Prodn. of olefins
A technology for olefins and dienes, which is applied in the field of cracking olefin-rich hydrocarbon raw materials, and can solve problems such as catalyst stability issues that have not been raised
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
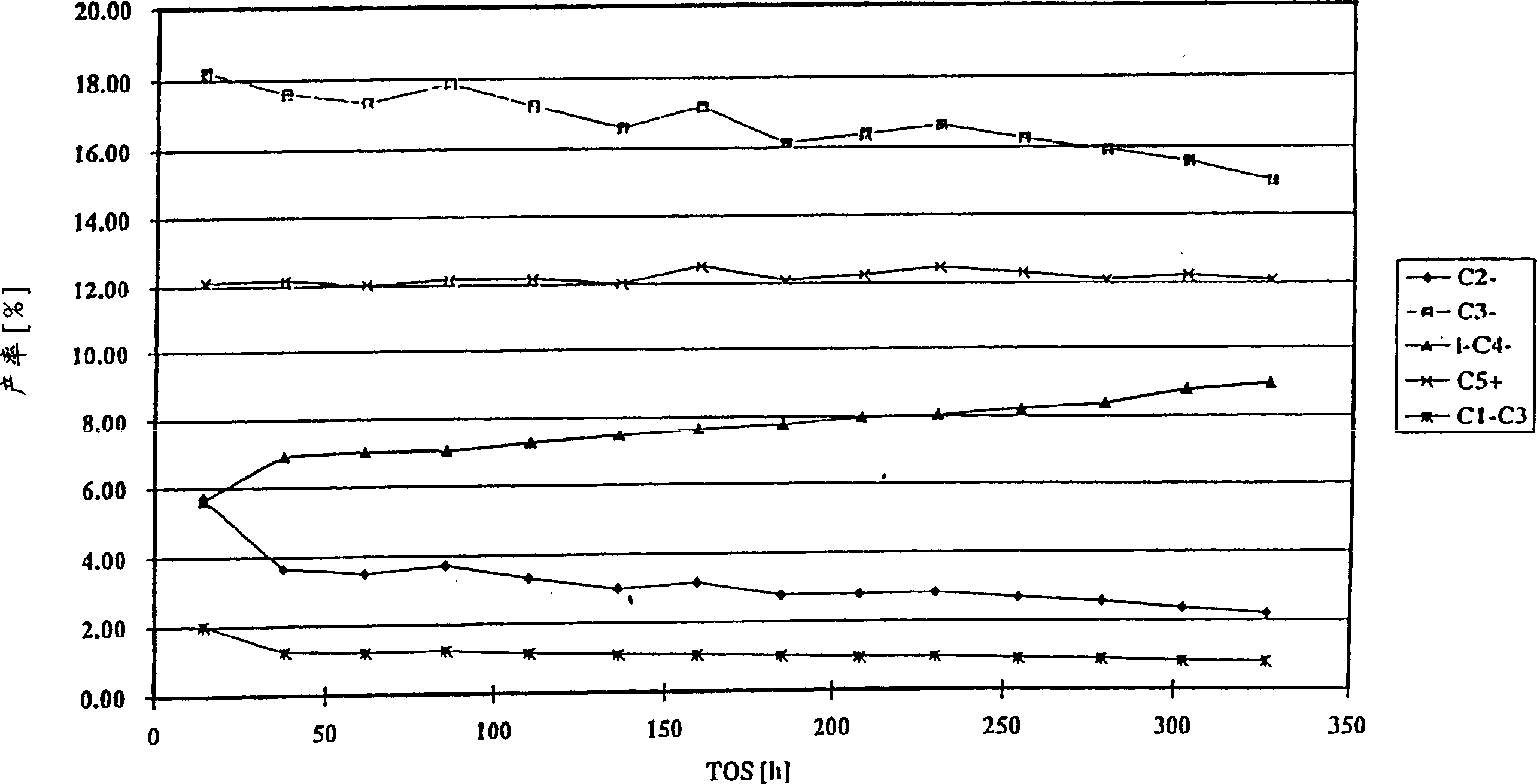
[0090] In this example, lightly cracked naphtha (LCN) was cracked in the presence of crystalline silicate. The catalyst is a silicalite formulated with a binder, which is pretreated by heating (in steam) (as described below), dealuminated with an aluminum complexing agent to extract aluminum from it, and finally calcined. The catalyst is then used to crack olefins in the hydrocarbon feedstock, and an effluent with substantially the same olefin content as the feedstock is produced through a catalytic cracking process.
[0091]In the catalyst pretreatment, silicalite obtained by the company UOP Molecular SievePlant of POBox 11486, Linde Drive, Chickasaw, AL 36611, USA under the trade name S115, is extruded into pellets together with a binder containing precipitated silica. The binder accounts for 50% by weight of the silicalite / binder mixture obtained. More specifically, 538 g of precipitated silica (commercially available from Degussa AG of Frankfurt, Germany under the trade name F...
