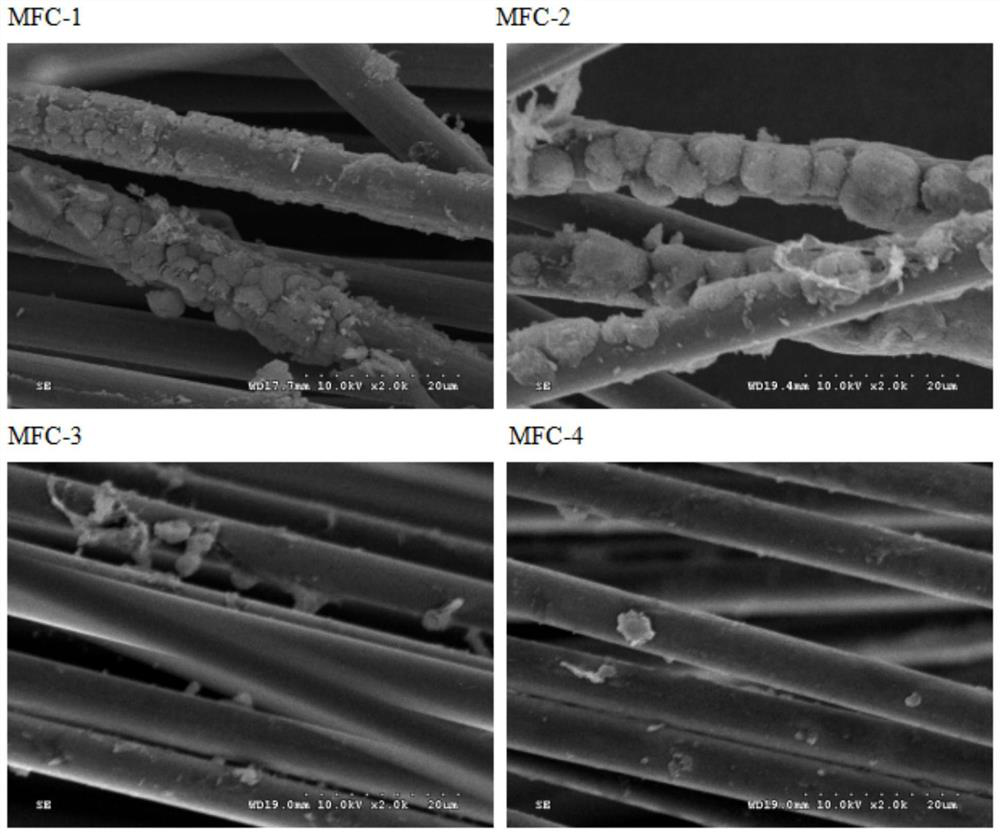
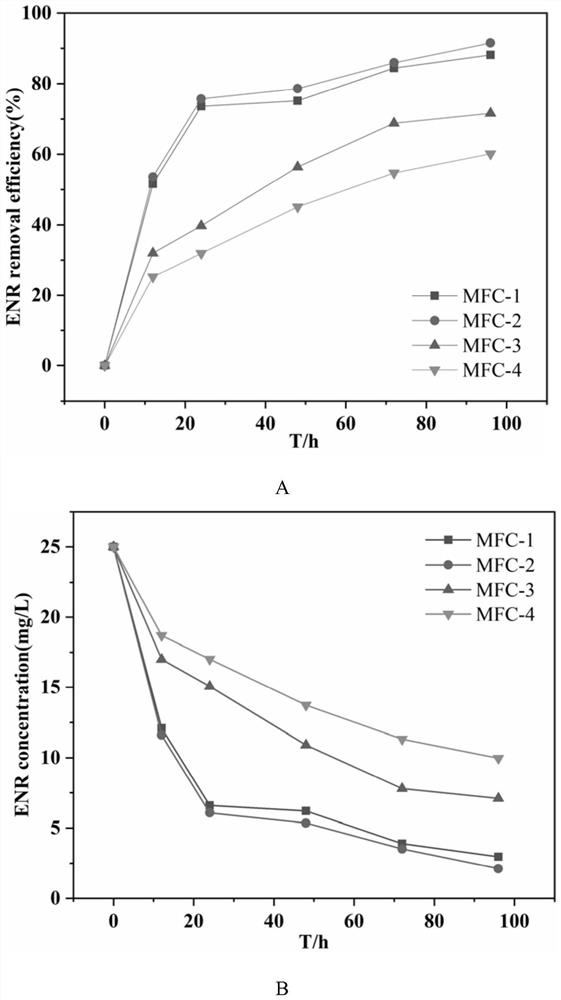
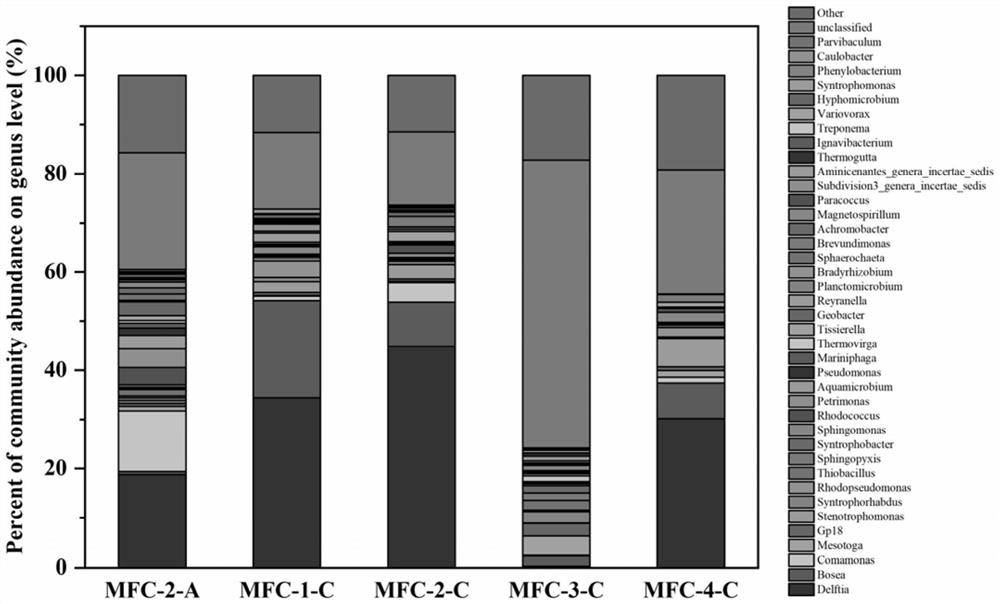
Method for reducing and degrading enrofloxacin by using biological cathode co-metabolism system
A technology of enrofloxacin and biocathode, which is applied in biological treatment devices, chemical instruments and methods, biological water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems that do not involve ENR removal performance and dominant microbial communities, and achieve rich quantity and variety , reduce toxicity, promote the effect of reductive degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] A method for reducing and degrading enrofloxacin by using a biocathode co-metabolism system, the anode chamber and the cathode chamber of the MFC reactor are respectively injected with anolyte and catholyte:
[0027] Anolyte, every 1L of water includes the following components by weight: 1.28g sodium acetate, 0.13g KCl, 0.31g NH 4 Cl, 11.55g Na 2 HPO 4 -12H 2 O, 2.77g NaH 2 PO 4 -2H 2 O, 1mL Wolfe vitamin trace element solution and 1mL Wolfe mineral element solution;
[0028] Catholyte, every 1L of water includes the following components by weight: 0.025g enrofloxacin, 1.28g sodium acetate, 0.13gKCl, 0.31g NH 4 Cl, 11.55g Na 2 HPO 4 -12H 2 O, 2.77g NaH 2 PO 4 -2H 2 O, 1mL Wolfe vitamin trace element solution and 1mL Wolfe mineral element solution;
[0029] Among them, Wolfe vitamin trace element solution contains the following components by weight per 1L of water: 2mg vitamin H, 2mg folic acid, 10mg pyridoxine hydrochloride, 5mg thiamine, 5mg riboflavin, 5m...
Embodiment 2
[0032] A method for reducing and degrading enrofloxacin by using a biocathode co-metabolism system, the anode chamber and the cathode chamber of the MFC reactor are respectively injected with anolyte and catholyte:
