Multi-physical field time domain model order reduction method in data-driven electromagnetic system
A multi-physics and electromagnetic system technology, applied in the field of multi-physics time-domain model reduction, can solve problems such as inability to solve the problem of model reduction, high training cost, and difficulty in applying distributed power generation networks, and achieves good generalization. , high expansion, and the effect of improving time-domain computing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0054] The present invention will be described in further detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings. The following examples will help those skilled in the art to further understand the present invention, but do not limit the present invention in any form. It should be noted that, for those skilled in the art, several changes and improvements can be made without departing from the inventive concept. These all belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
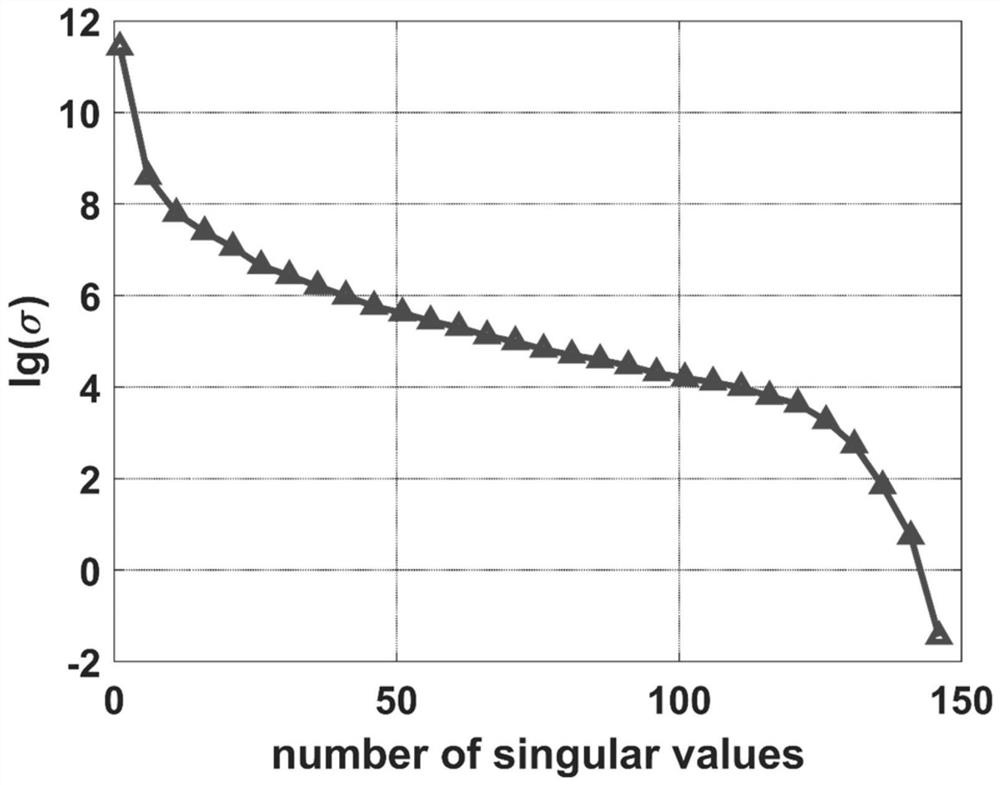
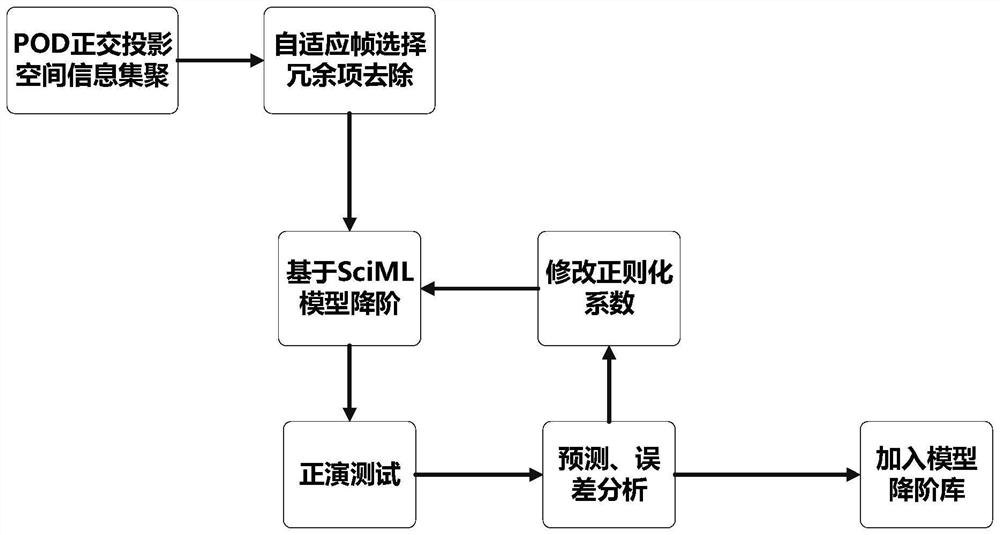
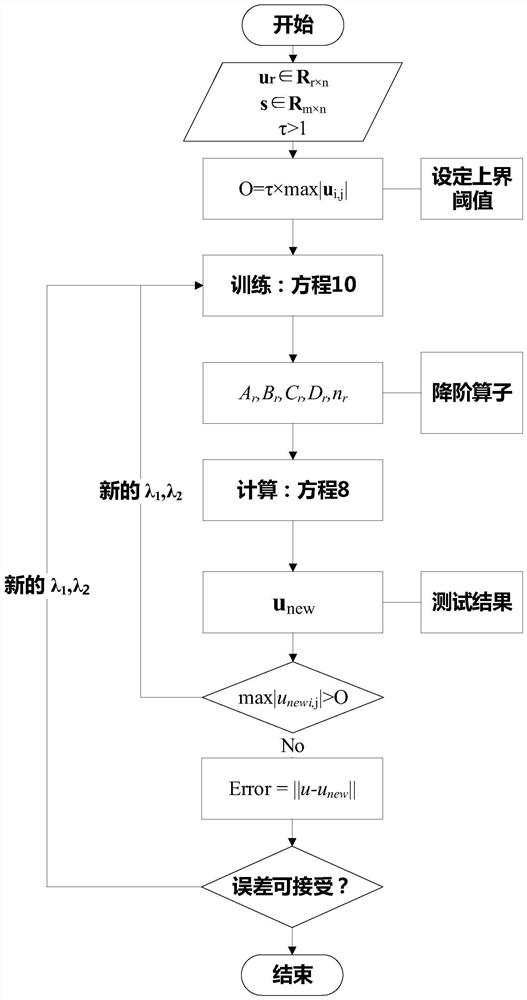
[0055] The first step of the present invention is to perform eigenorthogonal decomposition (POD) on the dataset.
[0056] It is a mathematical method for extracting characteristic information of discrete data. The purpose of the POD method is to describe the multi-dimensional random process in a low-dimensional approximation and to extract the characteristic parameters of the complex random process. The basic idea is to decompose the random quantity into a set of basis functions determined by its ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com