Cationic cholesterol derivative, nano-composite and preparation method and application of nano-composite
A technology of cationic cholesterol and nanocomposite, which is applied to other methods of inserting foreign genetic materials, steroids, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve the problems of Linker chain length, inability to detach from auxiliary lipids, and failure to provide preparation methods, etc. Achieve the effect of convenient preparation, significant transfection effect, and easy low-cost large-scale preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051]
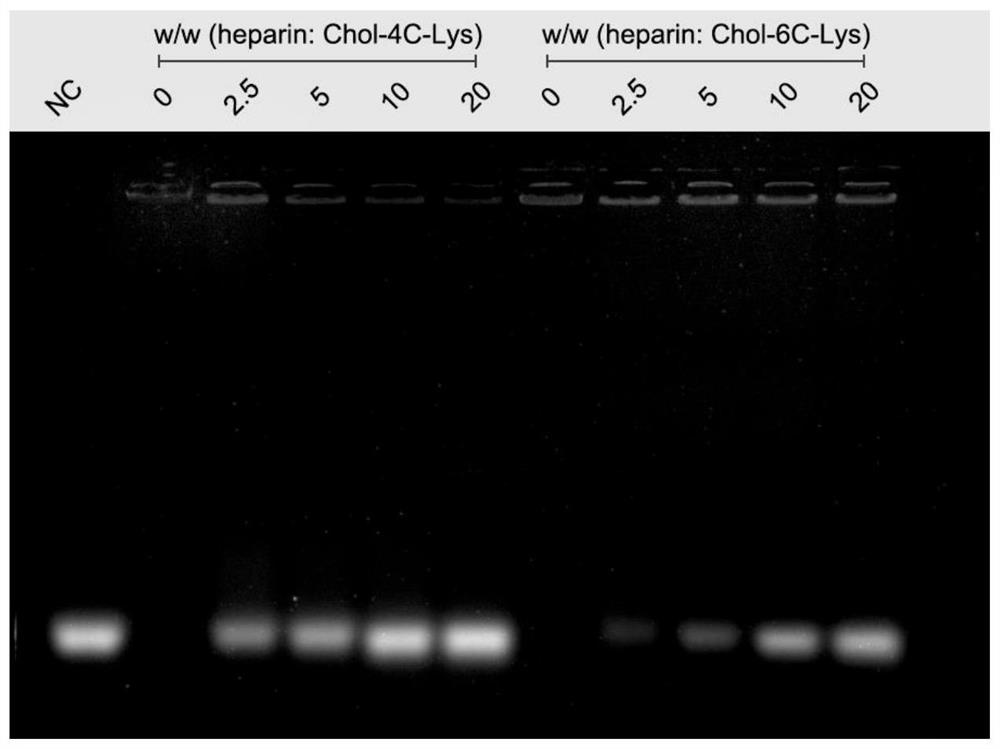
[0052] Preparation of Cationic Cholesterol Derivative Chol-6C-Lys
[0053] Step 1: Dissolve 1,6-hexanediol (23.6g, 0.2mol) in 80mL of fully dehydrated and dried dichloromethane, and slowly add dropwise to cholesterol chloride dissolved in 200mL of dry dichloromethane containing 0.4mL pyridine Formic acid ester (22.4g, 0.05mol), stirred at 45°C for 24h, distilled off dichloromethane, and the intermediate cholesterol monosubstituted hexanediol carbonate intermediate was obtained after column chromatography. The synthesis yield was 74%.
[0054] The second step: dissolve the L-lysine (7.3g, 0.05mol) protected by BOC (di-tert-butyl carbonate) in 100mL of dehydrated and dried methylene chloride, and slowly add it dropwise to the dichloromethane dissolved in dichloromethane under the catalysis of pyridine. In the first step of the preparation of methyl chloride, the obtained intermediate cholesterol monosubstituted hexanediol was added with dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC...
Embodiment 2
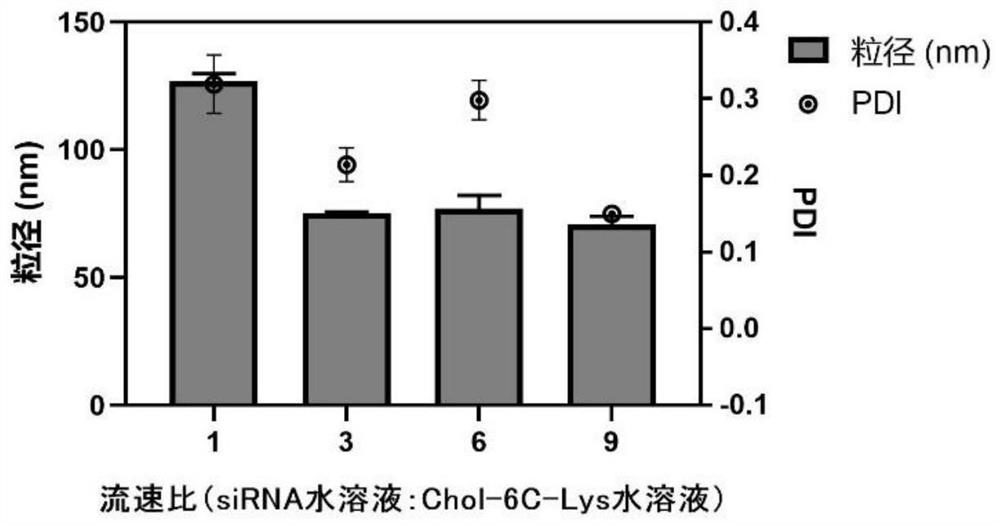
[0057] Preparation of siRNA / Chol-6C-Lys nanocomplex by microfluidic method.
