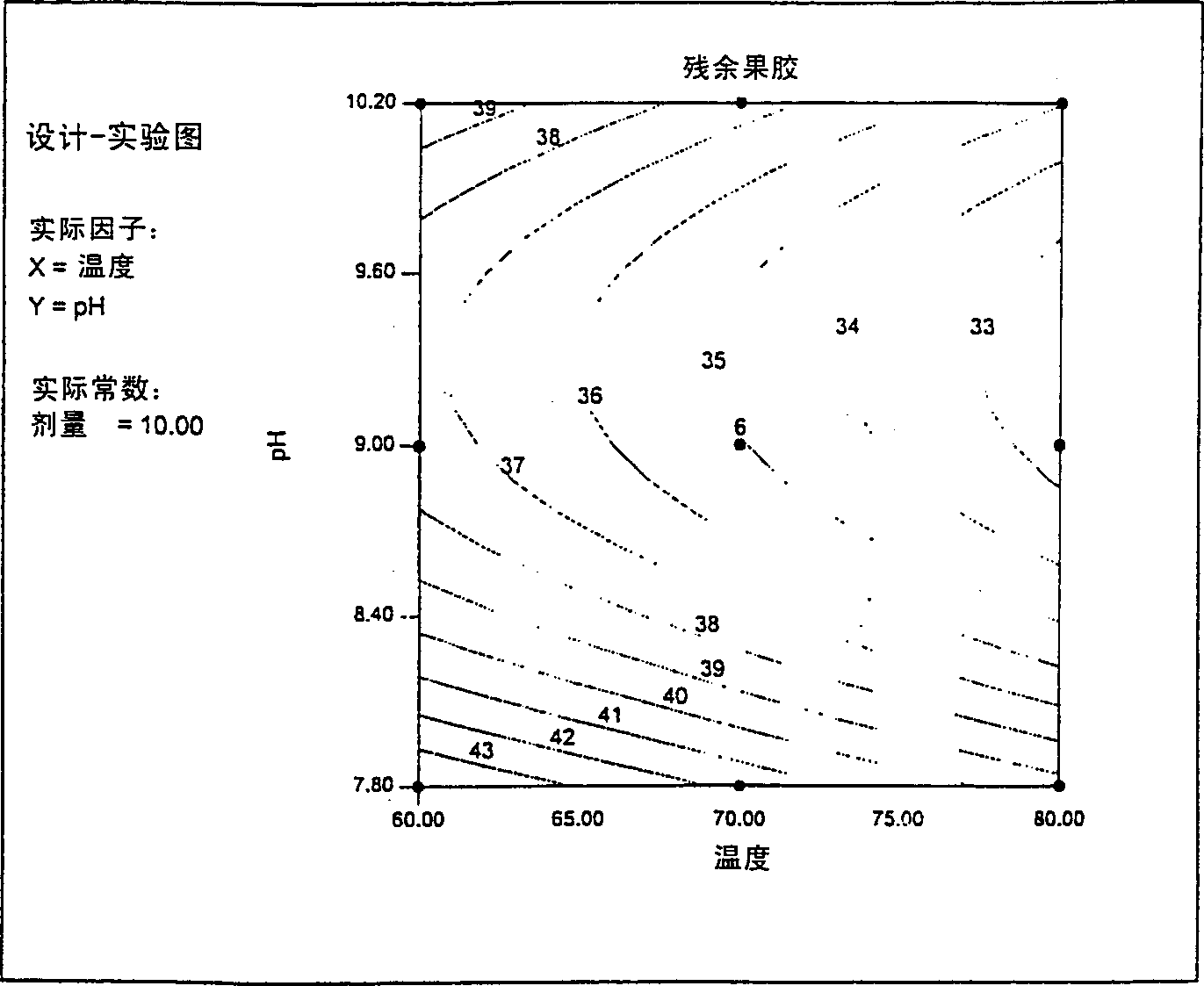
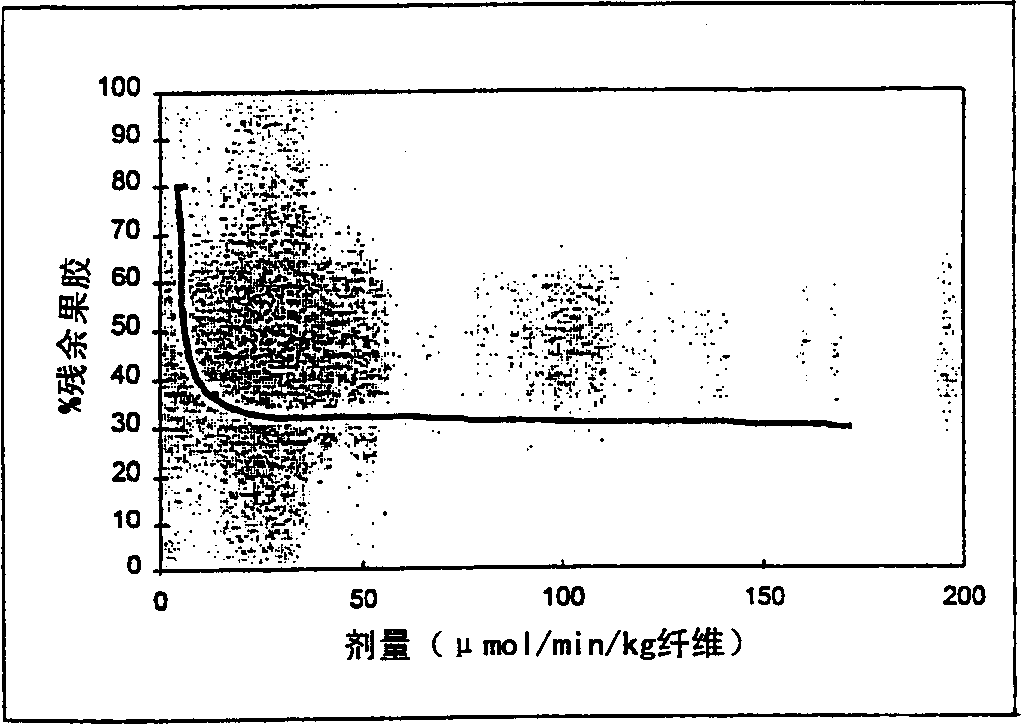
Biopreparation of textiles of high temp.
A technology for fabrics and compounds, applied in the field of cotton fabrics, can solve the problems of inactivity and limit the biological scouring of fabrics, and achieve the effects of short processing time, effective emulsification and dewaxing, and complete compatibility.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0025] It is understood that any polypeptide exhibiting the properties described above may be used in the practice of the present invention. In other words, pectate lyases derived from other organisms can be used as long as the polypeptides produced exhibit the above-mentioned high-temperature activity (and preferably, pH-optimum and divalent cation-independence of the activity), or derived from the above-mentioned enzymes by adding, Pectate lyases derived from deletion or substitution of one or more amino acids, including hybrid polypeptides. Such pectate lyase variants useful in the practice of the present invention can be generated using conventional mutagenesis procedures and identified using, for example, high throughput screening techniques such as the agar plate screening procedure described in Example 1 below.
[0026] The temperature, pH, and divalent cation dependencies of isolating pectate lyase can be determined using conventional methods. For example, an enzyme a...
Embodiment Embodiment 1
[0060] EXAMPLES Example 1: Determination of the properties of thermostable pectate lyases
[0061] The following method was used for qualitative analysis of pectate lyase activity. 1. Pectate lyase assay
[0062] For this experiment, a 0.1% sodium polygalacturonate (Sigma P-1879) solution was prepared in 0.1 M glycine buffer (pH 10). Take 4ml of this solution and preheat at 40°C for 5 minutes. Then, add 250 μl of enzyme (or enzyme diluent), mix the reaction system on the mixer at the highest speed for 10 seconds, and incubate at 40°C or other temperatures for 20 minutes, then measure the absorbance at 235nm: 0.5ml cuvettes, absorbance at 235nm was measured continuously on a HP diode array spectrophotometer in a temperature-controlled cuvette holder. For steady state, a linear increase of at least 200 seconds was used to calculate the rate.
[0063] For the calculation of the catalytic rate, an increase of 5.2A235 / min corresponds to the formation of 1 μ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com