Preparation method of yield-increasing disease-resistant biological bacterial fertilizer for field crops
A technology of biological bacterial fertilizer and field crops, applied in the field of fertilizers, can solve the problems of nitrogen volatilization loss, low bacterial content of bacterial fertilizer, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing losses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
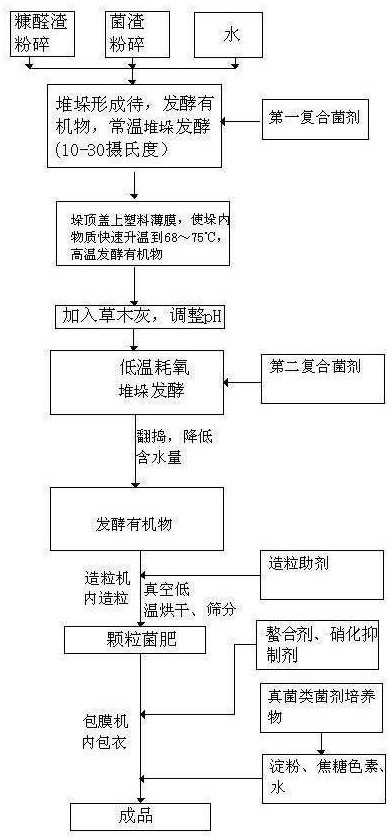
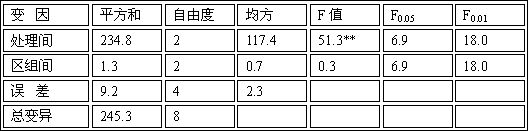
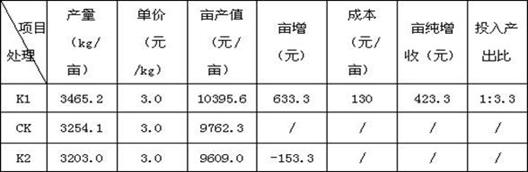
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Example 1. A method for preparing field crop production-increasing disease-resistant biological bacterial fertilizer, characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0047] Step 1: Protease-producing bacteria, lipase-producing bacteria, cellulase-producing bacteria, amylase-producing bacteria, potassium bacteria, and phosphorus bacteria obtained from the General Microbiology Center (CGMCC) of the China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee were respectively prepared according to the provided Bacterial Strain Explanation Carry out activation, step-by-step expansion culture, and prepare bacterial agent. The microbial enzyme activity unit of the international system of units is used as the measurement unit, wherein the cellulase activity unit is based on the FPA activity unit, according to protease: lipase: amylase: The ratio of cellulase=0.5: 0.2: 0.3: 0.8, then add 2% volume ratio of potassium bacteria agent and 5%% volume ratio of phosphorus ...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Example 2. A method for preparing field crop production-increasing disease-resistant biological bacterial fertilizer, characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0066] Step 1: Protease-producing bacteria, lipase-producing bacteria, cellulase-producing bacteria, amylase-producing bacteria, potassium bacteria, and phosphorus bacteria obtained from the General Microbiology Center (CGMCC) of the China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee were respectively prepared according to the provided Bacterial Strain Explanation Carry out activation, step-by-step expansion culture, and prepare bacterial agent. The microbial enzyme activity unit of the international system of units is used as the measurement unit, wherein the cellulase activity unit is based on the FPA activity unit, according to protease: lipase: amylase: The ratio of cellulase=0.7: 0.4: 0.5: 1.2, then add 15% volume ratio of potassium bacteria agent and 8% volume ratio of phosphorus ...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Example 3. A method for preparing field crop production-increasing disease-resistant biological bacterial fertilizer, characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0085] Step 1: Protease-producing bacteria, lipase-producing bacteria, cellulase-producing bacteria, amylase-producing bacteria, potassium bacteria, and phosphorus bacteria obtained from the General Microbiology Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee were respectively carried out according to the instructions of the provided strains Activation, step-by-step expansion culture, and preparation of bacterial agents, the microbial enzyme activity unit of the International System of Units is used as the measurement unit, wherein the cellulase activity unit is based on the FPA activity unit, according to protease: lipase: amylase: cellulase =0.5: 0.6: 0.4: 1.2 ratio, then add 18% volume ratio of potassium bacteria agent and 15% volume ratio of phosphorus bacteria agent, p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viable count | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com