Mutual exclusion group service routing calculation method and device in optical transmission network planning
A technology of optical transmission network and calculation method, applied in the field of service routing calculation of mutually exclusive groups in optical transmission network planning, can solve problems such as non-intersection, and achieve the effect of obvious theoretical and physical significance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
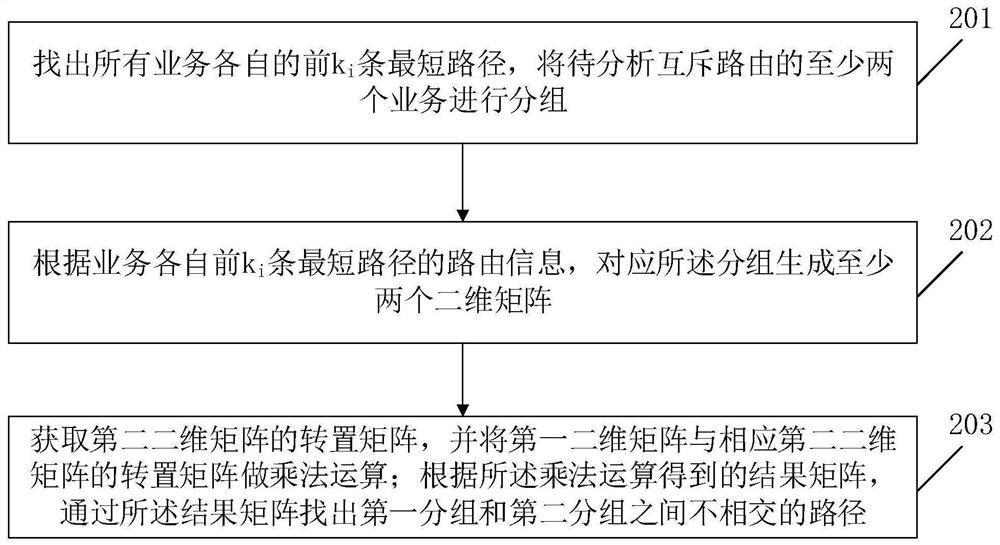
[0046] Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a method for calculating service routes of mutually exclusive groups in optical transmission network planning, such as figure 1 shown, including:
[0047] In step 201, find out the respective top k of all businesses i The shortest path is used to group at least two services of mutually exclusive routes to be analyzed.
[0048] Find the top k of all businesses as described i The shortest path (corresponding to different services, the corresponding number of shortest paths can take the same value or different values, which is usually selected according to the complexity of the actual network scene), specifically through the k-shortest path algorithm (K-Shortest Pathes, Abbreviated as: KSP) algorithm to find the top k of all businesses i the shortest path. The k-shortest path algorithm includes Yen's algorithm; Lawler's algorithm; Hoffman's algorithm; Katoh's algorithm and so on.
[0049] Among them, when the complexity o...
Embodiment 2
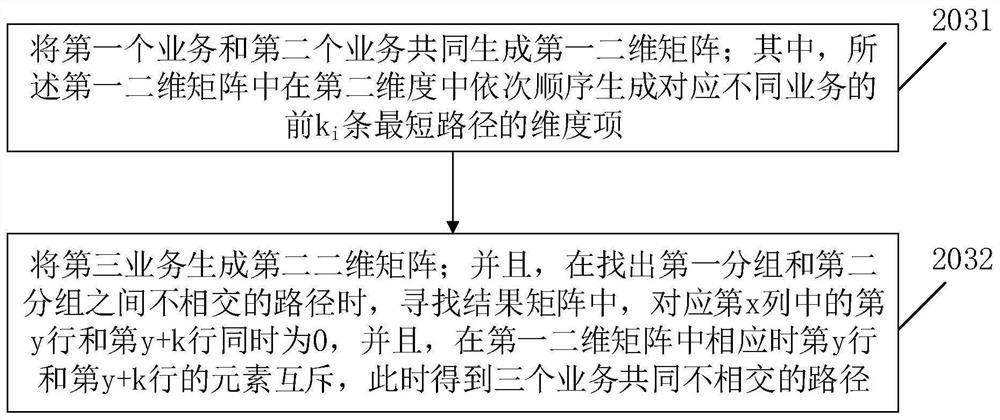
[0071] The embodiment of the present invention is based on the specific application performance of the technical solution proposed in Embodiment 1 in OTN network planning and optimization. The definition of related parameter symbols in the embodiment of the present invention will be more in line with the definition method in OTN network planning, so as to develop the technical solution of the present invention. For example, the network uses G=(V,E), where V=(v 1 ,v 2 ,...,v n ) represents a node in the network; E=(e 1 ,e 2 ,...,e m ) represent sub-links between related nodes in the network. Business C=(c 1 ,c 2 ,...,c p ) is a group of connection requests in the network; the business in C is grouped, and the symbol G=(g 1 , g 2 ,..., g o )To represent. Mutually exclusive constraints on groups, such as two i-th groups and j-th groups are mutually exclusive, g i and g j The groups are mutually exclusive, that is, the paths of the services in the two groups are disj...
