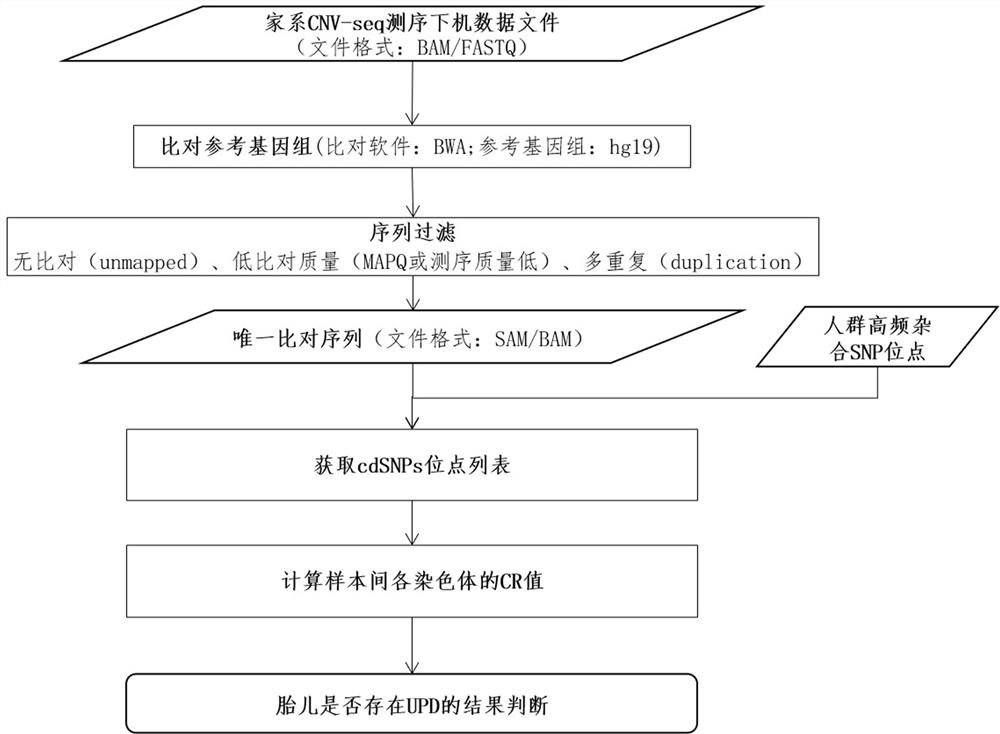
Family-based low-depth sequencing method for detecting chromosome monoparental disomes
A deep sequencing and chromosome technology, applied in the field of prenatal diagnosis molecular genetics detection, can solve the problems that the detection system cannot judge, there is no research detection problem, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
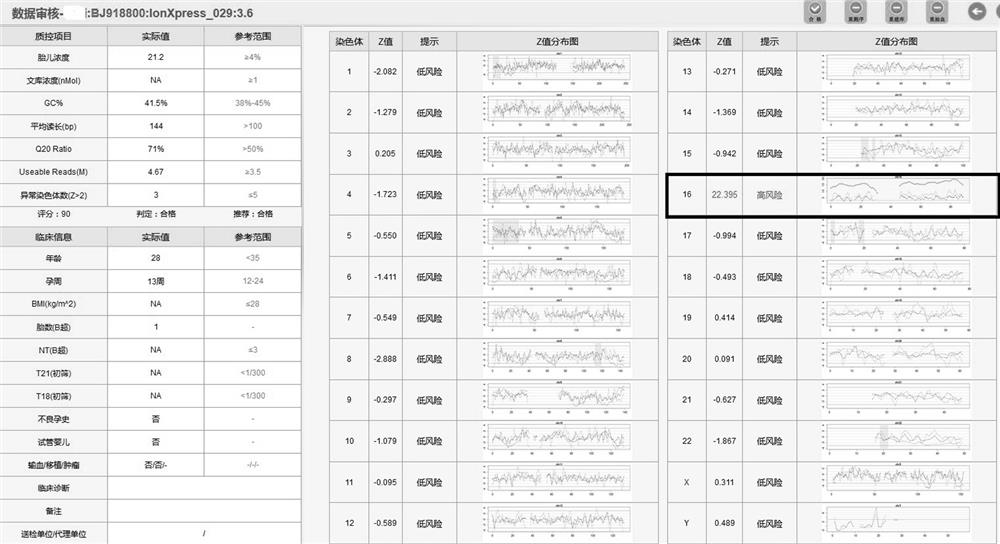
[0104] Example 1: Non-invasively found that the Z value of chromosome 16 was abnormal, and the karyotype of amniocentesis was normal. The microarray showed that there was ROH in the short arm of chromosome 16. After STR, the parent microarray verified that the fetus was matUPD16.
