Method for selectively leaching zinc in zinc ferrite-containing waste residues through mechanical activation and directional reduction
A mechanical activation, waste residue technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of waste, land occupation by zinc leaching residue, environmental threat of iron vanadium residue, etc., to reduce the generation of hazardous waste, reduce time and cost, and solve the problem of iron The effect of alum slag
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
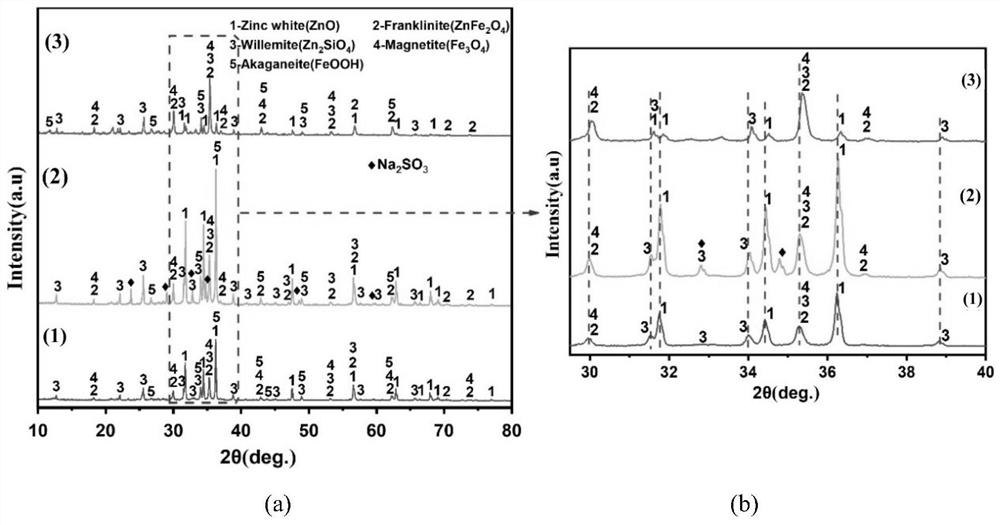
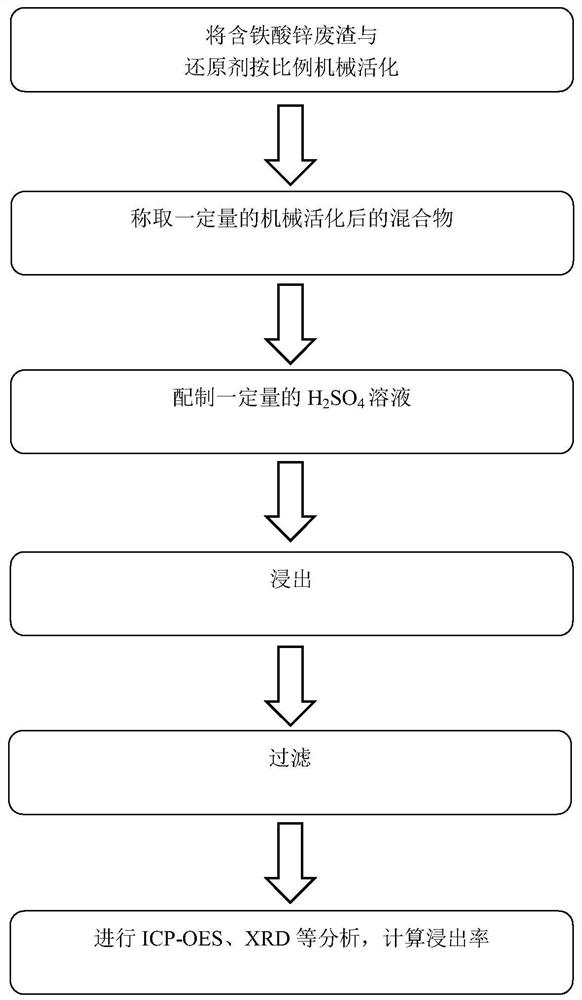
[0030] In this embodiment, the zinc in the zinc calcined sand is selectively leached through the mechanical activation method, and the flow process is as follows: figure 2 shown.
[0031] (1) Combine zinc calcine with Na 2 SO 3 Add the ratio of 50 g : 0.04 mol into the zirconia ball mill jar for mechanical activation together, add ball mill balls according to the ball-to-material ratio of 1 : 2, set the frequency to 30 Hz, and obtain mixture A after ball milling for 4 h; prepare a certain volume concentration of 50 g / L of H 2 SO 4 The solution is used as the leaching solution. According to the solid-liquid ratio of 100 g / L (the ratio of the mass of zinc calcine to the volume of the leaching solution), weigh a certain amount of mixture A, and slowly add the weighed mixture A to H under stirring. 2 SO 4 In the solution, mixed system B was obtained after 120 min of reaction;
[0032](2) After suction filtration and drying, the leaching amount of zinc was 28.36 g, and the l...
Embodiment 2
[0034] In this embodiment, the zinc in the zinc calcined sand is selectively leached through the mechanical activation method, and the flow process is as follows: figure 2 shown.
[0035] (1) Combine zinc calcine with Na 2 SO 3 Add 50 g: 0.04 mol into the spherical zirconia grinding tank together for mechanical activation, add ball milling balls according to the ball-to-material ratio of 1:2, set the frequency at 30 Hz, and obtain mixture A after ball milling for 2 h; prepare a certain volume of concentration H at 60 g / L 2 SO 4 The solution is used as the leaching solution. According to the solid-liquid ratio of 100 g / L (the ratio of the mass of zinc calcine to the volume of the leaching solution), weigh a certain amount of mixture A, and slowly add the weighed mixture A to H under stirring. 2 SO 4 In the solution, mixed system B was obtained after 120 min of reaction;
[0036] (2) After suction filtration and drying, the leaching amount of zinc was 31.24 g, and the lea...
Embodiment 3
[0038] In this embodiment, the zinc in the zinc calcined sand is selectively leached through the mechanical activation method, and the flow process is as follows: figure 2 shown.
[0039] (1) Combine zinc calcine with Na 2 SO 3 Add the ratio of 50 g : 0.04 mol into the zirconia ball mill jar for mechanical activation together, add ball mill balls according to the ball-to-material ratio of 1 : 2, set the frequency to 30 Hz, and obtain mixture A after ball milling for 4 h; prepare a certain volume concentration of 60 g / L H 2 SO 4 solution, according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 100 g / L (the ratio of the mass of the zinc calcine to the volume of the leaching solution), weigh a certain amount of mixture A, and slowly add the weighed mixture A into the sulfuric acid solution under stirring, and react Mixed system B was obtained after 120min;
[0040] (2) After suction filtration and drying, the leaching amount of zinc was 33.15 g, and the leaching rate of zinc was calculat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com