Group communication method and communication system based on hierarchical structure symmetric key pool
A group communication and hierarchical structure technology, applied to key distribution, can solve the problems of a large amount of time required for key pool update, failure of the group communication system, and huge amount of keys, so as to achieve unaffected security and protection measures Good, the effect of a small amount of key transmission
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
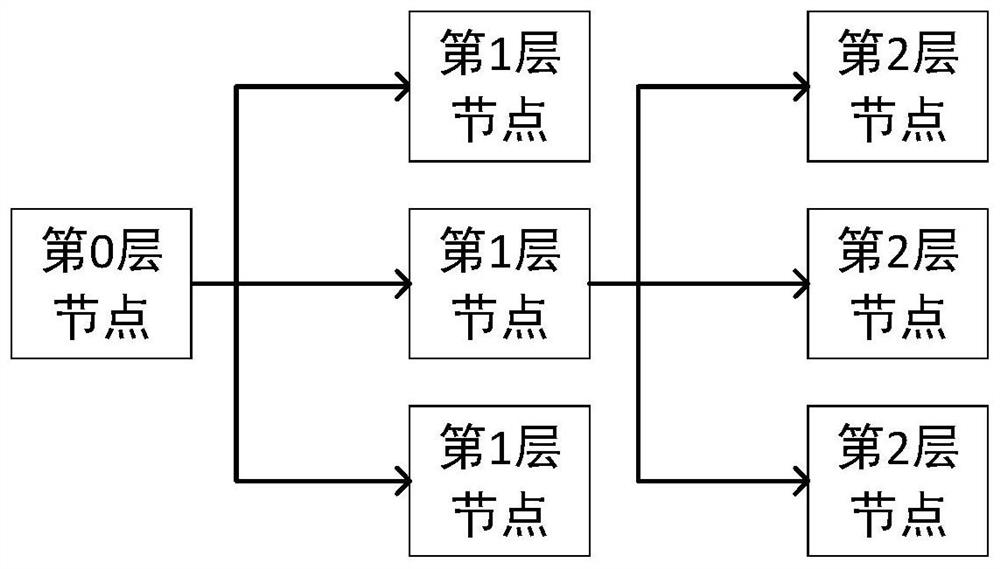
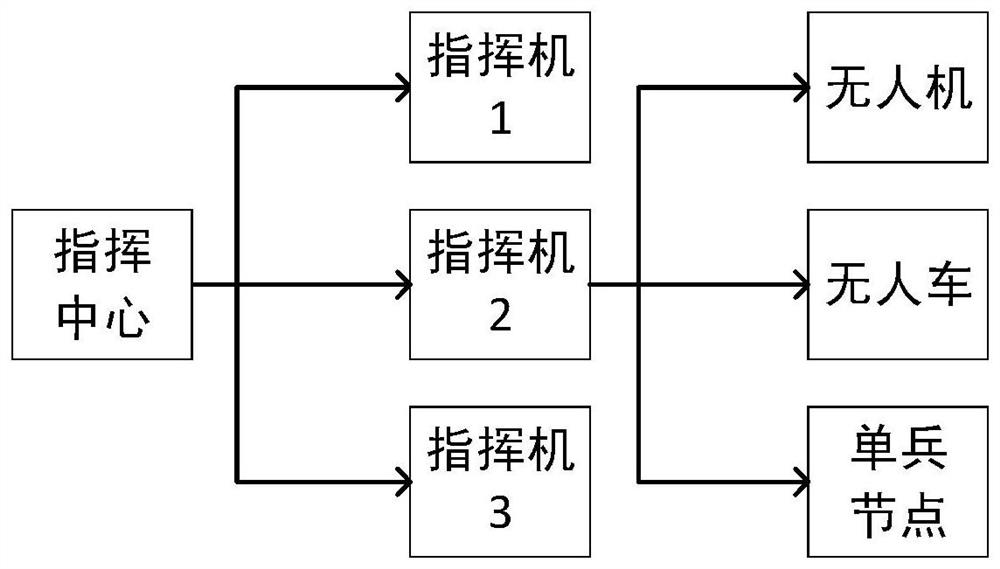
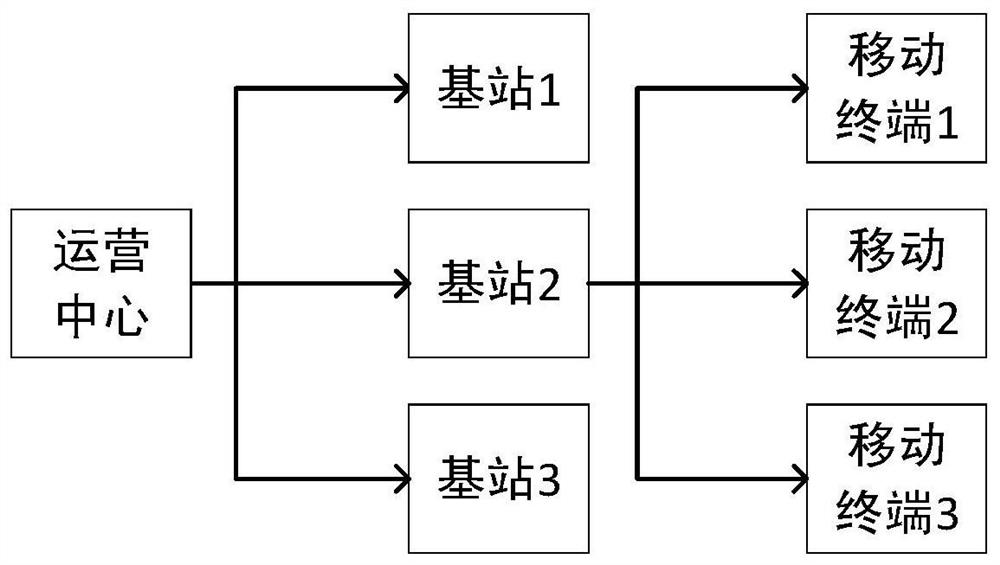
[0055] Embodiment 1: upper layer group communication
[0056] Case 1.1: Layer 0 A communicates with Layer 1 B.
[0057] Assume that the message to be sent by group member A is NTF, and a time stamp TNTF is generated for the message. A first calculates the key pool of B: A replaces the key KR according to itself A i.e. KR 0 , and B’s node ID to calculate B’s replacement key KR B , then by KR B The key pool of B can be obtained by comprehensive calculation with the key pool of A, and the length of the key pool is KPL.
[0058] A takes out the key KTA from the key pool of B. The key has N bits in total. The specific process of obtaining KTA is as follows: Figure 4 Shown:
[0059] The initial position pointer PK of the key KTA is calculated = FPK(TNTF) mod KPL, where mod represents a modulo operation. Calculate the step size in turn: LK 1 =FLK(PK||TNTF), LK 2 =FLK(LK 1 ||TNTF), LK 3 =FLK(LK 2 ||TNTF),...,LK N =FLK(LK N-1 ||TNTF). The functions FPK(*) and FLK(*) are...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Embodiment 2: Lower layer group communication in the case of fixed topology
[0066] Case 2.1: Layer 1 A communicates privately with Layer 2 B.
