Tri-part systems for protein dimerization and methods of use
A protein and target protein technology, applied in the three-part system and application field for protein dimerization, can solve problems such as harmful cells, affecting protein functions, and affecting cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0499] Example 1 - Materials and methods
[0500] Solvent accessible surface area calculation
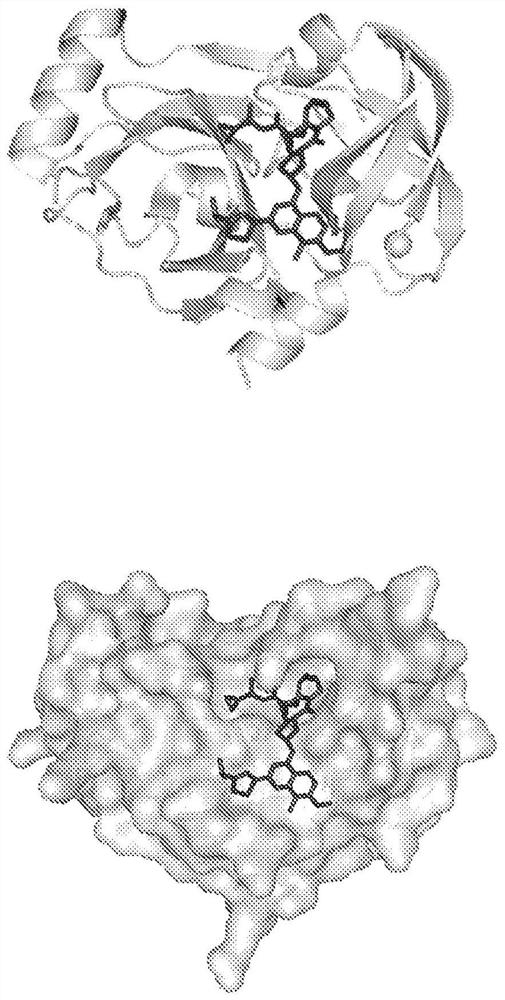
[0501] Using the measure sasa command built into the Visual Molecular Dynamics (VMD) software (University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign), available from the Protein Data Bank (PDB; http: / / www.rcsb.org / ) to calculate the solvent accessible surface area (SASA) from the three-dimensional structure of the HCV NS3 / 4A PR:simeprevir complex (PDB code 3KEE). -restrict option and The radius of was used to calculate the surface of simeprevir not bound to HCVNS3 / 4A PR, in other words, the solvent-accessible surface area.
[0502] Production of biotinylated HCVNS3 / 4A protease
[0503] The sequence used to design the HCV NS3 / 4A PR construct was derived from Uniprot accession number A8DG50 (hepatitis C virus subtype 1a genomic polyprotein) with additional modifications from US Pat. No. 6,800,456. The protease domain corresponds to residues 1030-1206 of polyprotein. A single chain consi...
example 2
[0607] Example 2 - Identification of simeprevir and HCVNS3 / 4 A PR
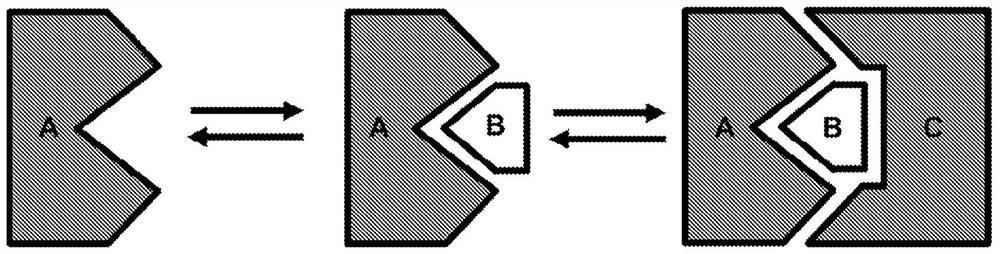
[0608] To generate de novo dimerization chemical inducer modules, we employed an approach where the small molecule inducer is a clinically approved small molecule and one of the protein components is the target of the small molecule (target protein). The second protein component (binding member) is derived from a library of binding molecules (Tn3 or scFv) and exhibits excellent selectivity for the target protein bound to the small molecule compared to the unbound target protein ( figure 1 ). By focusing on approved small molecules, we reasoned that the road to regulatory approval would be smoother given that small molecules are already considered safe for human use at appropriate doses. Instead of using small molecules that target human proteins, we decided to focus on small molecules that bind to non-human proteins, such as antiviral compounds. We infer that the advantage of this approach is that the s...
example 3
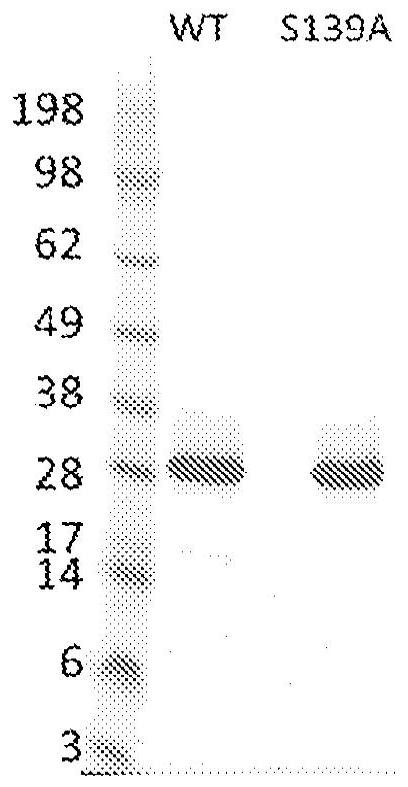
[0623] Example 3 - Mutant HCV NS3 / 4A PR(S139A) retains binding to simeprevir despite significantly reduced activity
[0624] HCV NS3 / 4A PR is an enzyme that cleaves at four junctions of the HCV polyprotein precursor and is known to cleave a limited number of endogenous human targets (Li, Sun et al., 2005; Li, Foy et al., 2005). To limit this activity in human cells, we reasoned that it would be necessary to identify a mutant form of HCV NS3 / 4A PR that is enzymatically inactive but retains binding to simeprevir. Active site mutants of HCV NS3 / 4A PR(S139A) have previously been shown to be significantly less active than their wild-type counterparts (Sabariegos et al. 2009). To confirm this, and to investigate whether mutant HCV NS3 / 4A PR would retain binding to simeprevir, the recombinant protein was expressed in E. coli and purified to homogeneity. HCV NS3 / 4A PR with N-terminal hexahistidine and AviTag (both WT (SEQ ID NO: 3) and S139A mutant (SEQ ID NO: 4)) in BL21 (DE3) in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com