Plant nematode control method
A technology for plant nematodes and nematodes, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, nematicides, plant protection, etc., can solve problems such as the dealkylation of nematodes that are not yet known, and achieve strong target specificity and high species broad spectrum. sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Example 1 Comparison of Nematode Steroid Metabolic Profiles Before and After DHCR24 Blocking
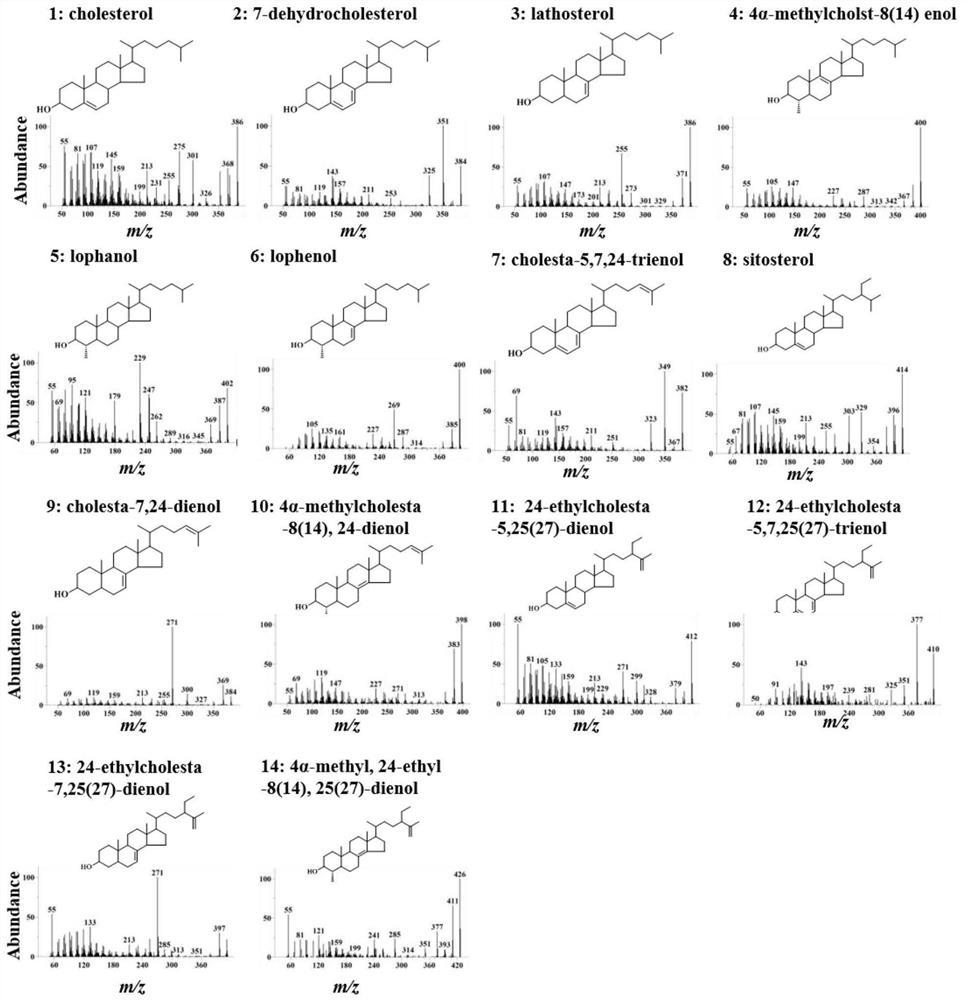
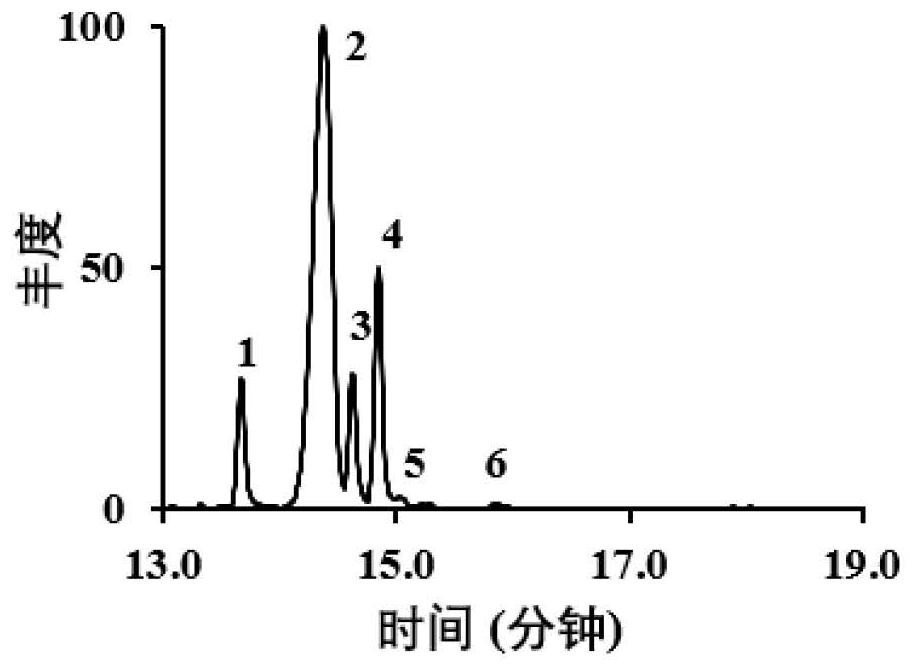
[0056] The present invention obtains Caenorhabditis elegans CeDHCR24 knockout mutant tm2141, the mutant is F52H2.6 / DHCR24 allele, the deletion range is 29539 to 30298, and the length is 760bp. This mutant allele lost exon 4 and part of exon 5. The tm2141 mutant can grow normally on the medium (NGM) containing 5mg / L cholesterol. Mutated anabolic cholesterol (1; figure 1 and figure 2 ) is metabolized to 7-dehydrocholesterol (2; figure 2 ), 7-enecholestanol (3; Lathosterol, figure 2 ), 4α-methylcholst-8(14)enol(4; figure 2 ), lophanol (5; figure 2 ) and lophenol (6; figure 2 ). Its sterol profile is very similar to that of wild Caenorhabditis elegans fed cholesterol (Chitwood, D.J., Lusby, W.R., Lozano, R., Thompson, M.J. & Svoboda, J.A. Sterol metabolism in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Lipids, 1984, 19, 500-506) Similarly, it was suggested that DHCR24 is i...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Example 2 Causes its developmental arrest by blocking the endogenous phytosterol conversion pathway of nematodes