[0058] 1. Reagent preparation
[0059] Enzyme-free aqueous phase: 5 mL of deionized water was treated with DEPC to make it RNase-free.
[0060] 2. Preparation of nanocomposites
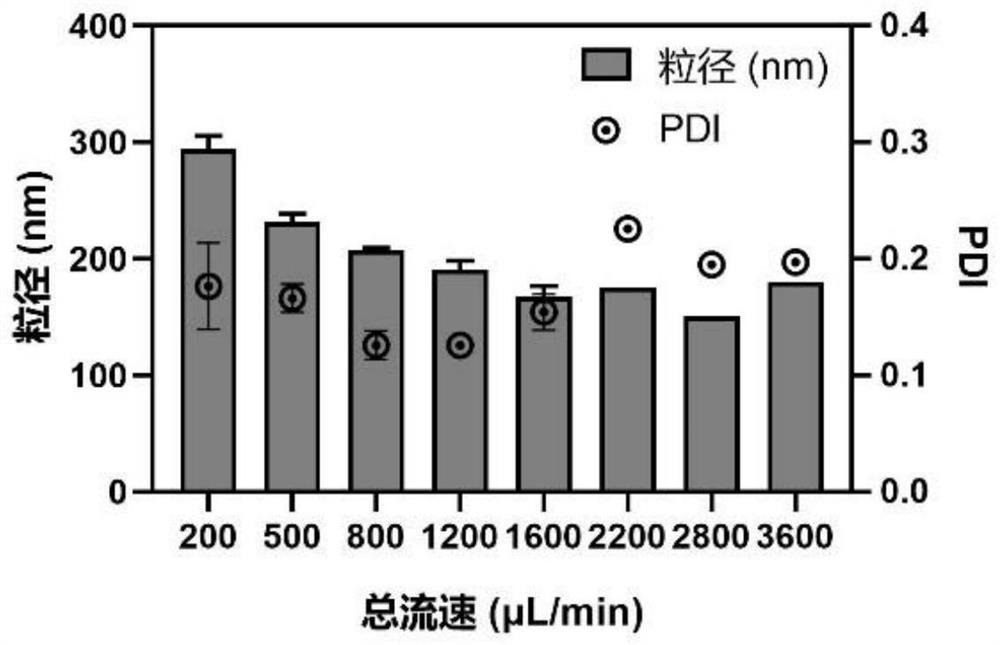
[0061] Weigh the cationic cholesterol derivative Chol-6C-Lys synthesized in Example 1 containing the natural cholesterol skeleton and lysine head group in a centrifuge tube without enzyme treatment, and dissolve it into a derivative solution with the water phase without enzyme treatment, The concentration of Chol-6C-Lys in the derivative solution is 2.5 mg / mL; the siRNA powder is dissolved in an enzyme-free aqueous phase to prepare an siRNA solution with an siRNA concentration of 8 μmol / L. The above-mentioned one derivative solution and one nucleic acid drug solution are respectively loaded into the two injection tubes of the microfluidic pump. The total flow rate of the microfluidic syringe pump was 200 μL / min, the flow ...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Preparation process of microRNA / Chol-6C-Lys nanocomplex.
[0067] 1. Reagent preparation
[0068] Enzyme-free aqueous phase: Treat 5 ml of 10mmol / L phosphate buffer with DEPC to make it free of RNase.
[0069] 2. Preparation of nanocomposites
[0070] Weigh the cationic cholesterol derivative Chol-6C-Lys synthesized in Example 1 containing the natural cholesterol skeleton and lysine head group in a centrifuge tube without enzyme treatment, and dissolve it into a derivative solution with the water phase without enzyme treatment, The concentration of Chol-6C-Lys in the derivative solution is 5 mg / mL; the microRNA powder is dissolved in an enzyme-free aqueous phase to prepare a microRNA solution with a concentration of 8 μmol / L. Take 500 μL cationic cholesterol derivative solution in a centrifuge tube, place it on a vortex mixer, then slowly add 500 μL microRNA solution dropwise, the vortex mixer rotates at 2000 rpm, vortex lasts for 20 seconds, and stands still for 30 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com