Embodiment 3
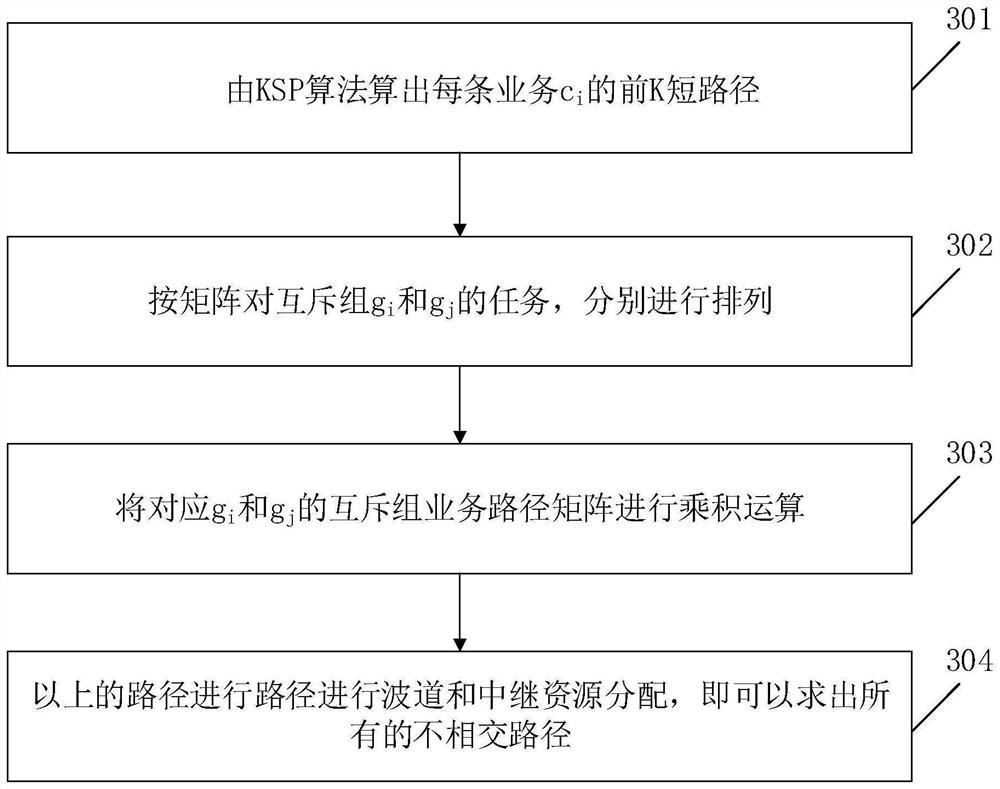
[0080] The embodiment of the present invention further provides a brief routing map, such as Figure 4 As shown, the technical solution proposed in Embodiment 1 of the present invention is described from a more intuitive technical perspective.
[0081] The topology is 8 nodes V=(Node1,Node2,…,Node8), and there are 9 sub-links E=(e 12 ,e 13 ,e 25 ,e 34 ,e 36 ,e 48 ,e 56 ,e 67 ,e 78 ), two businesses (c 1 ,c 2 ), business (c 1 ,c 2 ) are connection requests from nodes Node1->Node7; for business (c 1 ,c 2 ) for grouping: g 1 =(c 1 ), g 2 =(c 2 ). The goal is to find out the disjoint paths of two mutually exclusive groups and their resource allocation.
[0082] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the specific steps are as follows:
[0083] In step 401, the mutually exclusive group g is calculated according to the KSP algorithm 1 =(c 1 )’s top k=3 paths (here, for the convenience of description, the same top k paths are used for each business):
[0084] Node1->Node3...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com