Method for deducing submerging time of corpses in water after early death based on metabonomics markers and application of method
A technology of metabolomics data and markers, which is applied in the field of marker screening for inferring the submergence time of early corpses in water, can solve rare problems and achieve the effects of high contribution, close correlation and high predictive ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
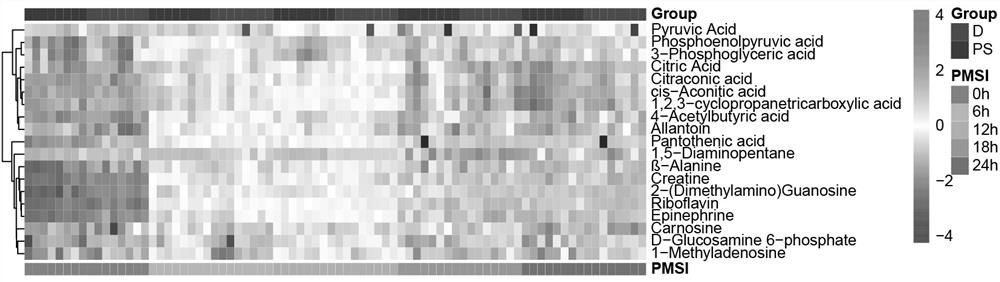
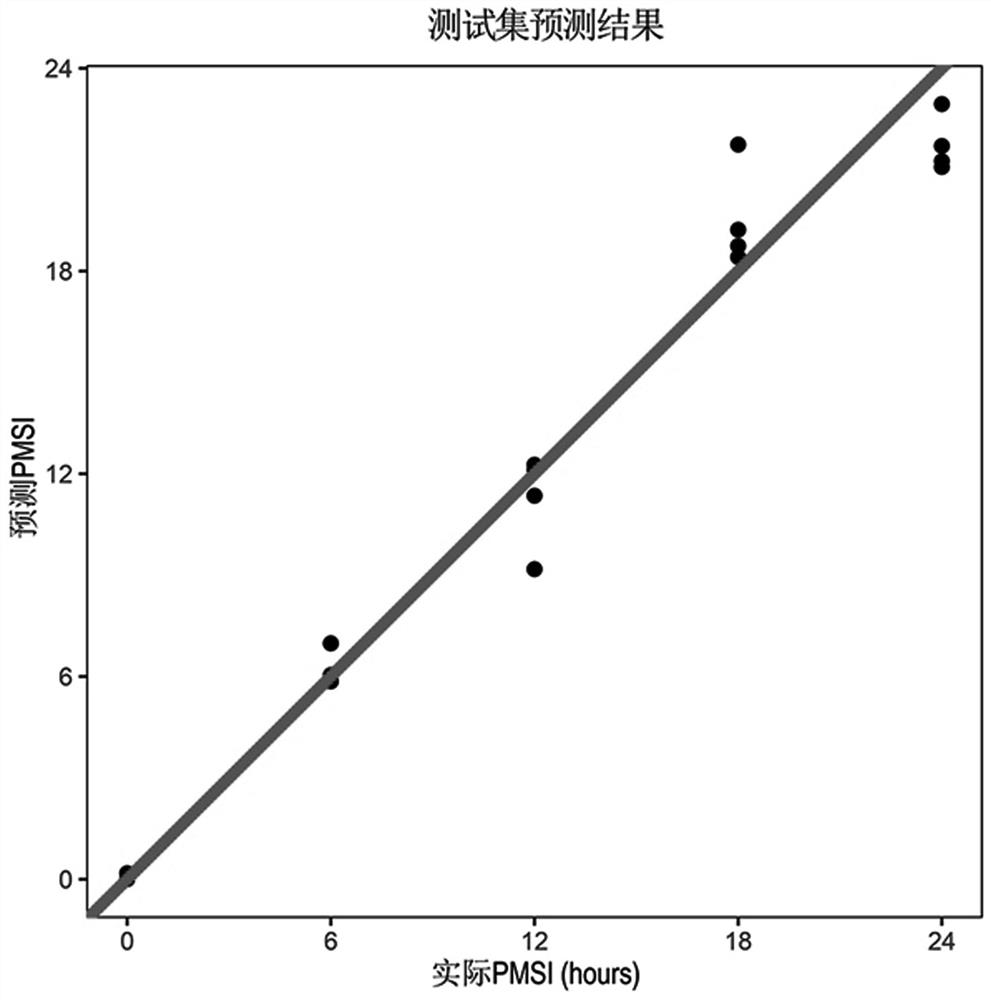
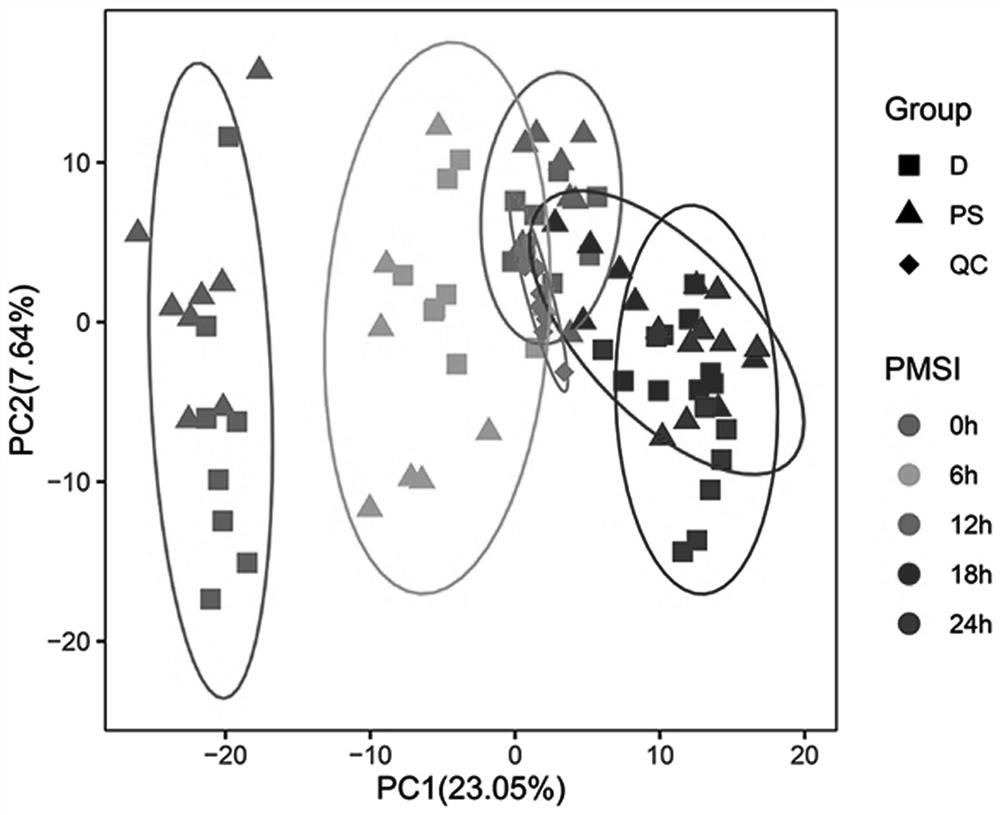
[0031] 1. Research object and grouping.
[0032] Training set: 80 male SD rats were randomly divided into drowning group (group D, T1-40) and postmortem submersion group (group PS, T41-80), with 40 rats in each group. The rats in the drowning group were immersed in river water (natural fresh water) and drowned, and the rats in the water group were taken with CO 2 After being asphyxiated by gas, they were immersed in river water, and the temperature of the river water was 20-25°C during the experiment. Heart blood (about 200 μL) was extracted at different time points (0h, 6h, 12h, 18h and 24h) after immersion in water after death, and 8 rat corpses were taken at each time point, and the samples were immediately placed in liquid nitrogen after collection. Then store at -80°C for future inspection.
[0033] Test set: 20 male SD rats were randomly divided into drowning group (V1-10) and postmortem submersion group (V11-20), with 10 rats in each group. The corpses of dead animal...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com