Pulmonary arterial hypertension non-human primate model and construction method thereof
A pulmonary arterial hypertension, primate technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problem of difficulty in establishing a non-human primate pulmonary arterial hypertension animal model, etc., and achieve the effect of good biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0030] The present invention provides a preparation method of degradable embolic particles, the preparation method comprising the following steps:
[0031] 1) After centrifuging the blood, take the supernatant layer, platelet layer and part of the red blood cell layer;
[0032] 2) Centrifuge again and discard part of the supernatant;
[0033] 3) After adding thrombin to the remaining system, inject it into the silicone tube, and let it stand to form a thrombus strip;
[0034] 4) After standing, the thrombus strip is taken out, and degradable embolic particles are obtained after permeable membrane filtration.
[0035] In one embodiment, the blood is selected from venous blood or arterial blood.
[0036] The blood is derived from autologous blood of experimental animals. Autologous blood prevents clotting. In the present invention, the experimental animals are experimental animals obtained in compliance with laws and administrative regulations. The experimental animals are,...
Embodiment 1
[0070] Example 1 Construction of a non-human primate model of pulmonary arterial hypertension using degradable embolic particles
[0071] 1. Mechanism of degradable embolic particles inducing pulmonary hypertension:
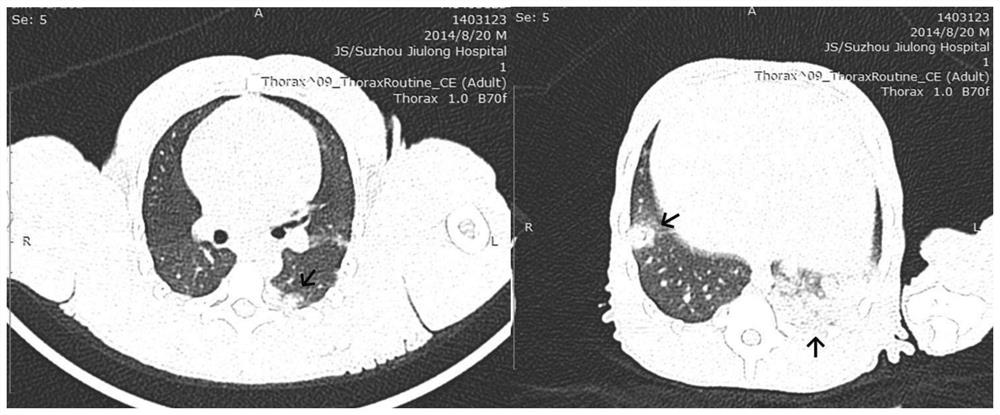
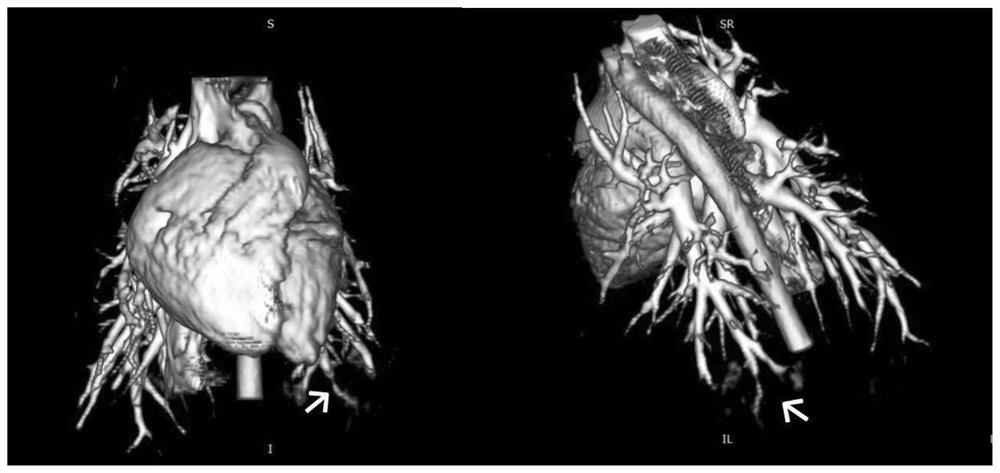
[0072] The non-human primate femoral vein was punctured by the Seldinger technique to establish a right heart catheter access, and the degradable biocompatible embolic particles were injected into the right atrium through the right heart catheter, and the main pulmonary artery, branches of the pulmonary artery, peripheral pulmonary arteries and capillaries were reached through blood circulation. The mesh is the first barrier encountered during its circulation. The diameter of the degradable biocompatible embolic particles is larger than the diameter of the peripheral pulmonary artery and capillary network, which leads to pulmonary hypertension by mechanically blocking the branches of the pulmonary artery and inducing autologous thrombosis.
[0073] 2. Inducing ma...
Embodiment 2
[0111] Example 2. Constructing a non-human primate model of pulmonary hypertension by using autologous thrombus
[0112] 1. Mechanism of autologous thrombosis-induced pulmonary hypertension:
[0113] The Seldinger technique is used to puncture the femoral vein to establish a right heart catheter access, and a certain size and length of autologous thromboembolism is injected into the right atrium through the right heart catheter, and then reaches the main pulmonary artery and branches of the pulmonary artery through blood circulation. The first barrier encountered during circulation, whose diameter is larger than the diameter of the peripheral pulmonary artery, can lead to pulmonary hypertension by mechanically occluding larger branches of the pulmonary artery and inducing autologous thrombosis.
[0114] 2. Embolization material: autologous thromboembolism
[0115] Preparation of autologous thrombus: 5 ml of animal autologous whole blood plus 20 ul of thrombin was quickly inje...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com