[0067] In this case, B is the leaf node of A, and A and B have the same key pool. Assume that the message to be sent by group member A is NTF, and a time stamp TNTF is generated for the message. A first calculates the key pool replaced by B's replacement key: A replaces the key KR according to itself Aand B's node ID to calculate B's replacement key KR B , then by KR B The key pool replaced by B's replacement key can be obtained through comprehensive calculation with A's key pool, and the length of the key pool is KPL.
[0068] A takes out the key KTA from the key pool replaced by B's replacement key. The key has N bits in total. The specific process of obtaining KTA is as follows: image 3 Shown:
[0069] Calculate the initial location pointer PK of the key KTA=FPK(TNTF)mod KPL. Calculate the step size in turn: LK 1 =...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Embodiment 3: Lower layer group communication in the case of roaming
[0083] set node ID ij From ID i Roam to ID I , the event is NTFroamer, and the timestamp is TNTFroamer.
[0084] ID ij Generate send to ID according to the method in case 2.2 I message NTF ij , and transfer the message to the ID I , ID I Get NTF from message ij . ID I After analyzing the message, it is found that the sender of the message is not a member of this group, so the message NTF ij is NTFroamee, the timestamp is TNTFroamee, and then generate a message NTF according to the method in case 1.2 I , and transmit the message to administrator A.
[0085] A Verify the ID according to the method in 1.2 I and the validity of NTFroamee, and then remove NTF from NTFroamee ij . A first calculates the ID i The replacement key and the key pool, and then calculate the ID accordingly ij The replacement key and key pool, and then verify the ID according to the method in case 2.2 ij and the e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com