System for simulating decision-making process in brain of mammal with respect to visually observed movement of body
A technology that simulates movement and mammals, applied in the field of detection and decision-making systems, can solve problems such as not very effective
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0093] Exemplary embodiments of the invention will now be described with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which:
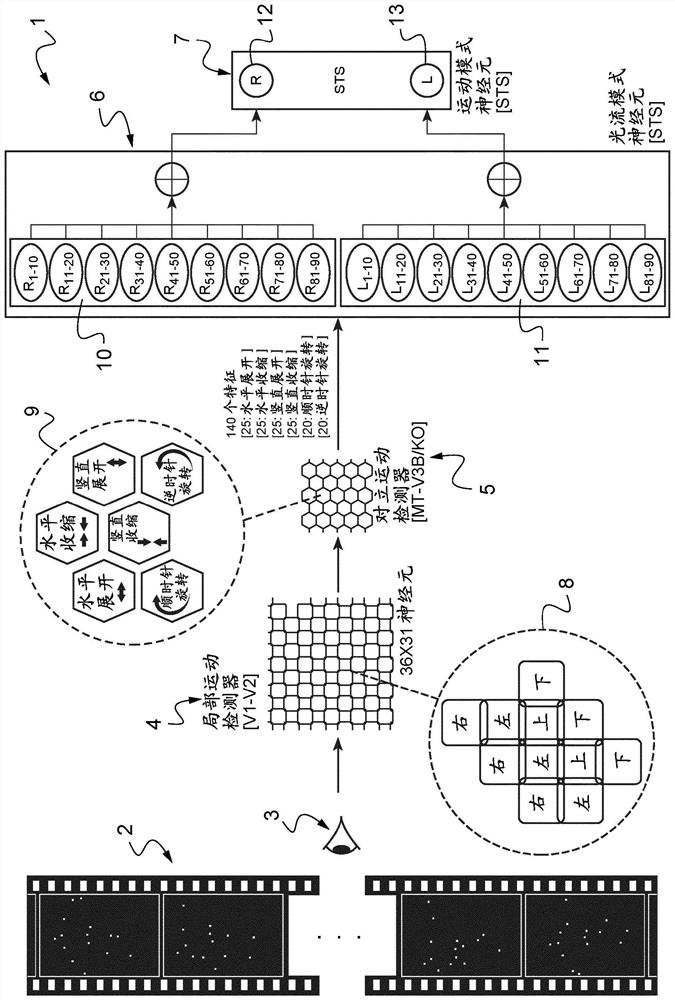
[0094] - figure 1 Schematically showing the structure of the system according to the invention in the case of monocular viewing,
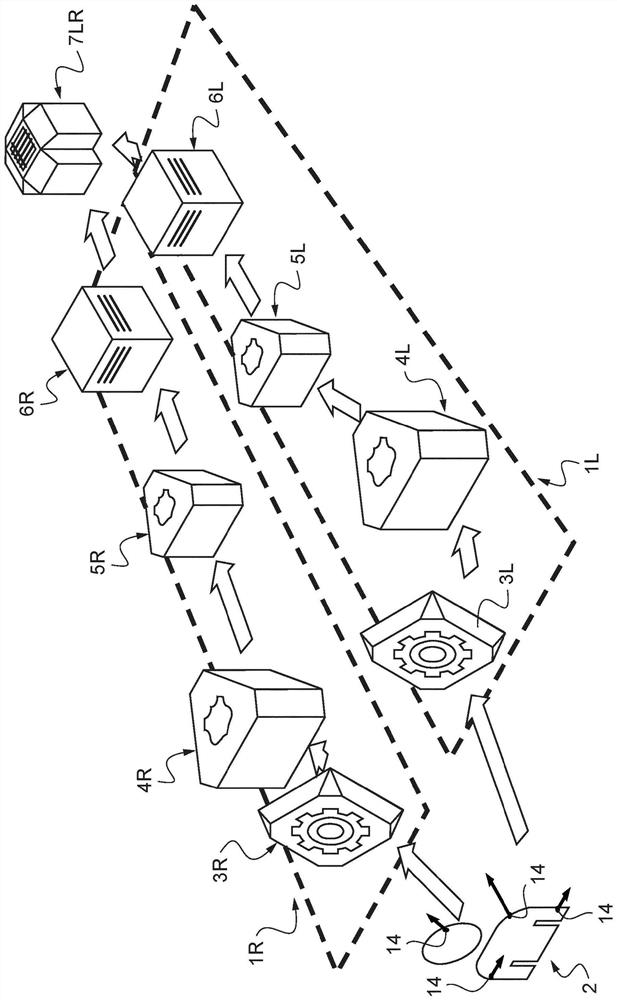
[0095] - figure 2 shows schematically the structure of the system according to the invention in the case of binocular viewing, and
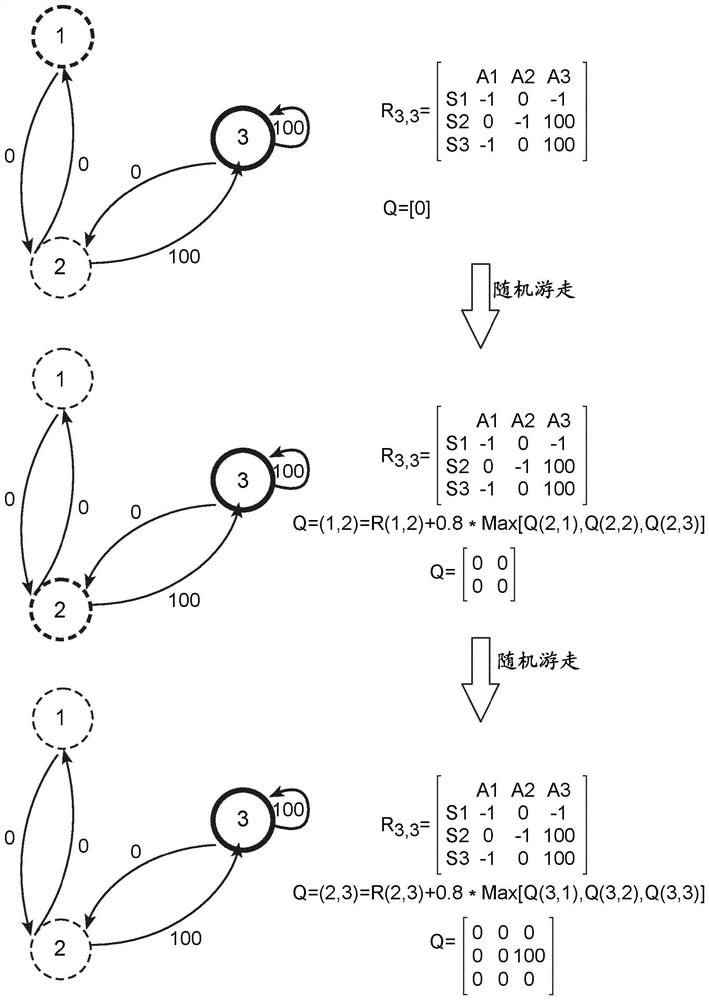
[0096] - image 3 is an example of the learning step of the Q-learning algorithm implemented in the third layer of the system.
[0097] The system of the invention will now be described with an exemplary embodiment, and then its application to a football match will be presented. Rather, this exemplary embodiment is a system capable of discerning the direction of a ball from a visual stimulus of a complex biokinetic soccer goal.
[0098] More generally, the system of the present invention for simulating decision-making processes is based on neuromimicry, and the system simulates the neuronal ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com