Yard rose tissue culture seedling ex-vitro rooting method
A technology for tissue culture seedlings and exogenous rooting, which is applied in the directions of botanical equipment and methods, cultivation, medium, etc., can solve the problems of low reproduction coefficient, less cuttings, and lower quality, so as to improve reproduction coefficient, simplify tissue culture procedures, The effect of improving the level of industrialization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] A method for rooting out of a garden rose tissue culture seedling bottle, the method comprising the following steps:
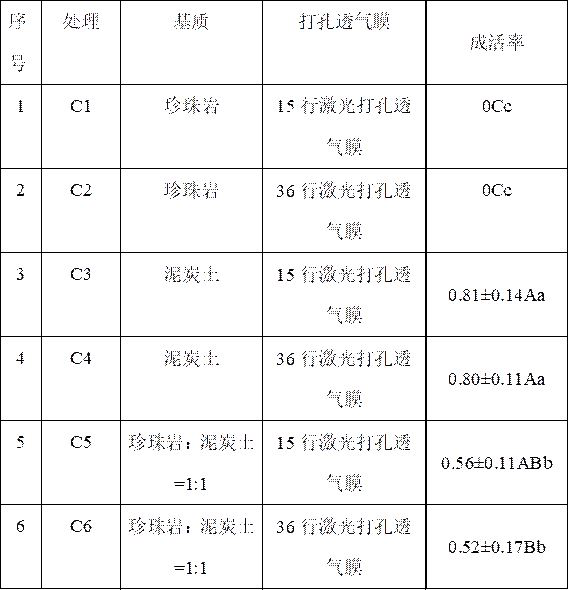
[0023] (1) Irrigate the pure peat soil with water, fully moisten it, and keep the humidity at about 65%, put it into a plastic bag made of high-temperature-resistant materials, and sterilize it at 121°C and 1.01KPa for 40 minutes.
[0024] (2) Fill the matrix sterilized in step (1) into a 126-hole tray on the ultra-clean workbench, and compact it.
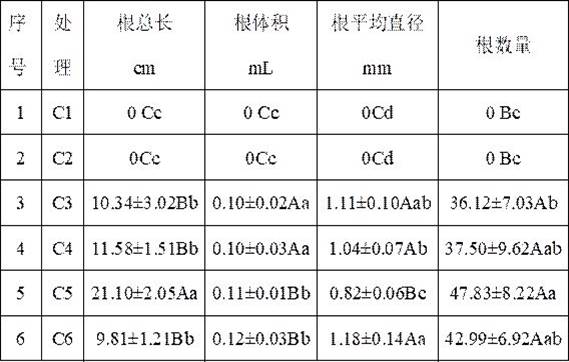
[0025] (3) Cut off the terminal buds of clustered sprouts that grow well in the bottle and have a seedling height of 5-6cm. The seedlings are 1-1.5cm long and are directly inserted into the sterilized subpackaged substrate in step (2). The tray was moved into the culture box, and 300 mL of sterile water was added along the edge of the box.
[0026] (4) Place the culture box on the sealing machine and seal it with 36 lines of laser perforated film.
[0027] (5) Place the culture box treated in step (4) in a...
Embodiment 2
[0029] A method for rooting out of a garden rose tissue culture seedling bottle, the method comprising the following steps:
[0030] (1) Irrigate the pure peat soil with water, fully moisten it, and keep the humidity at about 65%, put it into a plastic bag made of high-temperature-resistant materials, and sterilize it at 121°C and 1.01KPa for 40 minutes.
[0031] (2) Fill the matrix sterilized in step (1) into a 126-hole tray on the ultra-clean workbench, and compact it.
[0032] (3) Cut off the terminal buds of clustered sprouts that grow well in the bottle and have a seedling height of 5-6cm. The seedlings are 1-1.5cm long and are directly inserted into the sterilized subpackaged substrate in step (2). The dish was moved into the culture box, and 300 mL of sterile water was added along the edge of the box.
[0033] (4) Place the culture box on the sealing machine and seal it with 15 rows of laser perforated film.
[0034] (5) Place the culture box treated in step (4) in an...
Embodiment 3
[0036] A method for rooting out of a garden rose tissue culture seedling bottle, the method comprising the following steps:
[0037] (1) Pour the peat soil: perlite (volume ratio) = 1:1 matrix with water, fully moisten it, keep the humidity at about 65%, put it into a plastic bag made of high temperature resistant material, and store it at 121°C, 1.01 Sterilize at KPa for 40min.
[0038] (2) Fill the matrix sterilized in step (1) into a 126-hole tray on the ultra-clean workbench, and compact it.
[0039] (3) Cut off the terminal buds of clustered sprouts that grow well in the bottle and have a seedling height of 5-6cm. The seedlings are 1-1.5cm long and are directly inserted into the sterilized subpackaged substrate in step (2). The dish was moved into the culture box, and 300 mL of sterile water was added along the edge of the box.
[0040] (4) Place the culture box on the sealing machine and seal it with 36 lines of laser perforated film.
[0041] (5) Place the culture bo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com