Permanent magnet arc-shaped motor with wedge-shaped tooth variable cross-section winding
An arc-shaped motor and variable cross-section technology, applied in the shape/style/structure of winding conductors, electromechanical devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of low torque density, etc. The effect of reducing the tooth height
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
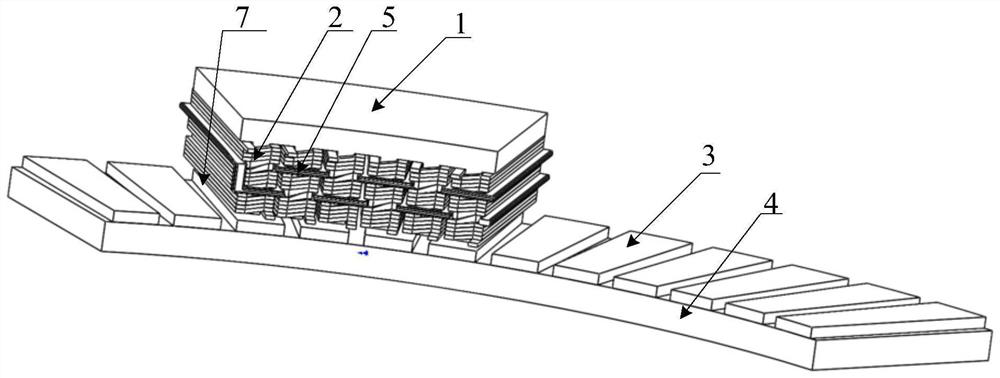
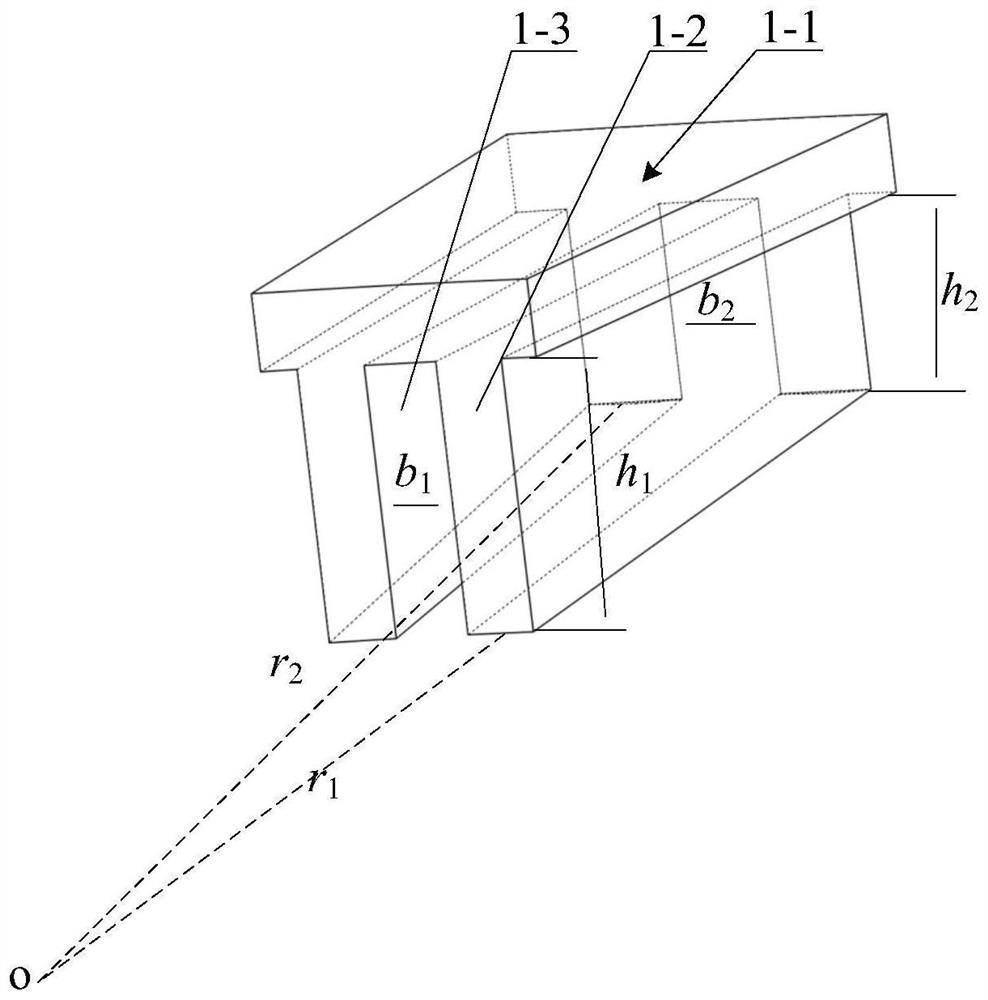
[0041] like figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, this embodiment is a wedge-shaped tooth variable-section winding permanent magnet arc motor, which includes a primary component and a secondary component. Both the primary and secondary components are arc-shaped. The primary assembly includes a primary iron core 1 and an armature winding 2, and a cooling pipe 5 or no cooling pipe 5 is provided, depending on actual needs. Slots are formed on the primary iron core to form a structure of a primary yoke 1-1, S primary teeth 1-2 and Q primary slots 1-3 (both S and Q are integers). The secondary assembly consists of the secondary iron core 4 and the permanent magnet 3 . Between the primary assembly and the secondary assembly is an air gap 7 structure.