[0105] Noninvasive results such as figure 2 Shown: suggesting a high risk of trisomy 16;
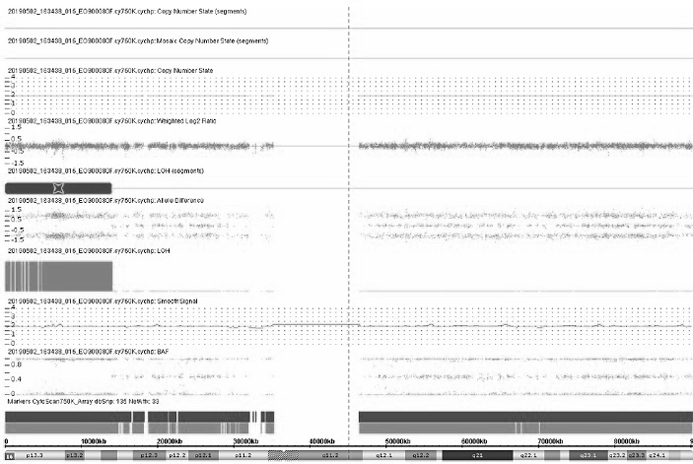
[0106] The results of the gene chip were as image 3 Shown:
[0107] ROH exists on fetal chromosome 16, such as Figure 4 Shown, verified as 16matUPD;
[0108] The family CNV-seq results are as follows:
[0109] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the fetus: No. EO900080FT, 46, XX, no obvious copy number abnormalities
[0110] Such as Figure 6 Shown, mother: No. EO900093BT, 46, XX, no obvious copy number abnormalities
[0111] Such as Figure 7 As shown, father: No. EO900094BT, 46, XY, no obvious copy number abnormalities
[0112] The cdSNP consistency analysis was performed on the original CNV-seq data of...
Embodiment 2
[0123] Example 2: Non-invasive T15, amniocentesis with normal karyotype, microarray showing ROH on chromosome 15, which was verified as patUPD15 by family STR.
[0124] Such as Figure 8 and Figure 9 Shown is the CMA report of the fetus;
[0125] The family CNV-seq results are as follows:
[0126] Such as Figure 10 Shown, fetus: No. EO002181DT, 46, XX, no obvious copy number abnormalities
[0127] Such as Figure 11 Shown, mother: No. E0000165BT, 46, XX, no obvious copy number abnormalities
[0128] Such as Figure 12 As shown, father: No. E0000166BT, 46, XY, no obvious copy number abnormalities
[0129] The cdSNP consistency analysis was performed on the original CNV-seq data of the above families:
[0130] 2.1 Sequence alignment, the three raw data files of family CNV-seq were compared by BWA to obtain three files with alignment information;
[0131] 2.2 Sequence filtering;
[0132] 2.3 Select the SNP site data set with high frequency heterozygosity in the popula...
Embodiment 3
[0140] Example 3: Non-invasive normal, amniocentesis with normal karyotype, the microarray showed that there was ROH on chromosome 6, and the parent microarray verified that the ROH of No. 6 was not UPD, and the ROH might be caused by kinship.
[0141] Such as Figure 13 and Figure 14 Shown is the CMA report of the fetus;
[0142] The heterozygous signal map of fetal chromosome 6, suggesting that there is a 10.6Mb region of homozygosity (ROH) at 6q24.3q25.3.
[0143] Such as Figure 15 As shown, the CMA analysis results of the family on chromosome 6 suggest that the ROH phenomenon is not caused by UPD.
[0144] The family CNV-seq results are as follows:
[0145] Such as Figure 16 Shown, fetus: number EO001478DT, 46, XY, dup(4): 168.3Mb-169.4Mb, consistent with the copy number abnormality reported by CMA.
[0146] Such as Figure 17 As shown, mother: No. EO001620BT, 46, XX, no obvious copy number abnormalities
[0147] Such as Figure 18As shown, the father: number E...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com