Interneuron-specific therapeutics for normalizing neuronal cell excitability and treating dravet syndrome
An interneuron-specific technology, applied in gene therapy, neurological diseases, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as deficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
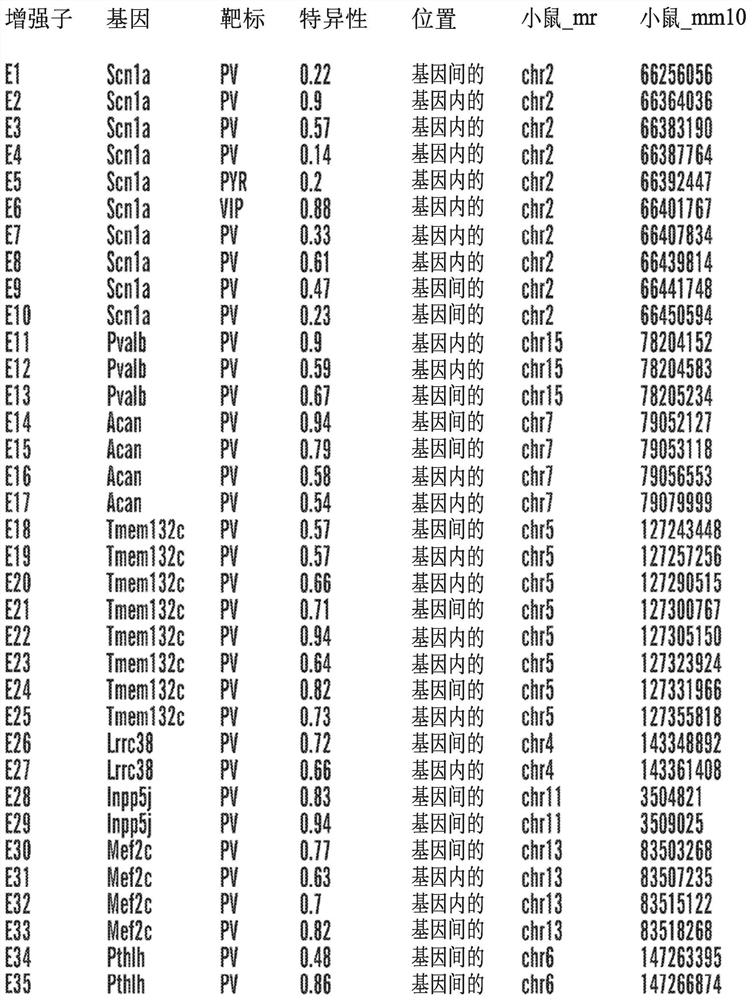
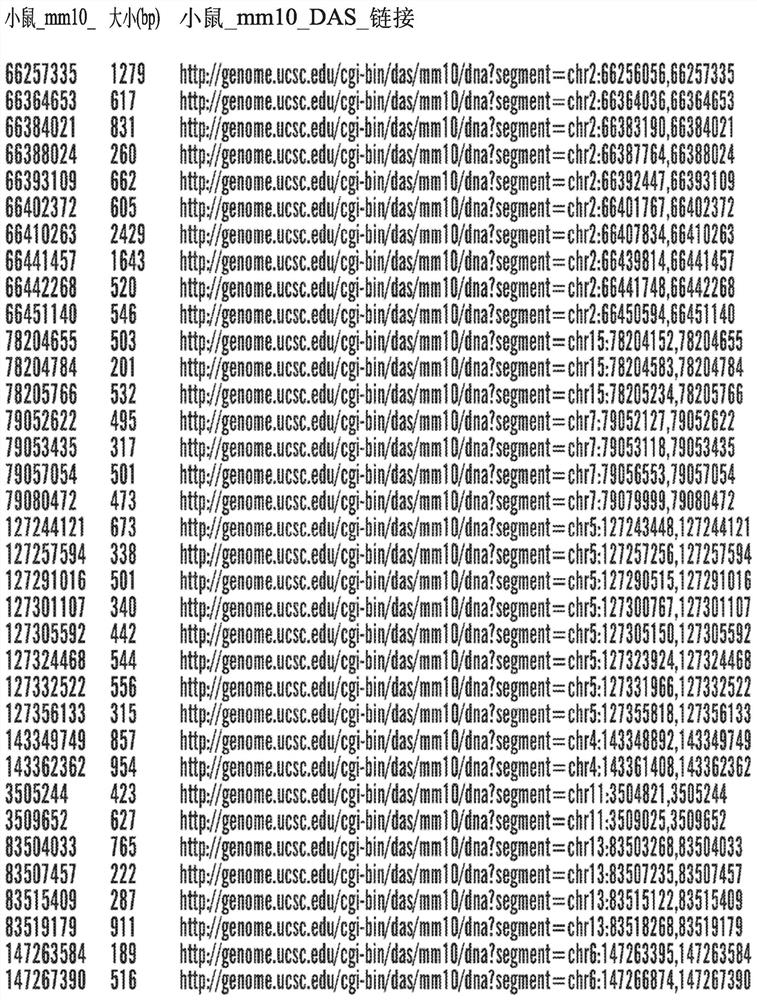
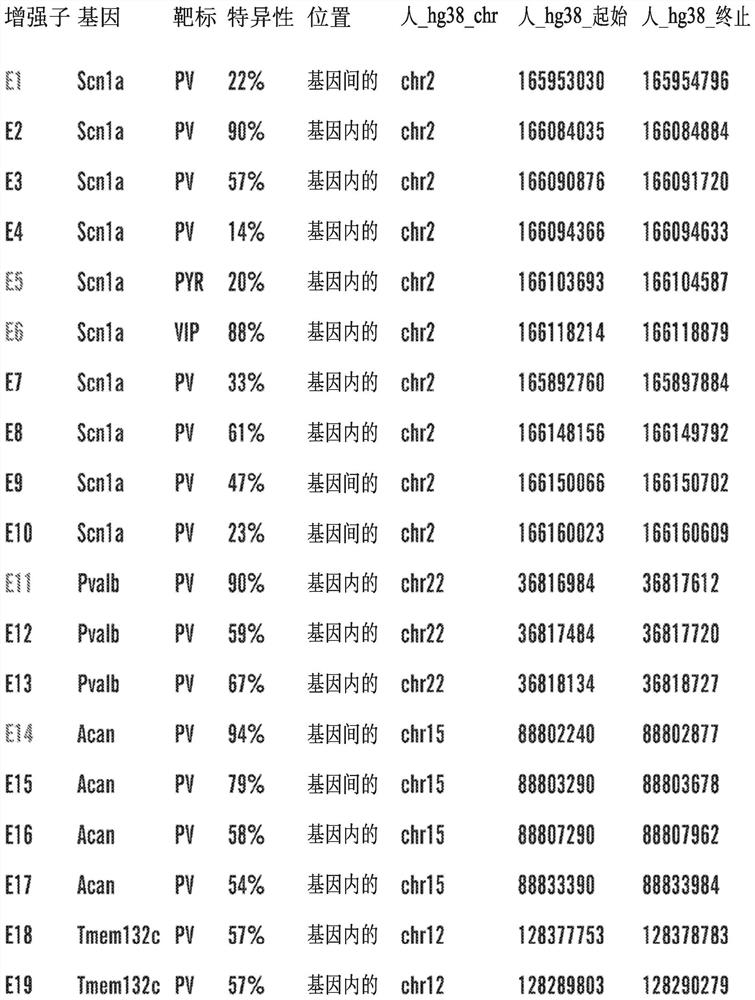
[0368] Example 1: Identification of Cis-Regulatory Sequences Restricting Reporter and Effector Gene Expression to PV-Expressing Cortical Interneuron Cell Populations (PV Interneuron-Specific Enhancer Sequences)
[0369] SCN1A, the gene encoding the Nav1.1 sodium channel, is expressed in multiple distinct neuronal populations in the cerebral cortex, including three non-overlapping neuronal populations: parvalbumin-expressing fast spike-forming cortical interneurons (PV cIN), Disinhibited cortical interneurons (VIP cIN) and layer 5 pyramidal neurons expressing vasoactive intestinal peptide. In a specific embodiment, SCN1A is expressed in PV-expressing cortical interneurons. SCN1A has attracted much attention because its loss of function has been linked to Della Virt syndrome, a premature and intractable epileptic encephalopathy characterized by early-onset seizures. More specifically, SCN1A haploinsufficiency or pathogenic variants trigger Dravet syndrome.
[0370] A comprehen...
Embodiment 2
[0378] Example 2: Viral targeting of mouse PV cortical interneurons (PV cIn)