[0042] The arc inner diameter of the permanent magnet arc motor with wedge tooth variable section winding is r 1 , the outer diameter of the arc is r 2 , that is, the radius at the inner diameter is r 1 , the radius at the outer dia...
Embodiment 2
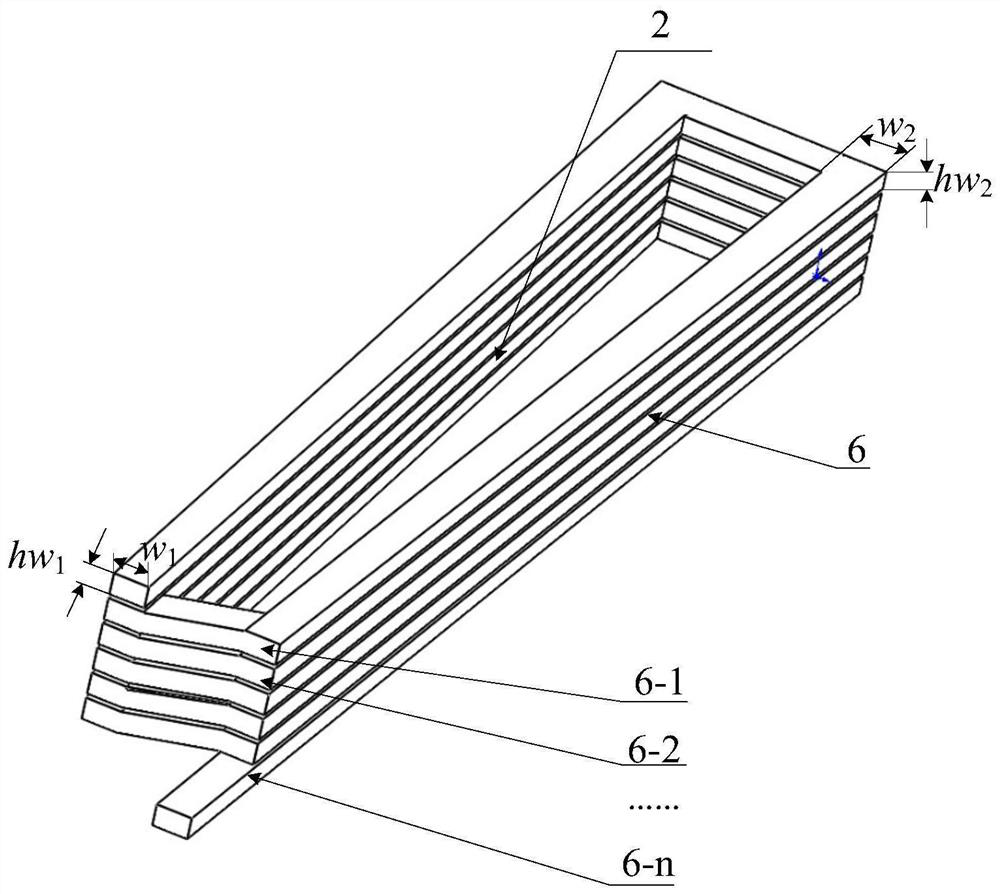
[0047] This example is further designed by, such as image 3 As shown, the cross section of each conductor of the armature winding is a rectangle, and at any arc radius r, the shape of the conductor adapts to the shape change of the primary slots 1-3. At the inner diameter of the arc, the width and height of the conductor cross-sections on both sides are respectively w 1 and hw 1 . At the outer diameter of the arc, the width and height of the conductor cross-section are respectively w 2 and hw 2 , w 1 ≠w 2 , hw 1 ≠hw 2 . Along the conductor winding direction, the inner diameter gradually changes from the outer diameter, the conductor cross-sectional shape changes, and the conductor cross-sectional width gradually changes from w 1 increase to w 2 , the height is given by hw 1 gradually decrease to hw 2 , the conductor cross-sectional area w at the inner diameter of the arc 1 ·h 1 Conductor cross-sectional area w with arc outer diameter 2 ·h 2 equal, i.e. w 1 ·h...
Embodiment 3
[0051] This example is further designed by, such as Figure 4 As shown, cooling pipes 5 can be arranged in the armature winding 2, and one cooling pipe is arranged in each primary slot 1-3. In the figure, the conductors 6-1, 6-2, 6-4, 6-5, 6-6 The structure of each layer is the same, and the cross-sectional shape of each position is the same. Each primary tank 1-3 is provided with a cooling pipe. In the figure, the cooling pipe 5-1 is in close contact with the conductor 6-3. Affected by the shape of the cooling pipe 5-1, the cross-sectional shape of the conductor 6-3 is different from that of the conductors 6-1, 6-2, 6-3, and 6 of other layers. -5, 6-6 are different, but the cross-sectional area is the same as the cross-sectional area of other layer conductors 6-1, 6-2, 6-4, 6-5, 6-6 at any cross-sectional position. The cooling pipe adopts an annular structure, and the cooling pipe 5-2 and the cooling pipe 5-2 are connected annular pipes, which are introduced from one side...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com