Magnetic parking sensor
A sensor and parking space technology, applied in the field of calculating the availability of parking spaces, manufacturing magnetic parking sensors, and computer program products, can solve the problems of manufacturing cost and maintenance cost constraints, and achieve the effect of long running time and high detection accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] The core idea of the present invention is especially to propose a low-cost magnetic parking sensor based on magnetic signal analysis.
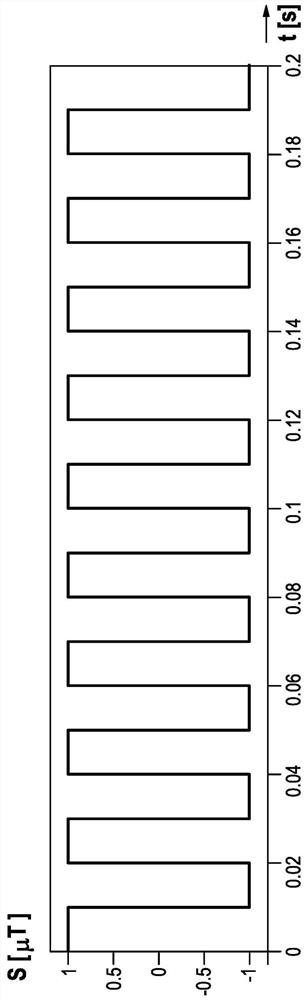
[0041] figure 1 The ideal time course of the signal S of a magnetic parking sensor (not shown) is shown. It can be seen that the signal S is ideally rectangular, wherein the upper value of the rectangular signal represents the occupied state of the parking space, and the lower value of the rectangular signal represents the free state of the parking space. Obviously, the assignments mentioned can also be reversed (ie upper values correspond to idle states, lower values correspond to occupied states, not shown). In this case, the variability of the signal S is 1.
[0042] In contrast, figure 2 The actual time course of the signal S of the magnetic parking sensor is shown. It can be seen that the signal is essentially strongly oscillating but has a rectangular component, which is caused, for example, by geomagnetic influences, e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com