Embodiment 2
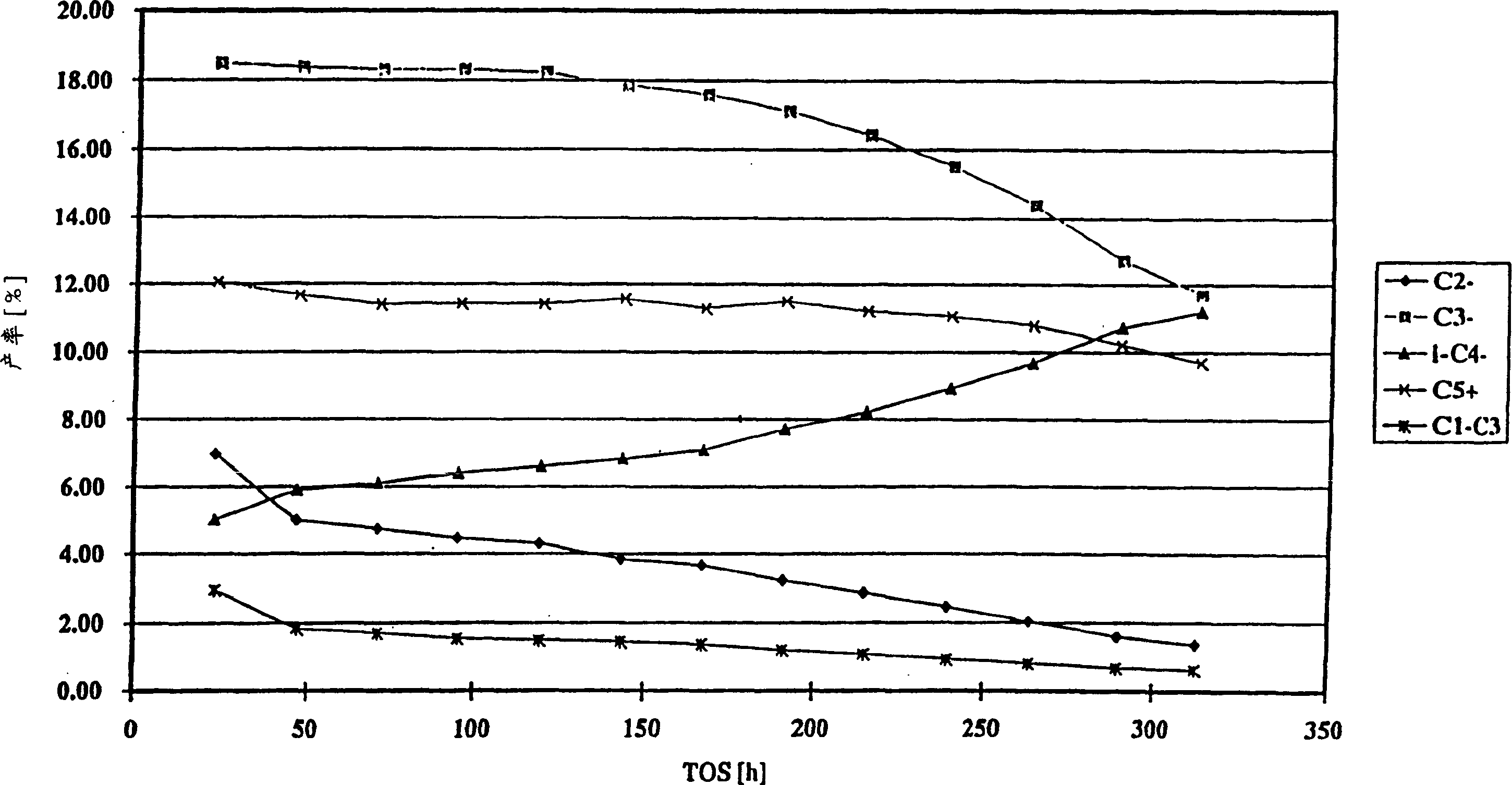
[0114] Example 1 was repeated using different raw materials. The raw material was not lightly cracked naphtha, but fractionated C obtained from lightly cracked naphtha. 5 Distillate. In addition, during the catalytic cracking process, the inlet temperature is 548℃, and the hydrocarbon outlet pressure is about 1×10 5 N / m 2 (1 bar) (ie normal pressure).
[0115] Table 4 shows the C from LCN 5 Distillate feedstock, such as the hydrogenation feedstock after diolefin hydrogenation in Example 1, and the distribution of hydrocarbon substances in the effluent after the cracking process. It can be seen that the raw material initially mainly contains C 5 After the catalytic cracking process, the olefin content is basically the same, but C in the effluent 5 The amount of the substance is significantly reduced compared to the amount of the substance in the original raw material. Similarly, C 2 -C 4 Light olefins can be easily fractionated from the effluent, leaving C with the composition show...
