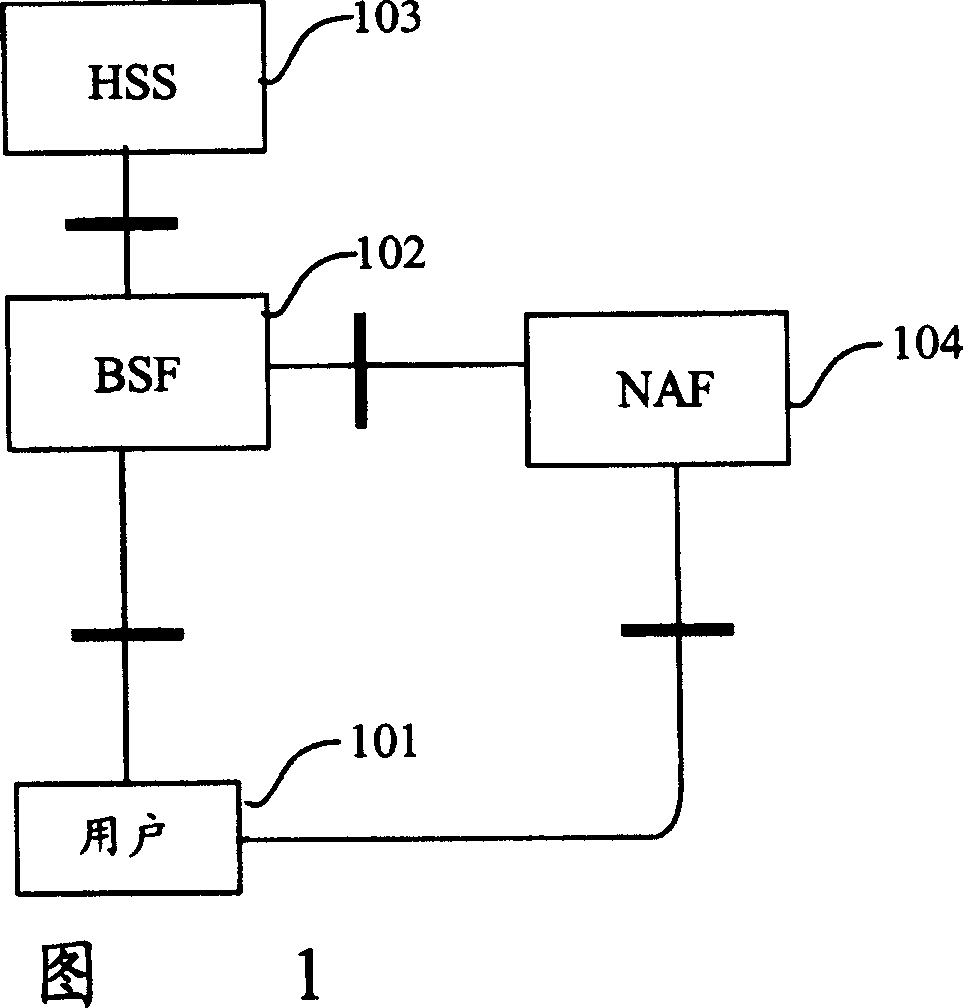
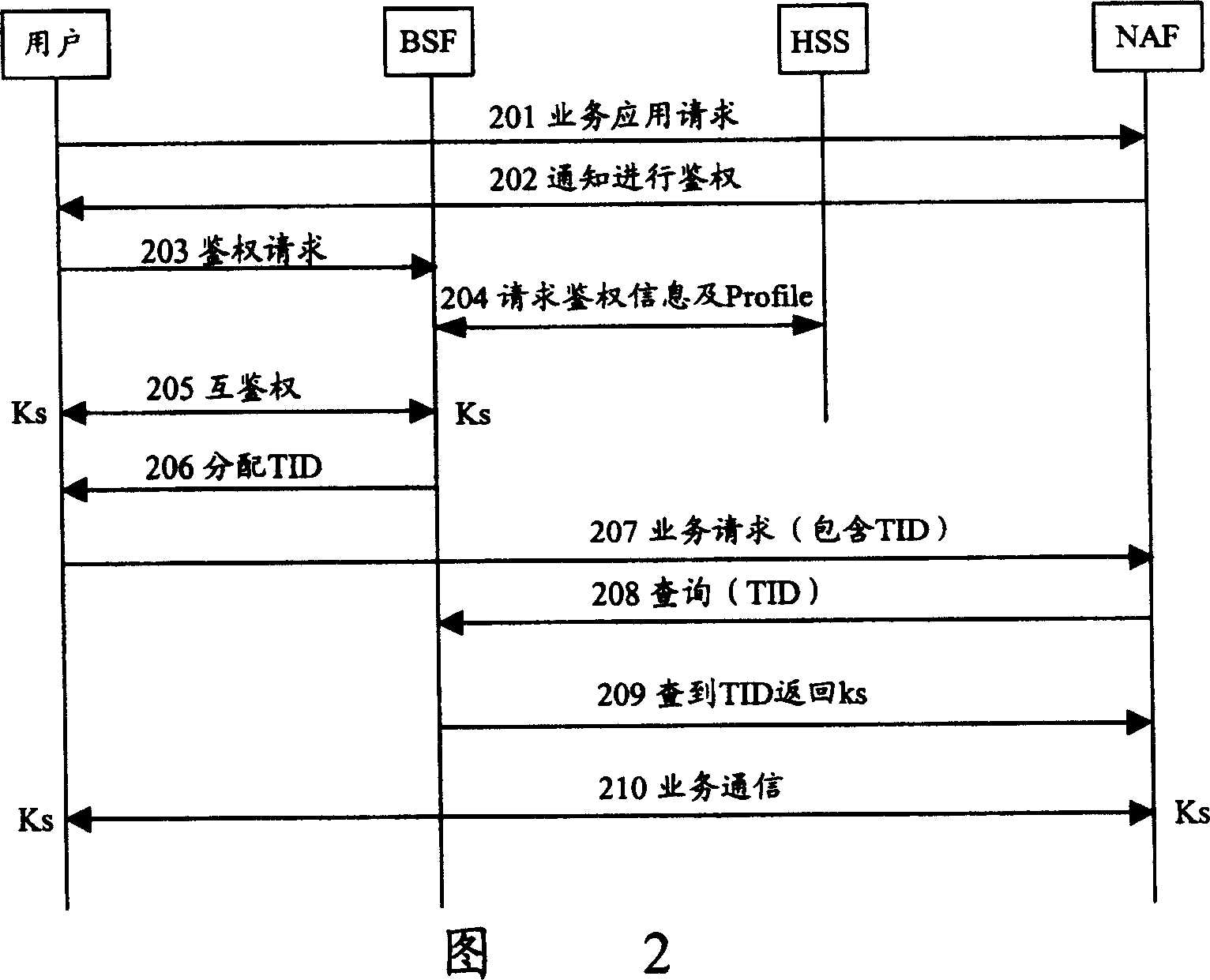
Method for authenticating users
A legality and user technology, applied in the direction of user identity/authority verification, wireless communication, digital transmission system, etc., can solve the problems of not specifying the composition of TID, increasing user key theft, and unable to manage TID, so as to reduce the number of keys Possibility of theft, effect of increasing security
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] The BSF assigns a TID valid for more than one NAF to the user at the same time, and does not encrypt the TID.
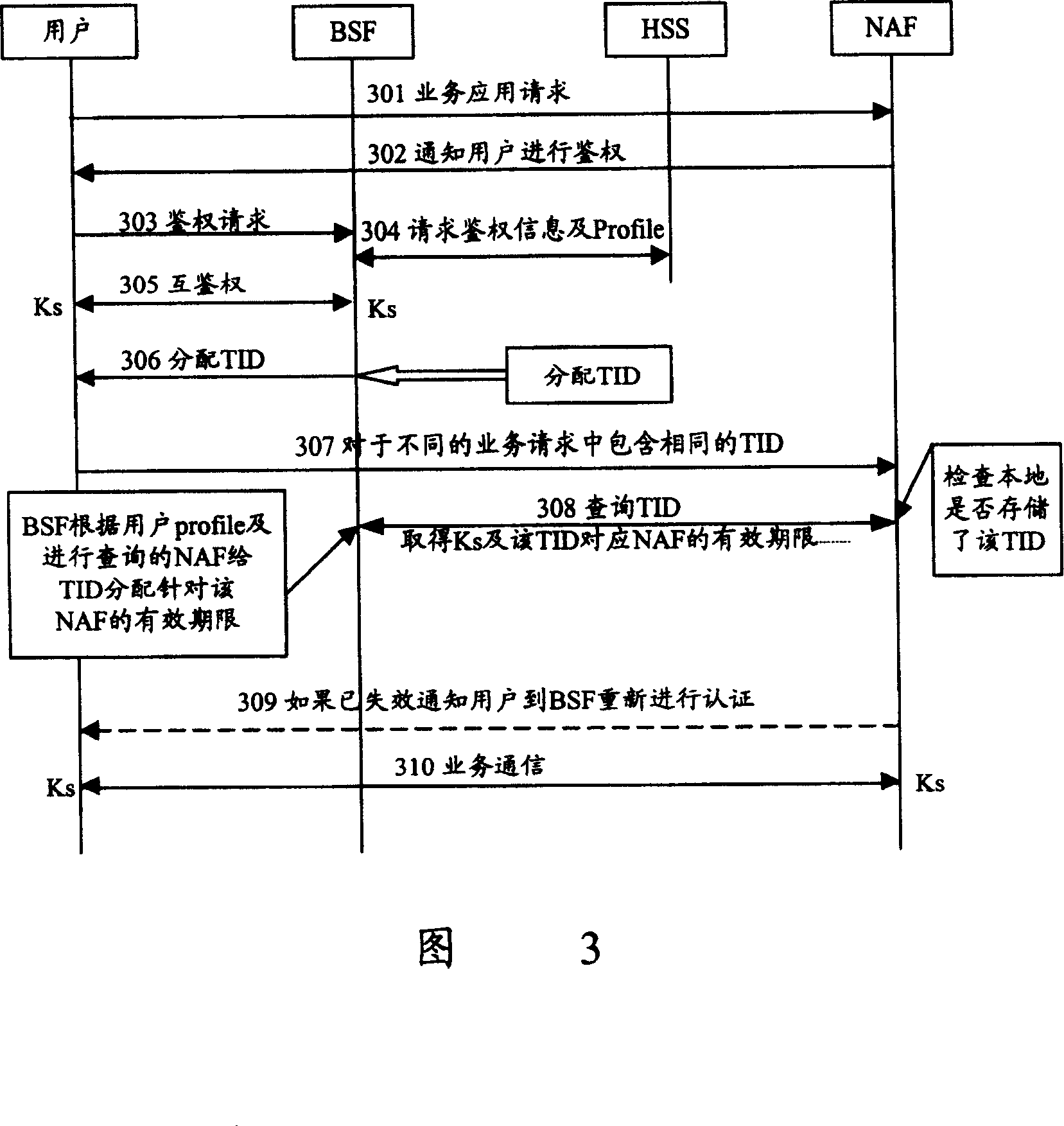
[0061] FIG. 3 is a flow chart of verifying user legitimacy according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
[0062] Step 301, the user sends a service application request message to the NAF;
[0063] Step 302, after receiving the message, the NAF notifies the user to go to the BSF for initial authentication;
[0064] Step 303, the user sends an authentication request message to the BSF;
[0065] Step 304, after receiving the user's authentication request message, the BSF queries the HSS for the user's authentication information and Profile;
