Transformer bias magnet current calculation method based on subway near-area earth and power grid model
A power grid model and current calculation technology, applied in calculation, computer-aided design, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of unseen calculation of 220kV transformer bias current in urban network and high calculation complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0050] The following is attached Figure 1-8 The present invention is described in further detail.
[0051] A method for calculating the bias current of a transformer based on the earth and power grid model in the vicinity of the subway, specifically comprising the following steps:
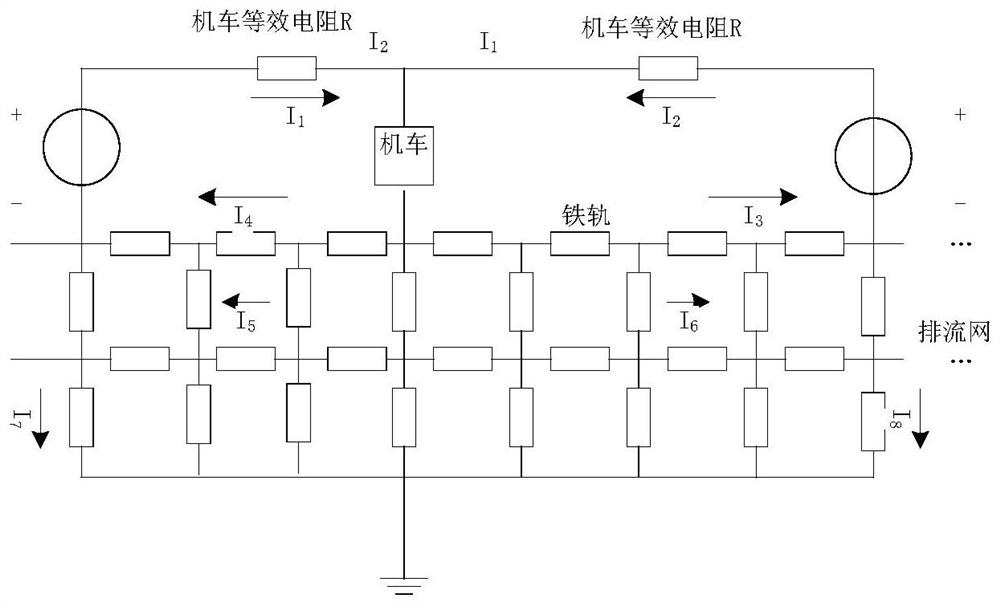
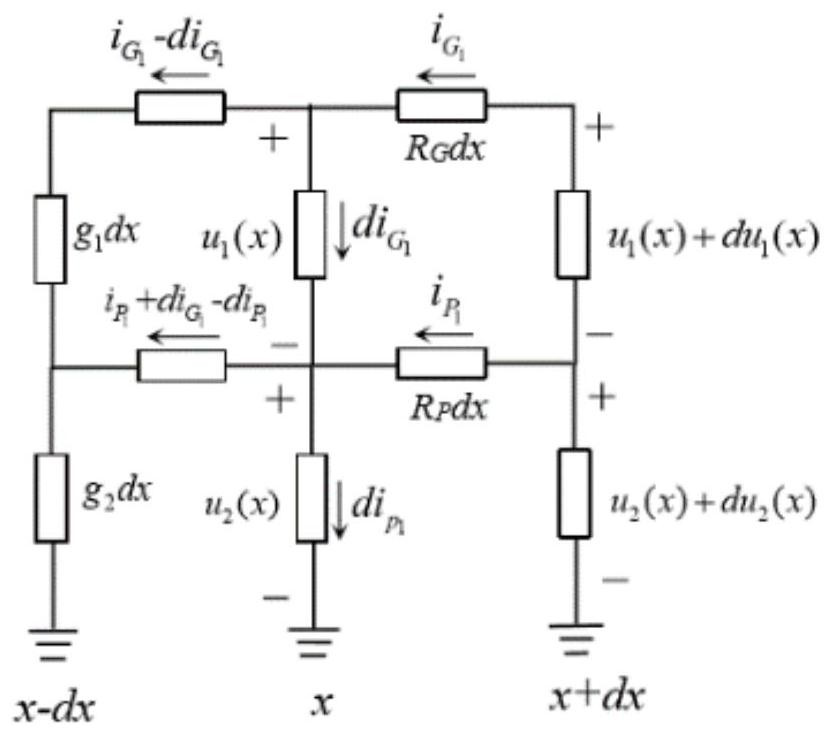
[0052] Step 1: Establish a resistance network model, and use the resistance network model to calculate the stray current flowing into the ground from rail leakage during subway operation;
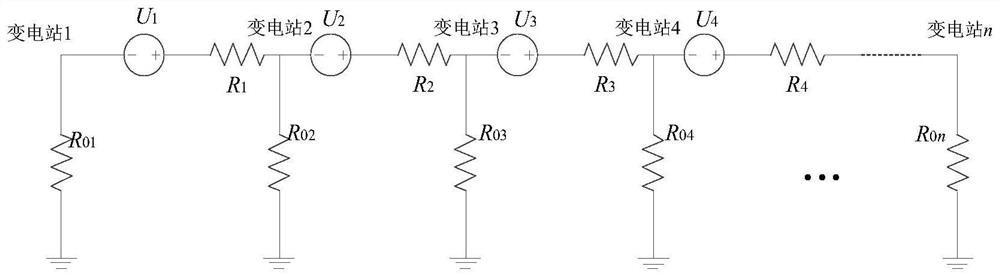
[0053]Step 2: Establish a three-dimensional resistivity model of the earth according to the electrical properties of the earth and its structural data, and use the three-dimensional resistivity model of the earth to calculate the ground potential of the substation in the vicinity of the subway;
[0054] Step 3: Analyze the influencing factors of the grid bias current, and use the GIC-Benchmark method to simplify the grid structure, wire resistance, transformer connection and winding resistance and other data a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com