[0060] When cultured with sufficient cholesterol, tm2141 was able to complete the entire life cycle indistinguishable from wild-type C. elegans (N2) animals. After synchronization on cholesterol plates, L1 worms (see Caenorhabditis elegans life cycle: Fielenbach, N. & Antebi, A.C. elegans dauer formation and the molecular basis of plasticity. Genes & Development, 2008, 22, 2149-2165) were transferred to worms containing only gluten. Alcohol plate. After 48h at 25°C, 94% of wild-type worms grew to adults ( Figure 5 1 in the middle), while the development of tm2141 was significantly retarded, and only 20% of the worms reached the adult stage ( Figure 5 in 2). Progeny of tm2141 fed with sitosterol produced synchronized L1 worms. The worms were depleted of cholesterol and transferred to fresh sitosterol plates. After 48 hours of incubation at 25°C, 100% ...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Example 3 Causes growth arrest of nematodes after eating corresponding phytosterols by regulating sterol profiles in plants
[0063] Isotope labeling experiments showed that insect C24 and C25 hydrogens are essential for sterol dealkylation (Fujimoto, Y., Kimura, M., Takasu, A., Khalifa, F.A.M. & Ikekawa, N. Mechanism of stigmasteroldealkylation in insect. Tetrahedron Letters , 1984, 25, 1501–1504; Ikekawa, N., Morisaki, M. & Fujimoto, Y. Sterol metabolism in insects: dealkylation of phytosterol to cholesterol. Accounts of Chemical Research, 1993, 26, 139-146). Based on this, 24-ethylcholesterol 5,25(27)-dienol (clerosterol, CLE; 11, figure 1). CLE occurs naturally in plants but lacks the C25 hydrogen (for structure and mass spectra see figure 1 ).
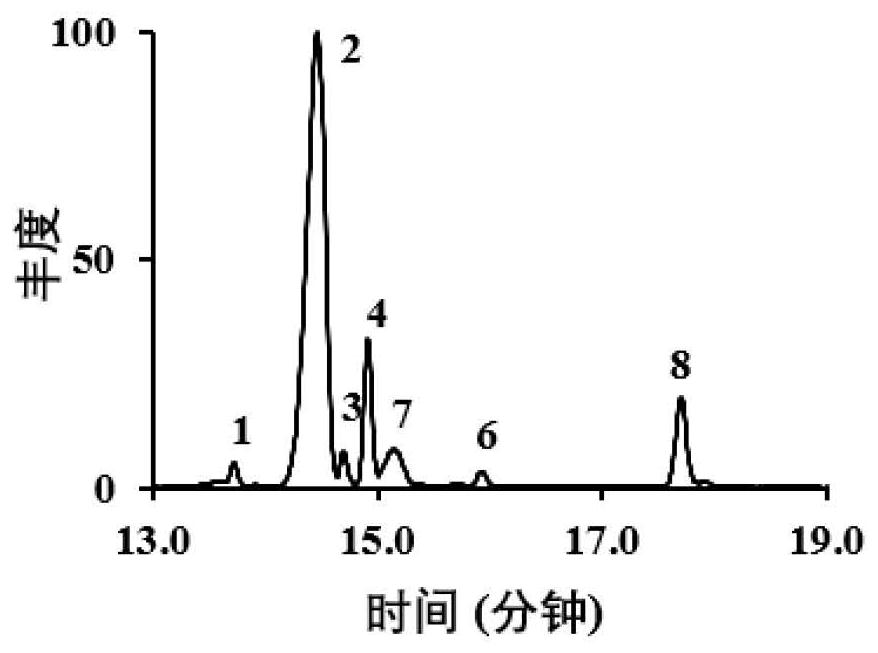
[0064] Exogenous sterols and their nuclear-modified intermediates are major constituents of worms ( image 3 ). Although no cholesterol was detected in animals, CLE was taken up and converted to 24-ethylcholesta-5,7,25...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com