[0066] Step 305: After receiving the response message sent by the HSS that contains the searched information, the BSF uses the found information to perform AKA mutual authentication with the user. The user and the user have a shared key Ks;
[0067] Step 306, the BSF assigns a TID including only the identification...
Embodiment 2
[0079] The BSF allocates a TID valid only for a certain NAF to the user, and the TID is encrypted. The method of assigning a TID to a user that is valid only for a certain NAF has been described in detail in the invention patent titled "A Method for Allocating Conversational Transaction Identifiers" submitted by the applicant on the same day;
[0080] FIG. 4 is a flow chart of verifying user legitimacy according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
[0081] Step 401, the user sends a service application request message to the NAF;
[0082] Step 402, after receiving the message, the NAF notifies the user to go to the BSF for initial authentication;
[0083] Step 403, the user sends an authentication request message to the BSF;
[0084] Step 404, after receiving the user's authentication request message, the BSF queries the HSS for the user's authentication information and Profile;
[0085] Step 405, after the BSF receives the response message sent by the HSS that contai...
Embodiment 3
[0096] The BSF allocates a TID valid only for a certain NAF to the user, and does not encrypt the TID.
[0097] FIG. 5 is a flow chart of verifying user legitimacy according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
[0098] Step 501, the user sends a service application request message to the NAF;
[0099] Step 502, after receiving the message, the NAF notifies the user to go to the BSF for initial authentication;
[0100] Step 503, the user sends an authentication request message to the BSF;
[0101] Step 504, after receiving the user's authentication request message, the BSF queries the HSS for the user's authentication information and Profile;
[0102] Step 505, after the BSF receives the response message sent by the HSS containing the searched information, it uses the found information to perform AKA mutual authentication with the user. The user and the user have a shared key Ks;
[0103] In step 506, the BSF allocates an identification number valid only for a certain...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com