Method for reducing temperature of molten steel of casting furnace
A heat and molten steel technology, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve problems such as unfavorable upgrading of old equipment, increased energy consumption due to corrosion of refractory materials, and breakout of mold shells, so as to avoid increased energy consumption and reduce casting defects. , the effect of improving quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
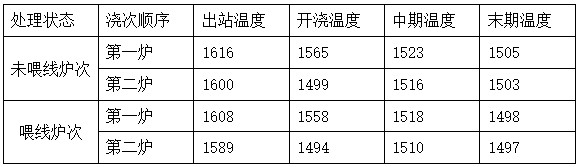
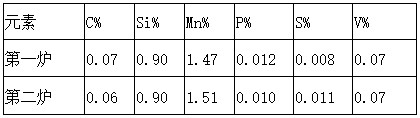
[0013] The type of steel used is HRB400, the theoretical solidification temperature of HRB400 is 1502°C, and the composition of the molten steel is shown in Table 1 below.
[0014] Table 1. Composition of HRB400 molten steel
[0015]
[0016] In the process of continuously pouring molten steel into the tundish during continuous casting, when the first furnace of molten steel reaches the pouring level of the tundish, the seamless calcium wire is drawn from the center of the nozzle center of the tundish within a diameter of 10cm to 11.4 Feed into the tundish at a speed of m / min. Under this feeding line speed, the molten steel level in the tundish fluctuates slightly, and the small bubbles in the feeding area blow away a circular range of about 20-25cm in diameter from the molten steel level. When the furnace molten steel is poured into the tundish to the middle stage, stop feeding the seamless calcium wire into the tundish. The feeding of the calcium wire can make the local t...
Embodiment 2
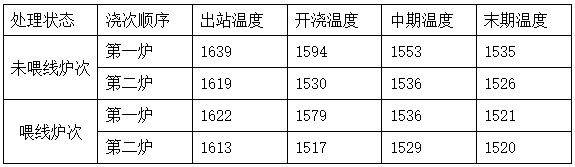
[0024] The type of steel used is 65#, and the theoretical solidification temperature of 65# is 1490°C. The composition of the molten steel is shown in Table 3 below.
[0025] Table 3. Composition of 65# molten steel
[0026]
[0027] In the process of continuously pouring molten steel into the tundish during continuous casting, when the first furnace of molten steel reaches the pouring level of the tundish, the seamless calcium wire is drawn from the center of the nozzle center of the tundish within 10cm in diameter by 8.8 Feed into the tundish at a speed of m / min. It is advisable that the molten steel level fluctuates slightly. When the second furnace molten steel is poured into the tundish to the middle stage, stop feeding the seamless calcium wire into the tundish and pass through the calcium wire. The feeding can make the local temperature of the molten steel directly above the tundish nozzle block rise, and the molten steel flow is more active, avoiding the blockage of...
Embodiment 3
[0035] The experimental steel type used is ER70S-6X, the theoretical solidification temperature of ER70S-6X is 1515°C, and the molten steel composition is shown in Table 5 below.
[0036] Table 5. ER70S-6X molten steel composition
[0037]
[0038] In the process of continuously pouring molten steel into the tundish during continuous casting, when the first furnace of molten steel reaches the pouring level of the tundish, the seamless calcium wire is drawn from the center of the nozzle center of the tundish within 10cm in diameter by 10.3 Feed into the tundish at a speed of m / min. It is advisable that the molten steel level fluctuates slightly. When the second furnace molten steel is poured into the tundish to the middle stage, stop feeding the seamless calcium wire into the tundish and pass through the calcium wire. The feeding can make the local temperature of the molten steel directly above the tundish nozzle block rise, and the molten steel flow is more active, avoiding...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com