Flexible power tracking control method of photovoltaic power generation unit and application thereof
A technology of photovoltaic power generation and power tracking, which is used in photovoltaic power generation, control/adjustment system, regulating power variables and other directions. It can solve the problems of increased the cost of heat dissipation device, the temperature increase of subway traction power supply systems, to achieve extended life, reduce waste, reduce Cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
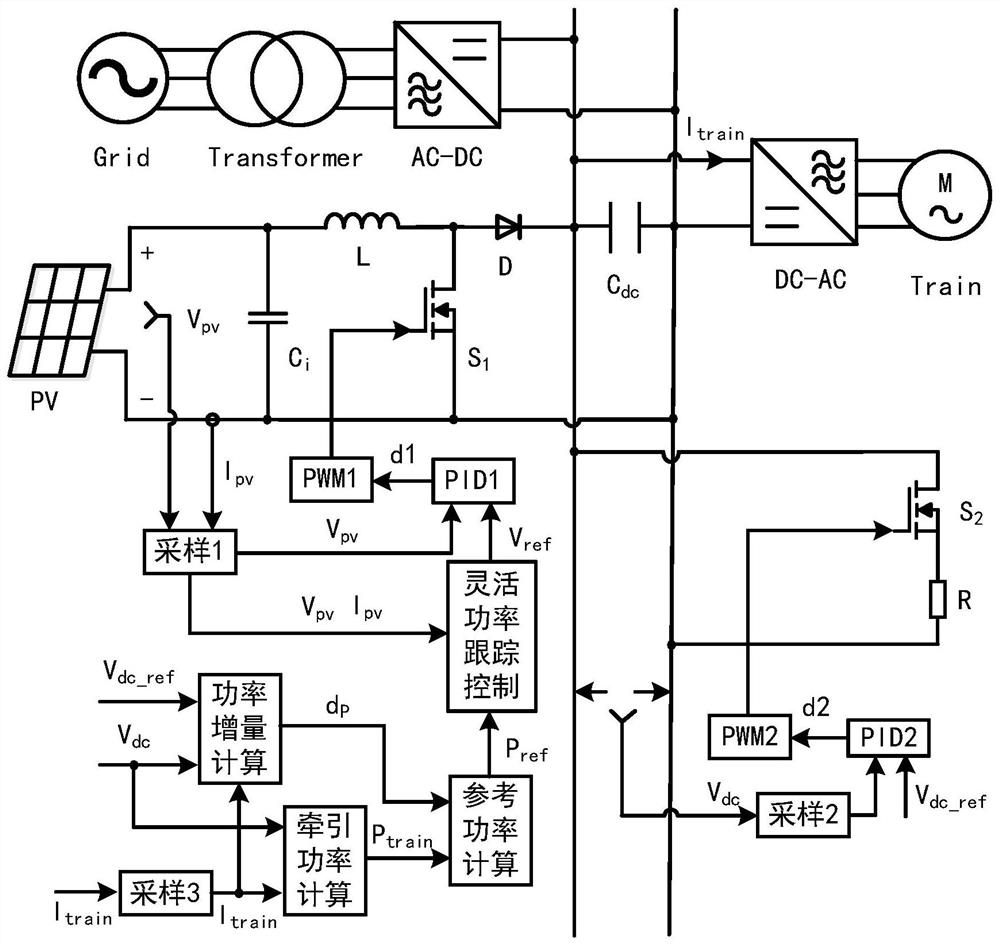
[0038] like figure 1 , the specific method is:
[0039] Step 1: Initialize parameters. Specifically include setting: the upper and lower limits of the DC bus voltage, the reference voltage of the DC bus, the sampling period of the flexible power tracking, the initial reference voltage of the photovoltaic array and other parameters.
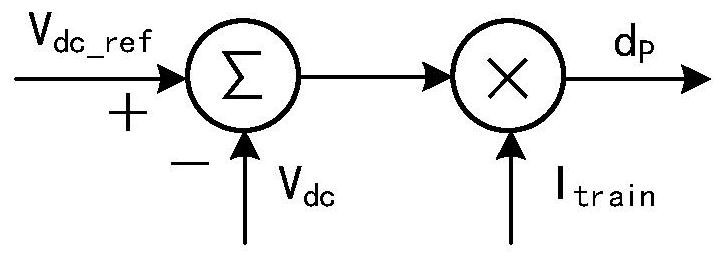
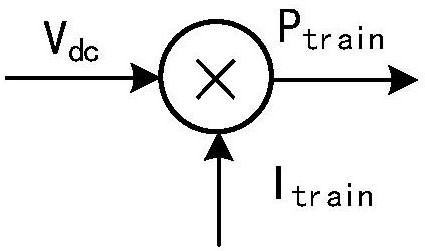
[0040] Step 2: Calculate the power reference value of photovoltaic power generation. First, the DC bus voltage is collected, the difference between the bus voltage and the corresponding reference value is calculated, and the power increment is calculated by combining the voltage difference and the input current of the locomotive. Then, the traction power of the locomotive is calculated through the bus voltage and the input current of the locomotive. Finally, the power needed to be provided by the traction power supply system is calculated by combining the power increment and the traction power of the locomotive, which is used as a power reference...
Embodiment 2
[0058] like Figure 9 As shown, the difference from the first embodiment is that the system controlled in this example is a DC microgrid system. Compared with Embodiment 1, the system of this embodiment can be applied to remote areas without power grids where power supply is inconvenient. In addition to the DC system in the above embodiments, the present invention can also be used in other rail traction power supply systems, AC microgrid systems and other systems including photovoltaic power generation units.
Embodiment 3
[0060] like Figure 10 As shown, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the subway traction power supply system of this example consists of a high-voltage power grid, a transformer, a traction substation, a photovoltaic array, a DC-DC converter, a locomotive, a supercapacitor, and a bidirectional DC-DC converter composition. Among them, the bidirectional flow of energy of the supercapacitor is realized by controlling the bidirectional DC-DC converter through the inner voltage loop and the outer current loop. Compared with Embodiment 1, the system of this example can use the supercapacitor to balance the power difference between the photovoltaic array and the locomotive, and use the supercapacitor to release energy when the bus voltage of the catenary decreases; Capacitors absorb excess energy and reduce energy waste. In addition to the subway traction power supply system in the above embodiments, the present invention can also be used in a subway traction power supply syst...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com