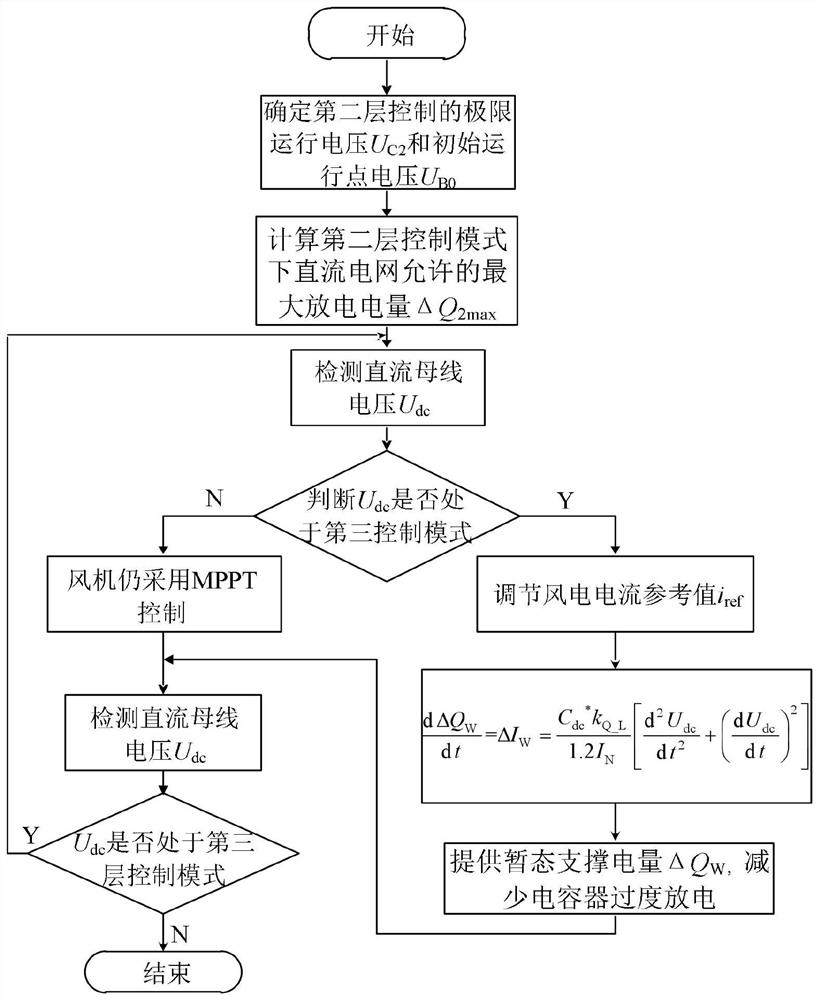
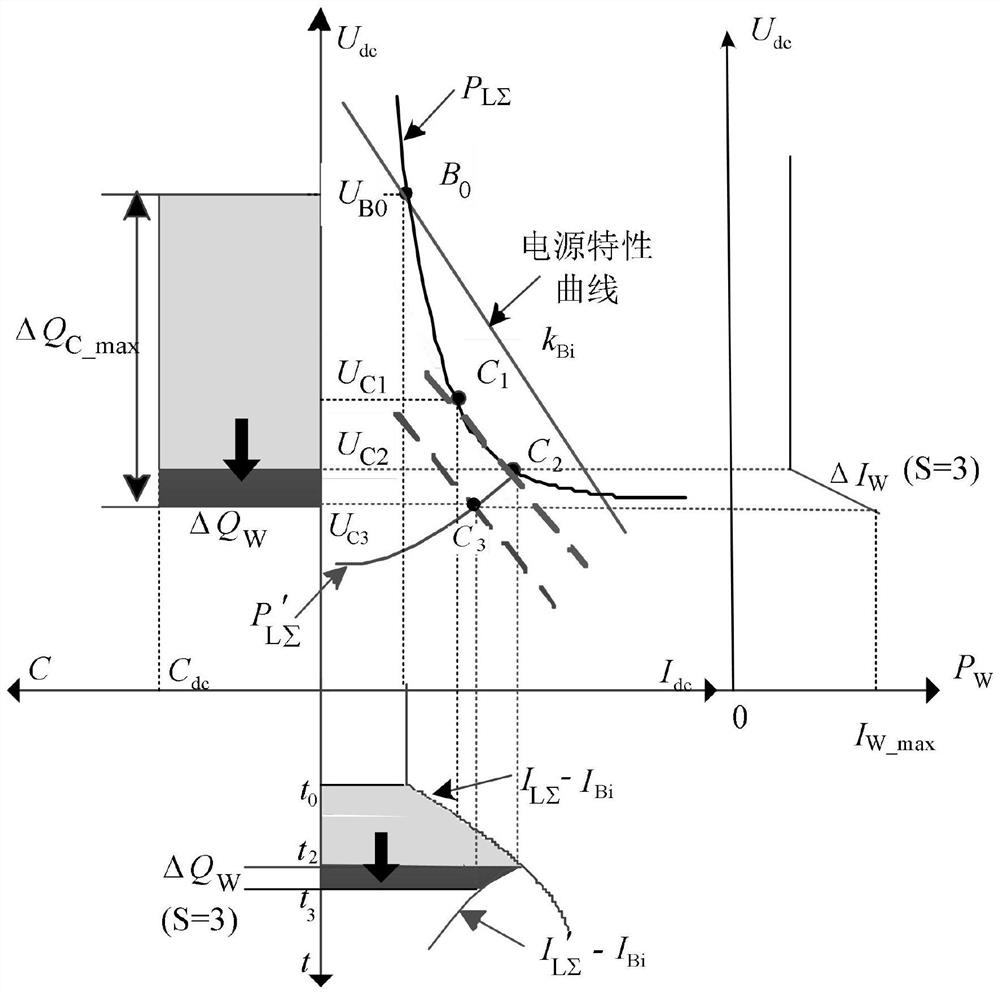
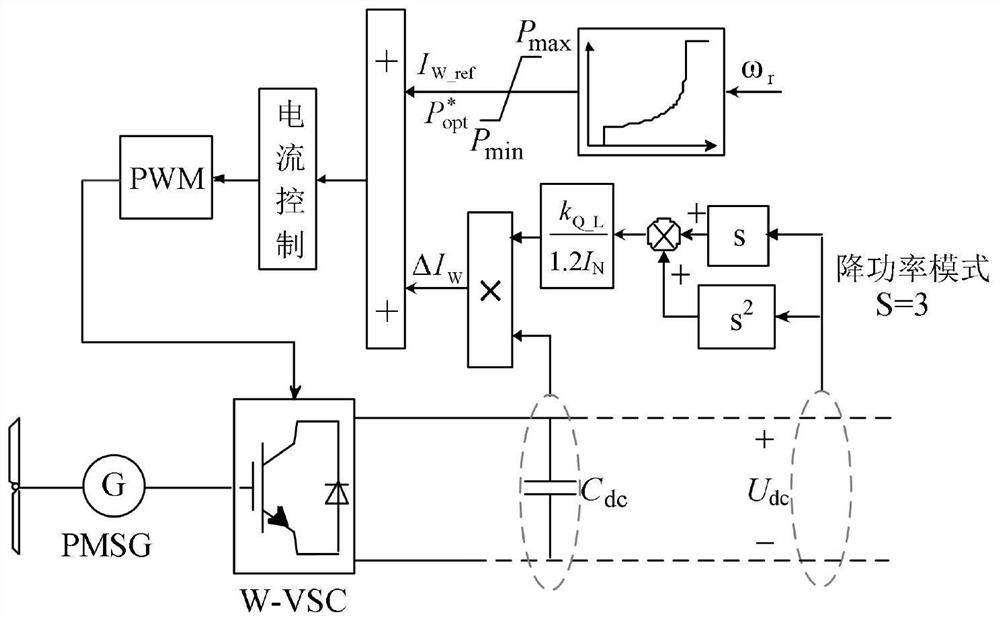
Method and system for controlling transient electric quantity of fan
A control method and transient current technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, DC power supply parallel operation, load balance in DC network, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient voltage inertia, poor DC voltage mutation ability, small value of voltage stabilizing capacitor, etc. To achieve the effect of expanding the voltage margin, increasing the electromagnetic power, and reducing the rotor speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0092] In order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed control strategy, this embodiment builds a DC power grid hardware-in-the-loop simulation test system, such as Figure 4 shown. In the test system, the energy storage side converter B-DC adopts the U-I droop control method; the load side converter L-VSC (AC load) and L-DC (DC load) both adopt constant power control; the fan adopts MPPT ( Maximum Power Point Tracking (Maximum Power Point Tracking) control, the power collected by the wind turbine side converter W-VSC is connected to the DC grid. The basic parameters of the model are shown in Table 1. In order to test whether the DC voltage limit value is consistent with the theoretical analysis, the droop characteristic coefficient is set to k in the test system Bi = 3, the value of this coefficient is slightly larger than the droop coefficient in traditional control, and it is used to simulate the low-pressure operating state of the system.
[0093] Table 1 Model par...
example 2
