Gate source impedance dynamic adjustment active current sharing SiC MOSFET parallel drive circuit
A technology of impedance dynamics and driving circuits, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, high-efficiency power electronic conversion, output power conversion devices, etc., can solve the problems of reducing power density, unbalanced branch current, unbalanced quiescent current, etc., to achieve the suppression of parallel Uneven current, no increase in loss, and obvious effect of current equalization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] The present invention will be further explained below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
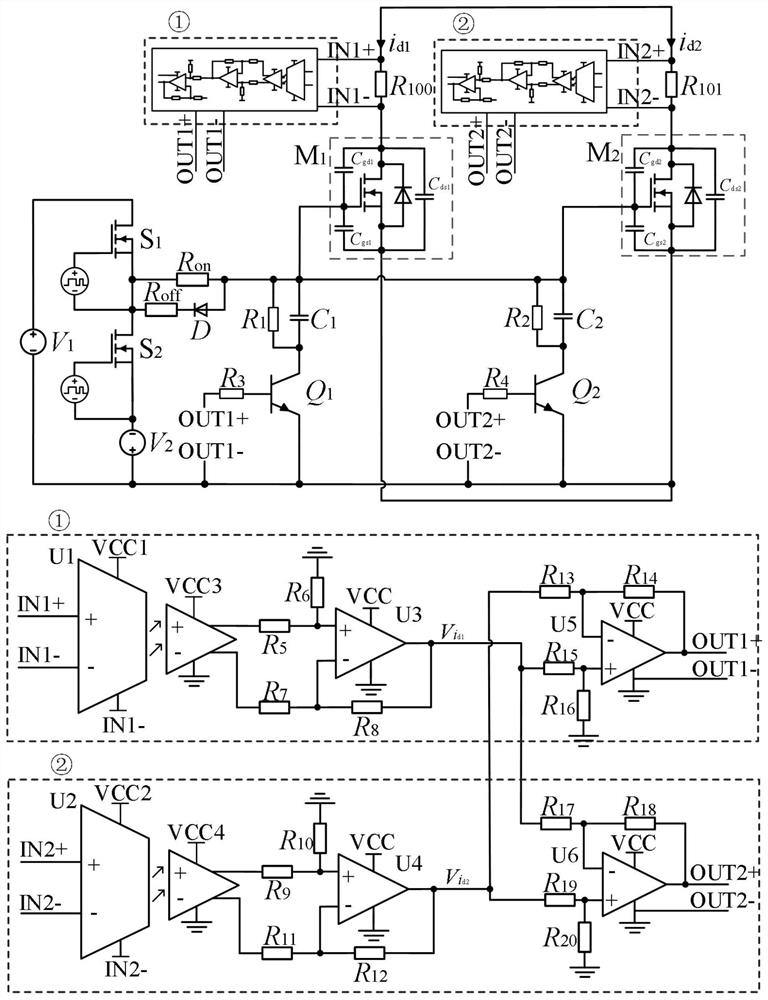
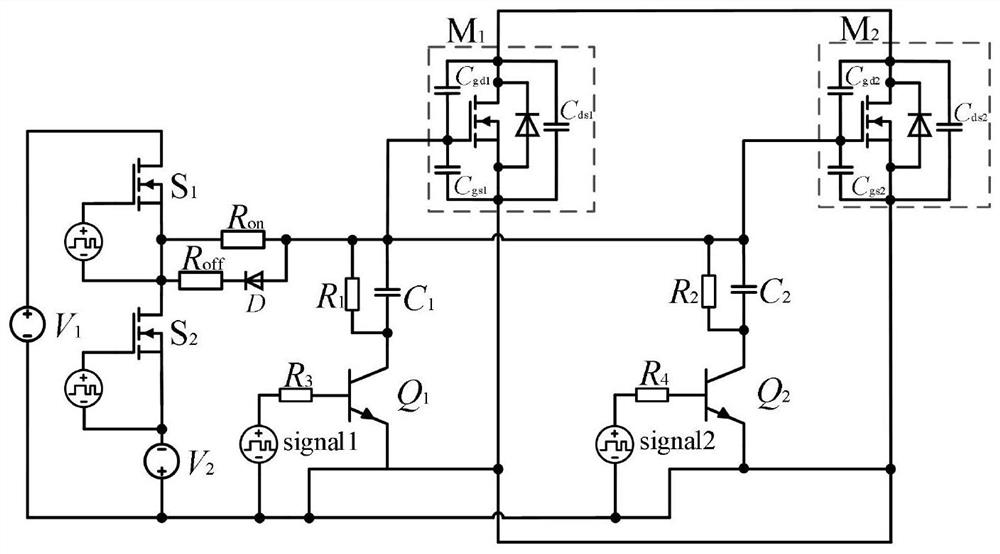
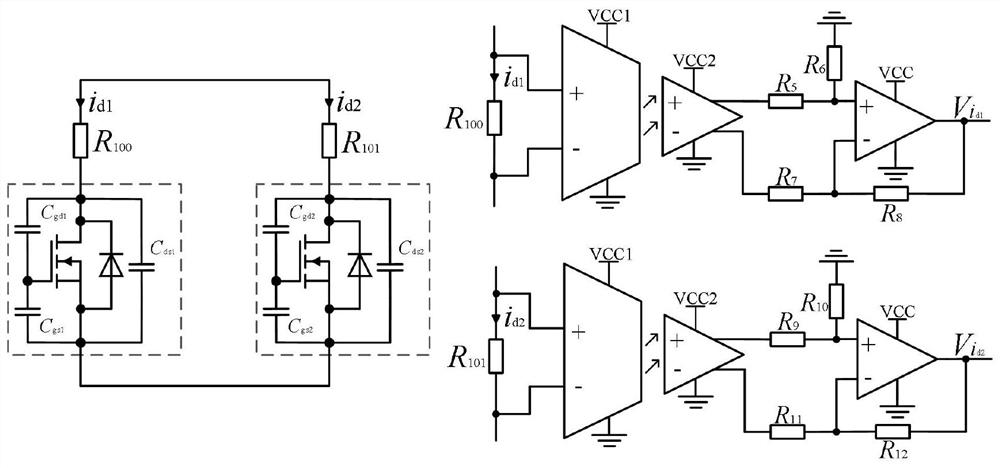
[0034] like figure 1 As shown, a parallel driving circuit for SiC MOSFETs with dynamic adjustment of gate-source impedance and active current sharing, including SiC MOSFET M 1 、SiC MOSFET M 2 , current acquisition circuit, differential amplification isolation circuit, current difference feedback circuit, gate-source low impedance circuit and SiC MOSFET basic drive circuit. The current acquisition circuit includes a shunt R 100 and R 101 , respectively for the SiC MOSFET M in series 1 branch and SiC MOSFET M 2 branch road. The differential amplification isolation circuit is connected with the current difference feedback circuit, which is used to measure the potential difference on the shunt to indirectly measure the SiC MOSFET M 1 branch and SiC MOSFET M 2 When the current of the branch circuit is unbalanced in the SiC MOSFET parallel circuit, the control signal...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com