[0033] Anolyte, every 1L of water includes the following components by weight: 1.00g sodium acetate, 0.13g KCl, 0.31g NH 4 Cl, 11.55g Na 2 HPO 4 -12H 2 O, 2.77g NaH 2 PO 4 -2H 2 O, 1mL Wolfe vitamin trace element solution and 1mL Wolfe mineral element solution;
[0034] Catholyte, every 1L of water includes the following components by weight: 0.02g enrofloxacin, 1.00g sodium acetate, 0.13gKCl, 0.31g NH 4 Cl, 11.55g Na 2 HPO 4 -12H 2 O, 2.77g NaH 2 PO 4 -2H 2 O, 1mL Wolfe vitamin trace element solution and 1mL Wolfe mineral element solution;
[0035] Among them, Wolfe vitamin trace element solution contains the following components by weight per 1L of water: 2mg vitamin H, 2mg folic acid, 10mg pyridoxine hydrochloride, 5mg thiamine, 5mg riboflavin, 5mg...
Embodiment 3
[0038] A method for reducing and degrading enrofloxacin by using a biocathode co-metabolism system, the anode chamber and the cathode chamber of the MFC reactor are respectively injected with anolyte and catholyte:
[0039] Anolyte, every 1L of water includes the following components by weight: 1.68g sodium acetate, 0.13g KCl, 0.31g NH 4 Cl, 11.55g Na 2 HPO 4 -12H 2 O, 2.77g NaH 2 PO 4 -2H 2 O, 1mL Wolfe vitamin trace element solution and 1mL Wolfe mineral element solution;
[0040] Catholyte, each 1L of water includes the following components by weight: 0.03g enrofloxacin, 1.80g sodium acetate, 0.13gKCl, 0.31g NH 4 Cl, 11.55g Na 2 HPO 4 -12H 2 O, 2.77g NaH 2 PO 4 -2H 2 O, 1mL Wolfe vitamin trace element solution and 1mL Wolfe mineral element solution;
[0041] Among them, Wolfe vitamin trace element solution contains the following components by weight per 1L of water: 2mg vitamin H, 2mg folic acid, 10mg pyridoxine hydrochloride, 5mg thiamine, 5mg riboflavin, 5mg ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com