[0379] E2 regulatory elements display 90% specificity for PV cIN, and this specificity provides a means of targeting fast-spiking neurons (e.g., basket and chandelier cells), which collectively account for all cortical (GABAergic) neurons. ) of 40% of interneurons. These neurons have strong inhibitory effects on local networks, and their dysfunction has been directly linked to neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders, including Dravet syndrome, focal epilepsy, autism spectrum disorder (ASD), and schizophrenia disease. Therefore, controlling the activity of these neurons is particularly important for both basic research and clinical applications. Therefore, E2 regulatory elements are studied and characterized for the development of agents with broad utility, eg as viral tools or therapeutics.
[0380] After systemic injection of rAAV-E2-dTomato into adult mice, the expression of the viral repor...
Embodiment 3
[0385] Example 3: Viral monitoring and manipulation of PV cortical interneurons in mice
[0386] As described in Example 2, having demonstrated the precise expression of E2 against PVcIN using different injection modes and at various developmental stages, this vector was evaluated for studying connectivity (using a presynaptic reporter gene) and activity (using a presynaptic reporter gene). imaging technology, coupled with the availability of genetically encoded calcium reporters). When E2 is used to drive the synaptophysin-tdTomato fusion gene (see, e.g., Madisen, L. et al., 2012, Nat Neurosci, 15(5):793-802), expression of the reporter gene is restricted to the presynaptic PV cIN, the terminal body is located on the pyramidal neurons ( Figure 5A ). When this vector was used to drive GCaMP6f expression (Chen, T.W. et al., Nature, 499:295-300 (2013)), it was demonstrated that PV cIN was recruited upon whisker stimulation ( Figure 5B and Figure 9A ). Together these resu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com