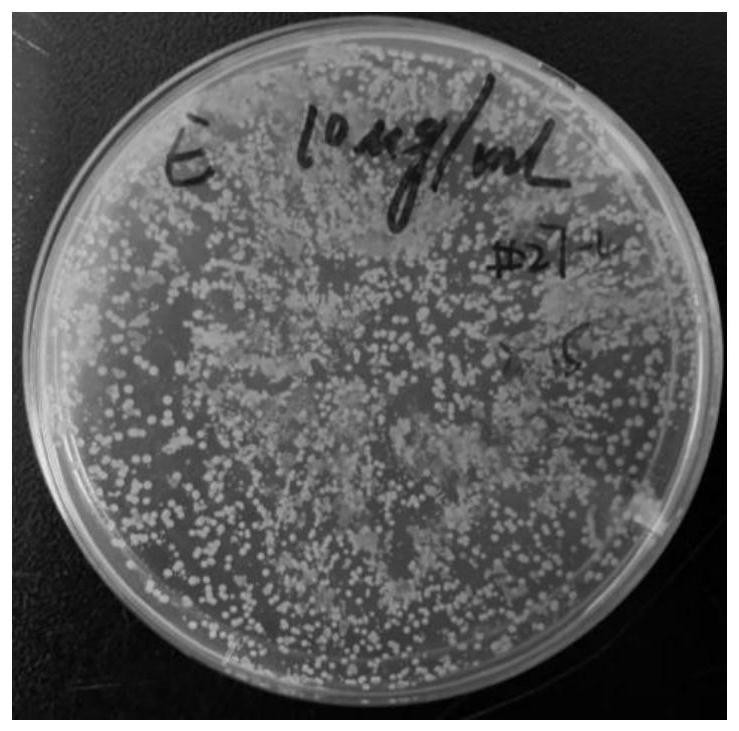
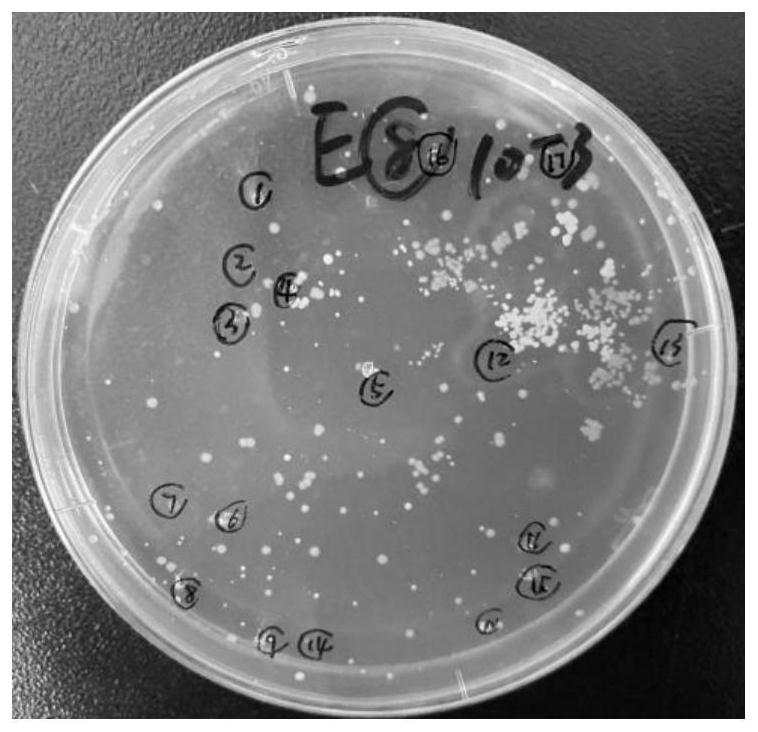
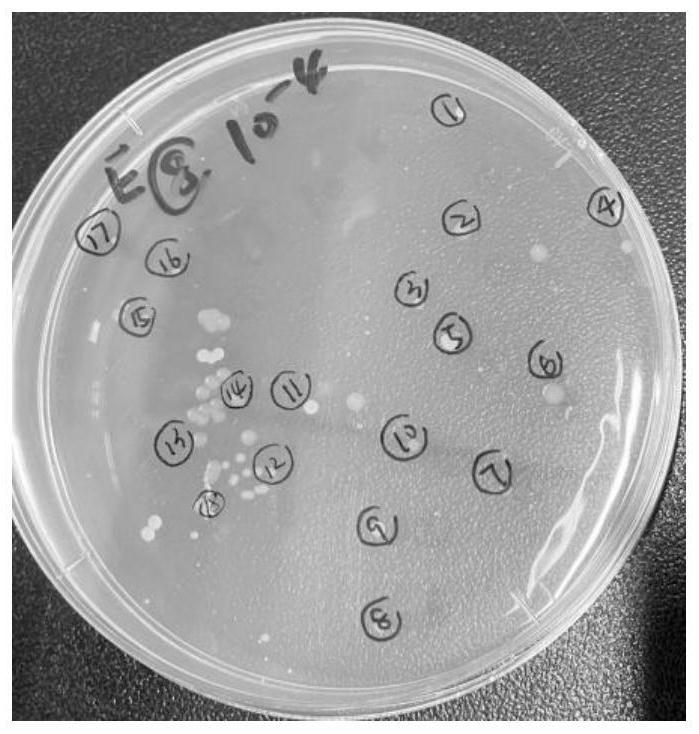
Method for screening and identifying antibiotic resistant bacteria
A technology of antibiotic resistance and polymyxin sulfate, which is applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of discounted bacteria screening effect, poor effect, and difficulty in determining the concentration of antibiotics, so as to avoid the effect of consuming a lot of time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] S1, LB medium preparation:
[0033] LB liquid medium: Weigh 10 g of peptone, 5 g of yeast extract, and 10 g of sodium chloride, add 900 mL of distilled water and make it volume up to 1 L, then divide the medium into Erlenmeyer flasks, cover with sealing film, and sterilize under high pressure (121 ℃, 20min), cooled to room temperature for later use.
[0034] LB solid medium: Weigh 10g of peptone, 5g of yeast extract, 10g of sodium chloride, 20g of agar powder, add 900mL of distilled water and make up to 1L, then divide the medium into Erlenmeyer flasks, cover with sealing film, and pressurize Sterilize (121°C, 20min), cool to 45°C, pour the plates for use.
[0035] S2. Weigh 0.5g of erythromycin into a test tube, add 10mL of absolute ethanol to fully dissolve (concentration is 50mg / mL), divide into small portions and store at -20°C, and finally add LB at a concentration of 15ug / mL for solid culture base; dissolve 0.5g streptomycin sulfate in sufficient water, dilute t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com