Embodiment 3
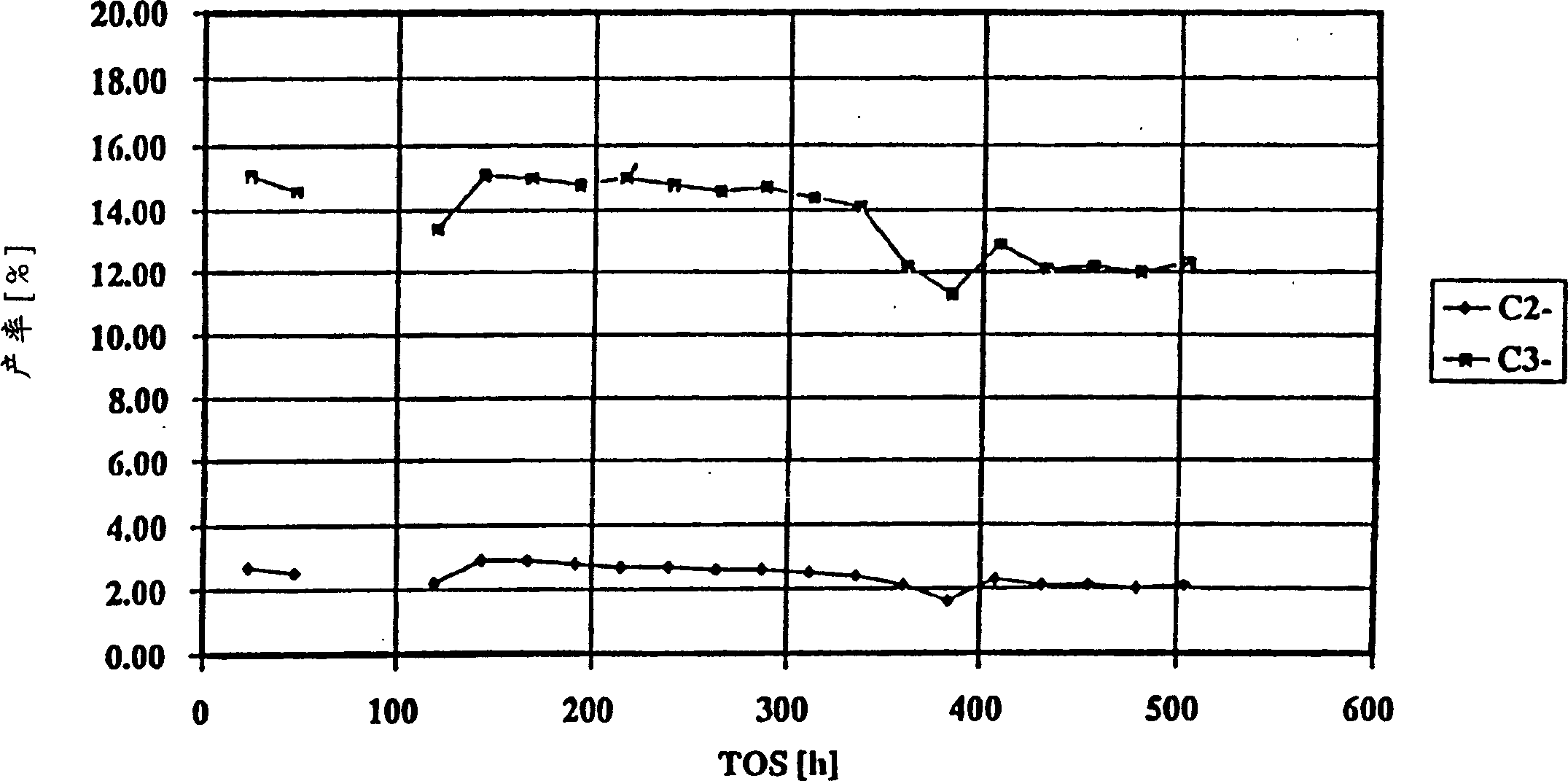
[0118] Use C from the MTBE unit of the refinery 4 The raffinate (raffinate II) was used as a raw material instead of slightly cracked naphtha to repeat Example 1. In addition, the inlet temperature of the feedstock is about 560°C, and the hydrocarbon outlet pressure is about 1×10 5 N / m 2 (1 bar) (atmospheric pressure).
[0119] It can be seen from Table 7-9 that C 2 And the main C 3 Alkenes from C 4 The olefin feedstock is prepared according to the method of the present invention. About 34.5% of the olefin content in the effluent as C 2 And / or C 3 Alkenes exist, C 2 And / or C 3 The olefins are easily fractionated from the effluent, and the propylene yield based on olefins is 29%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com