Method for reducing abundance of antibiotic resistance gene in soil by using edible fungi
An antibiotic resistance, soil technology, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as damage to soil quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
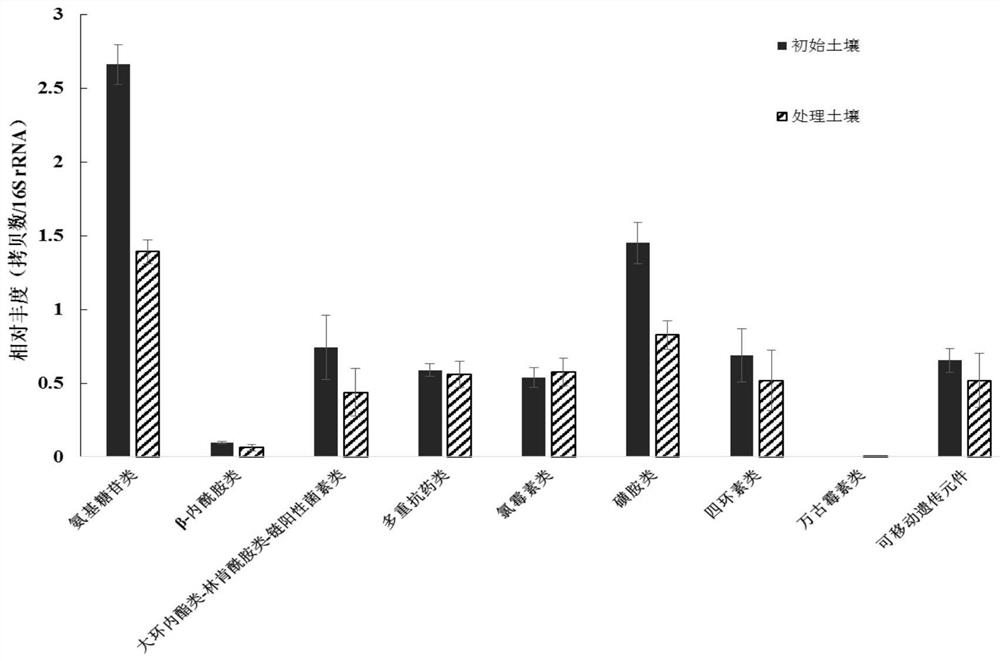
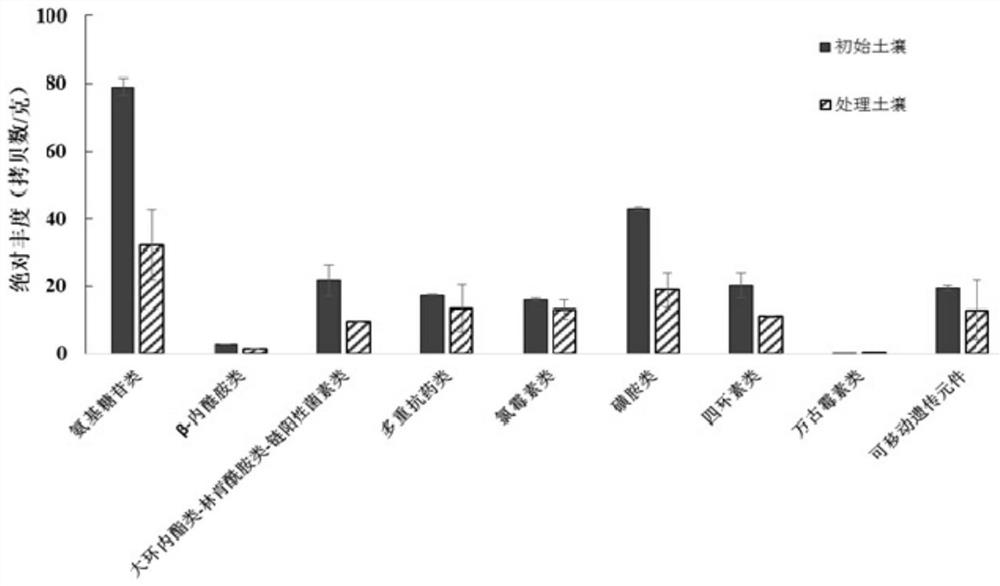
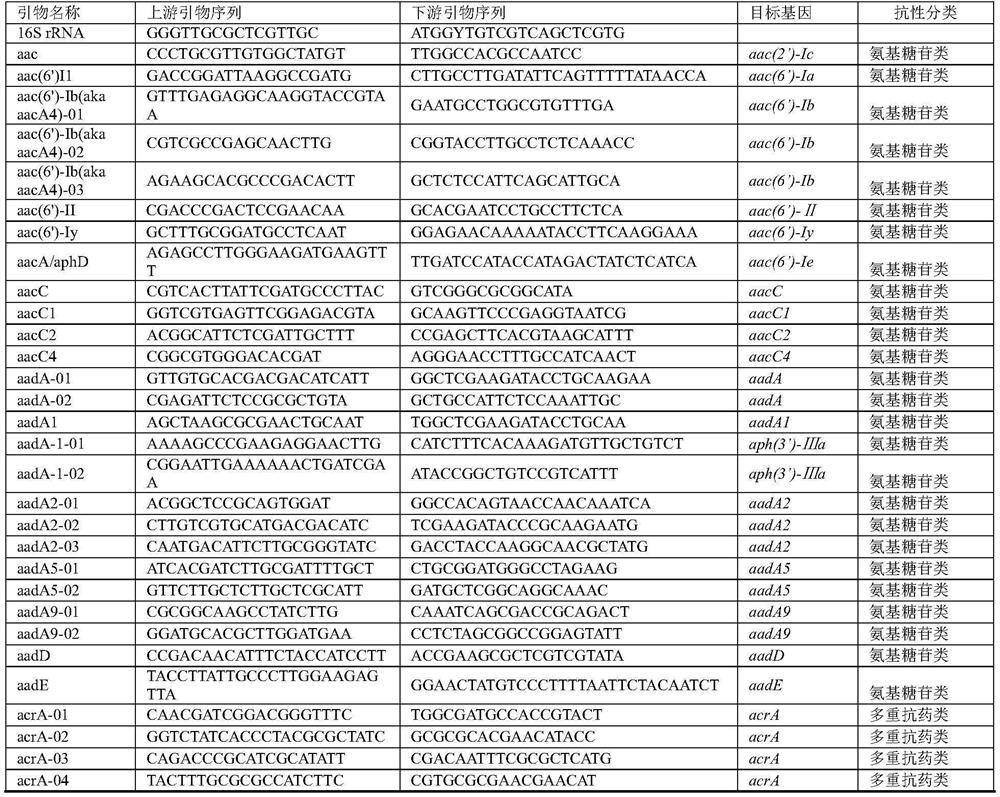
[0032] Example 1, using the evaluation to reduce the abundance of antibiotic resistance genes in soil
[0033] 1. Materials and methods
[0034] 1. Test material
[0035] The soil used in the test was collected from vegetable greenhouses in the suburbs of Beijing and applied chicken manure organic fertilizer.
[0036] The edible fungus variety is Pleurotus ostreatus 4195, which is recorded in the article "Song Qinggang et al. Cotton dregs as a new type of cultivation substrate for Pleurotus ostreatus. Screening test of formula. Edible fungus Vegetables 2020.2", the public can obtain it from the applicant and can only be used to repeat the present invention For experimental use, not for other use. Pleurotus ostreatus 4195 is currently preserved in the Institute of Plant Protection, Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com