FGFR2c extracellular domain analogue as well as coding gene and application thereof
A technology encoding gene and extracellular segment, which is applied to FGFR2c extracellular segment analogs and their encoded genes and application fields, can solve the problem of polypeptide stability to be improved, and achieve the effect of inhibiting pulmonary fibrosis.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
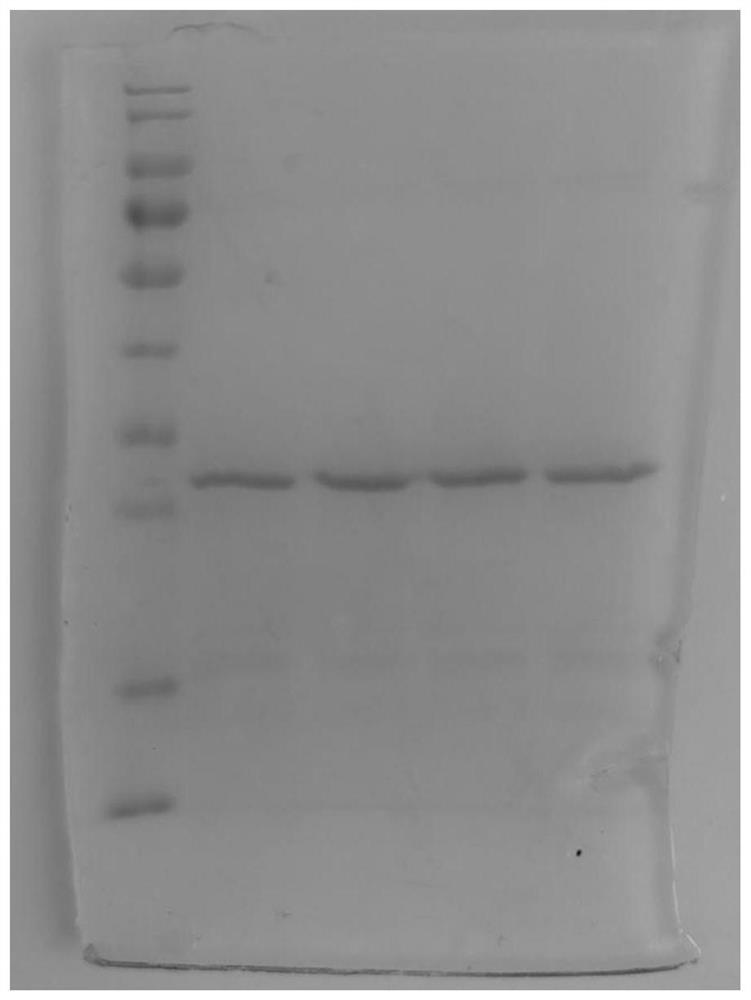
[0054] Example 1: Expression of wild-type and mutant FGFR2c extracellular segment analog polypeptide genes in Escherichia coli Prokaryotic expression of the 149-382th amino acid FGFR2c extracellular segment
[0055] 1. Construction of recombinant plasmid and expression and identification of FGFR2c extracellular segment by double enzyme digestion and ligation reaction
[0056] Artificially synthesized DNA sequences (SEQ ID NO.3 and SEQ ID NO.4) of wild-type and mutant FGFR2c extracellular segments (149-382 amino acids), with primers added at both ends:
[0057] F: CG CATATG AATAAACGTGCGCCGT (SEQ ID NO.5); the horizontal line is the NdeI restriction site;
[0058] R: AT GGATCC CGCGATTTCCAGGTAA (SEQ ID NO.6); the crossed line is the restriction site of BamH I.
[0059] The extracellular segment gene of FGFR2c was inserted into the prokaryotic expression vector pET30a by restriction endonuclease cutting sites NdeI and BamH I, and the accuracy of the recombinant expression vec...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Example 2: Expression of wild-type and mutant FGFR2c extracellular segment analog polypeptide gene plus Fc segment in CHO cells
[0066] Eukaryotic expression of wild-type and mutant FGFR2c extracellular segment (149-382 amino acids) plus Fc segment fusion protein
[0067] 1. Acquisition of the Fc segment gene
[0068] (1) Primer design:
[0069] F9-Fc:
[0070] 5'-CCCAAGAGCTGCGACAAGACCCACACCTGCCCCCCCTGTCCTGCTCCAGAACTCCTGGGCGGACCCAGCGTGTTCCTGTTCCCCCCAAAGCCCAAGGACACCCTG-3' SEQ ID NO. 7;
[0071] F8-Fc:
[0072]5'-AAGCCCAAGGACACCCTGATGATCAGCAGGACCCCCGAGGTGACCTGCGTGGTGGTGGACGTGAGCCACGAGGACCCACAGGTCAAGTTCAACTGGTACGTGGAC-3' SEQ ID NO.8;
[0073] F7-Fc:
[0074] 5'-TTCAACTGGTACGTGGACGGCGTGCAGGTGCACAACGCCAAGACCAAGCCCCGGGAGCAGCAGTACAACTCCACCTACAGGTGGTGTCCGTGCTGACCGTGCTG-3' SEQ ID NO.9;
[0075] F6-Fc:
[0076] 5'-TCCGTGCTGACCGTGCTGCACCAGAACTGGCTGGACGGCAAAGAGTACAAGTGCAAGGTCTCCAAACAAGGCCCTGCCAGCCCCCATC GAGAAAACCATCAGCAAG-3' SEQ ID NO.10;
[0077] R6-Fc:
[0078] 5'-CAGGG...
Embodiment 3
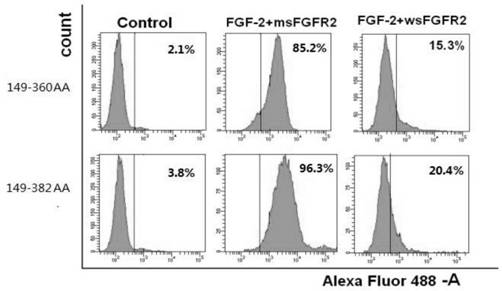
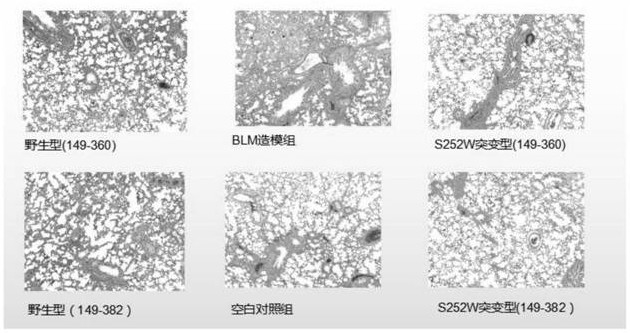
[0120] Example 3 The extracellular segment of FGFR2c (149-382) can better bind the ligand FGF-2
[0121]The inventor previously applied for and authorized the patent "201410347938.0: FGFR2c Extracellular Segment Analogs and Its Encoding Genes and Applications". 366) and (151-377) and (150-366) are more stable, and now a new sequence (149-382) is designed, compared with the extracellular segment of (149-360), the increased (360-382 ) segment is mainly hydrophilic amino acids, according to the literature (M.Mohammadi et al. / Cytokine&Growth Factor Reviews, 16(2005):107–137), the specificity of FGFR2c subtype receptors binding to ligands mainly comes from the large amount of D3 loop Therefore, a hydrophilic environment is more suitable for better binding of FGF-2 ligands. Most of the amino acids from 382 to the C-terminus of the extracellular segment are hydrophobic amino acids, which are not conducive to the binding of the receptor and the ligand, and cause steric hindrance to t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com