[0099] In order to verify the voltage limit value in the second layer control mode of the DC grid, the system is in different degrees of step-down operation state by changing the voltage droop reference value of the energy storage side converter. The following three schemes are selected: at 1.0s, the DC voltage droop control reference value is reduced from the initial value of 500V to 485V, 470V, and 450V, respectively, and they are all restored after 1.5s. DC current I of equivalent load dc , DC voltage U dc and active power P LΣ The dynamic response of Figure 5 , 6 , 7 shown.
[0100] combine Figure 8 , in the first two calculation examples, the calculated values of the stable DC voltage are 312V and 270V respectively, which are higher than the limit value of 233V, and the unbalanced current accumulated power ΔQ LΣ -ΔQ sΣ They are 0.075C and 0.195C respectively, both of which are less than the maximum charge ΔQ allowed by the system 2max . However, in Calculatio...
example 3
[0103] In order to verify the support effect of wind turbine transient power control on DC voltage transient stability, the following three calculation examples are set up:
[0104] 1) With traditional control, the voltage drops to U dc C2 , remove the fault;
[0105] 2) The fan side adopts transient power control, and the voltage drops to U dc C2 , remove the fault;
[0106] 3) Transient power control is adopted on the fan side, and the failure time is further extended. The dynamic response of the system is as Figure 9 shown.
[0107] Known U dc * =500V, C dc = 3mF, combined with the test data in Example 1, when the traditional control is adopted, the actual initial voltage U of the stable operation of the system B0 = 330V. Such as Figure 9 As shown, in Calculation Example 1, after a fault occurs on the DC side, the bus voltage drops rapidly to 230V, which is close to the theoretically calculated voltage limit. After the fault is cleared, since the converters at ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com