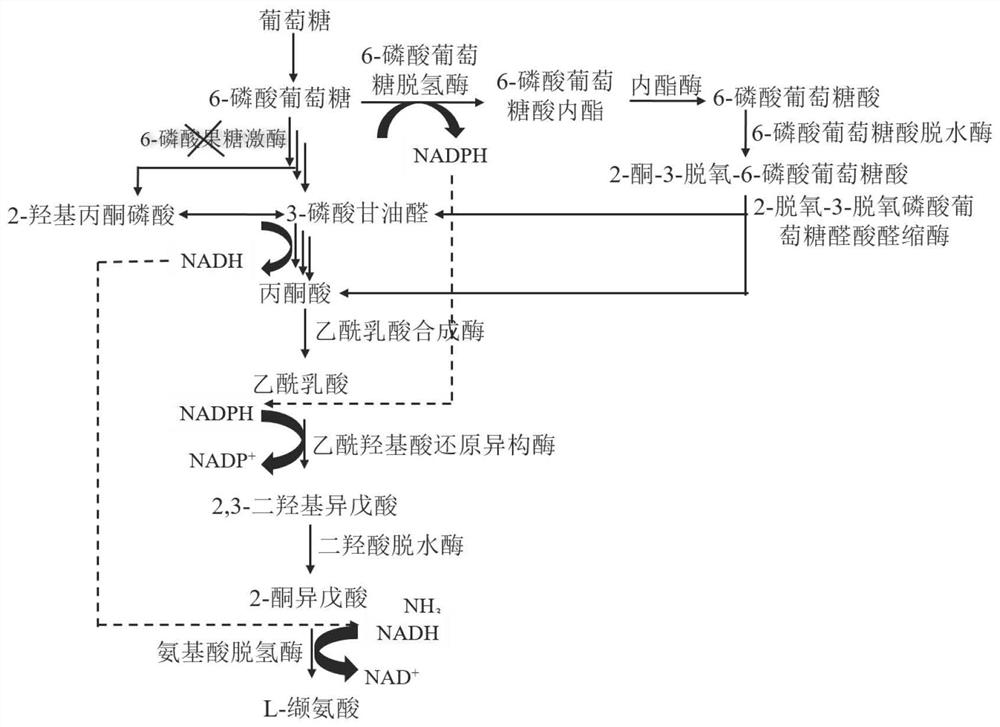
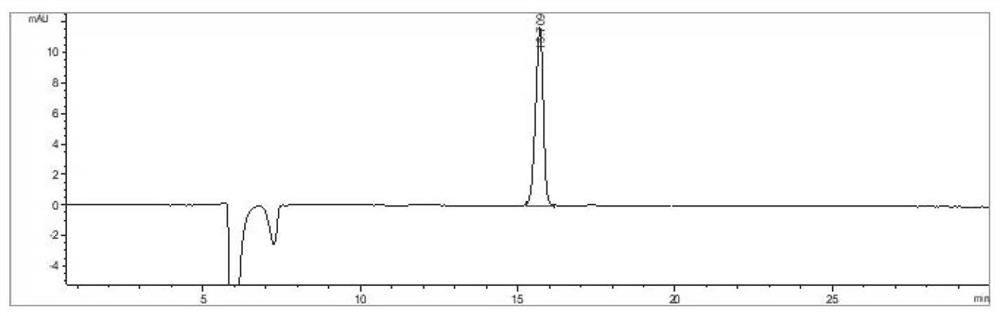
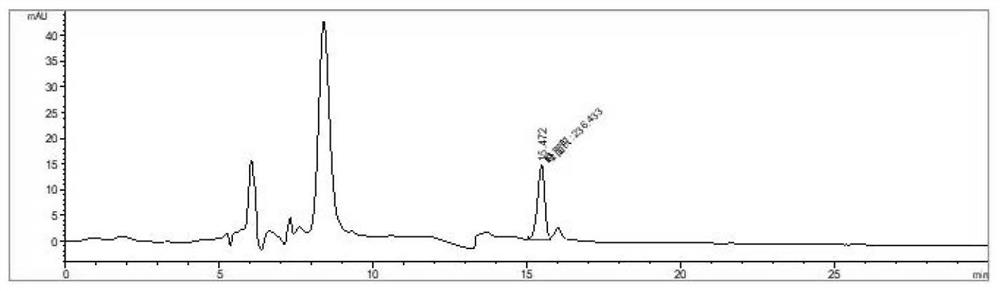
Recombinant escherichia coli for producing L-valine and application thereof
A valine and amino acid technology, applied in the direction of recombinant DNA technology, microorganism-based methods, bacteria, etc., can solve the problems of unbalanced reducing power, etc., to reduce production costs, increase yield and conversion rate, and cell tolerance, The production process is stable and easy to operate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0111] Example 1: Knockout of methyladehane coding gene Mgsa in ATCC8739 strains
[0112] From E. coli ATCC8739, a two-step homologous reorganization method knockout methylene ethyl aldehyde enzyme encoding gene MGSA, the specific steps are as follows:
[0113] In the first step, 2719 bp DNA fragment I was amplified by PXZ-Cs Plasmid DNA using PXZ-CS plasmid DNA, and 2719 bp DNA fragment I was used to amplify the first step homologous recombination.
[0114] The amplification system is: 10 μl of NewenglandBiolabs, DNTP (10 mm per DNTP) 1 μL, DNA template 20 ng, 2 μl of the primer (10 μm), PHUSONHHIGH-FideEndNa polymerase (2.5 u / μl) 0.5 μL The distilled water was 33.5 μL, and the total volume was 50 μL.
[0115] The amplification conditions were 98 ° C for 2 minutes (1 cycle); 98 ° C denaturation for 10 seconds, 56 ° C for 10 seconds, 72 ° C for 2 minutes (30 cycles); 72 ° C extends for 10 minutes (1 cycle).
[0116] The DNA fragment 1 is used for the first homologous recombinati...
Embodiment 2
[0120] Example 2: Urna of the lactate dehydrogenase encoding gene LDHA
[0121] From SVAL002, the lactate dehydrogenase encoding gene LDHA is knocking through two-step homologous recombination method, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0122] In the first step, the PXZ-CS plasmid DNA was used as a template, and the 2719 BP DNA fragment I was amplified using primer LDHA-CS-UP / LDHA-CS-DOWN for the first step homologous recombination. The amplification system and amplification conditions are consistent with the first embodiment. The DNA fragment I is electrically rotated to SVAL002.
[0123] The DNA fragment 1 was used for the first homologous recombination: first converted to E. coli SVAL002 by electro-conversion method, and then electrically converted to Escherichia coli SVAL002 with PKD46.
[0124] The electric turn conditions and steps are consistent with the first step of the MGSA gene knockout as described in Example 1. The 200 μl of bacteria was coated with an LB plate...
Embodiment 3
[0127] Example 3: Phosphate Code Enzyme Coded Gene PTA and Kinase Coded Gene ACKA Knockout
[0128] From SVAL004, the specific steps are as follows: The specific steps are as follows: The specific steps are processed from SVAL004.
[0129] In the first step, 2719 bp DNA fragment I was amplified by PXZ-Cs Plasmid DNA using PXZ-CS plasmid DNA using primer ACKA-CS-UP / PTA-CS-DOWN for the first step homologous recombination. The amplification system and amplification conditions are consistent with the first embodiment. The DNA fragment I is electrically rotated to SVAL004.
[0130] The DNA fragment 1 was used for the first homologous recombination: first converted to E. coli SVAL004 by electro-conversion, and then electrically rotated DNA fragment I to Escherichia coli SVAL004 with PKD46.
[0131] The electric turn conditions and steps are consistent with the first step of the MGSA gene knockout as described in Example 1. The 200 μl of bacteria was coated with an LB plate containing ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com