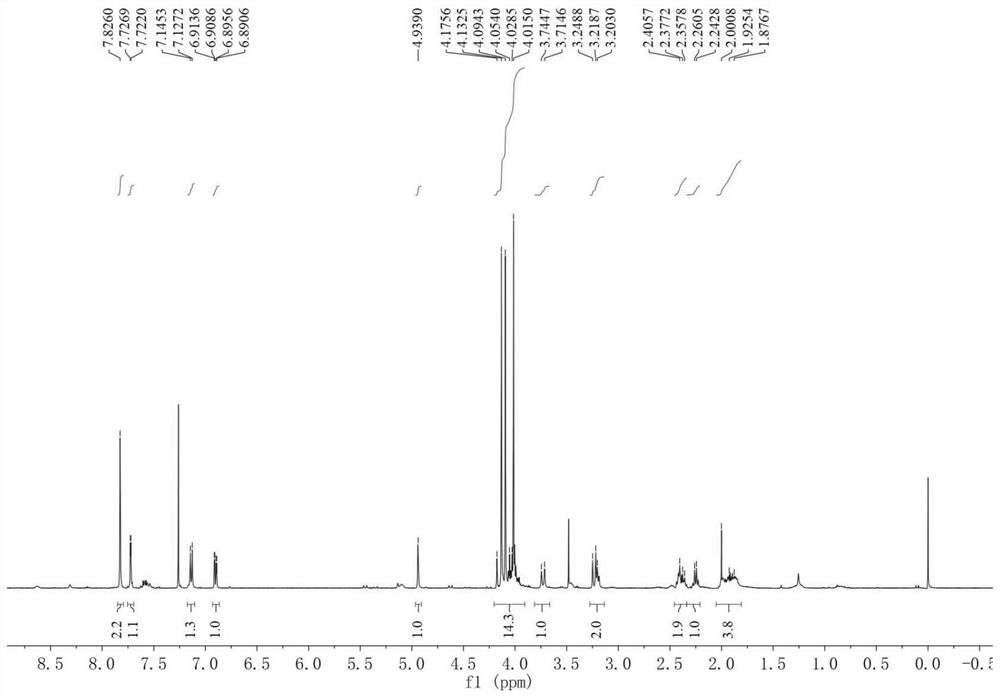
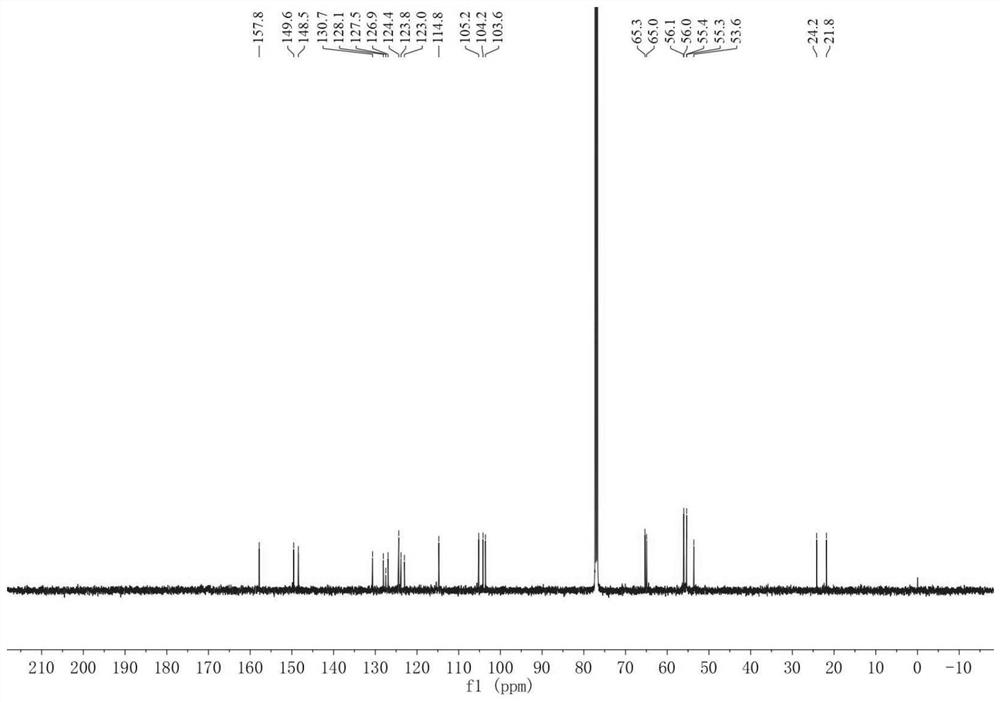
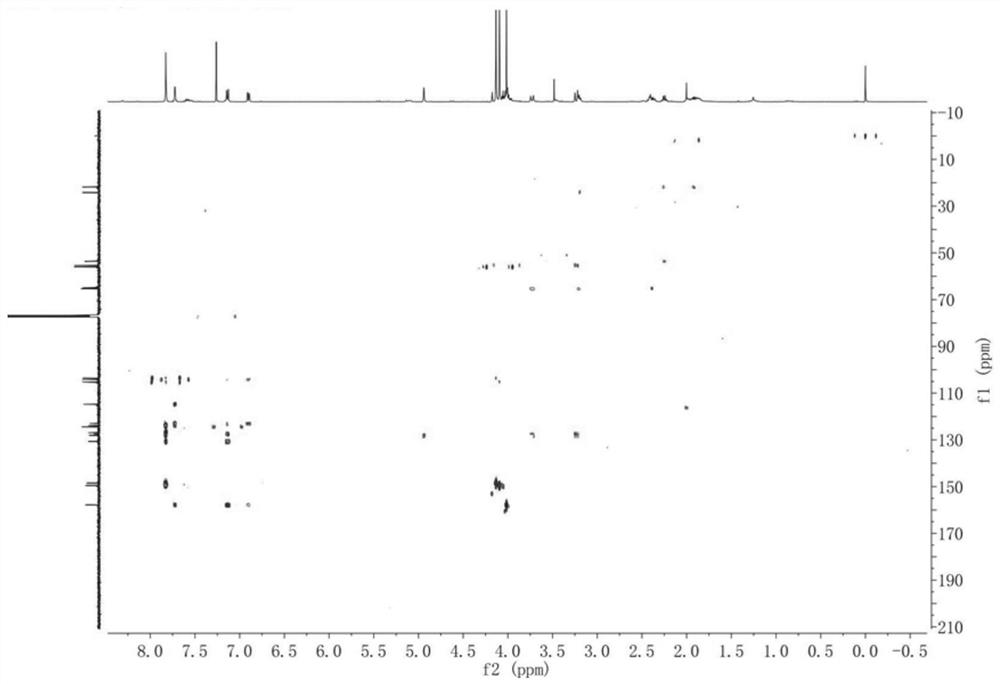
Liver cancer cell inhibitor
A liver cancer cell and inhibitor technology, applied in medical preparations containing active ingredients, organic active ingredients, drug combinations, etc., can solve problems such as high recurrence rate, poor prognosis, and limited treatment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] Embodiment 1, HTBPI and / or BA1 anti-liver cancer activity experiment
[0057] 1. Preparation of liver cancer cell inhibitors
[0058] This embodiment provides three liver cancer cell inhibitors, namely inhibitor B, inhibitor H and inhibitor HTBPI+BA1. The active ingredient of inhibitor B is BA1, the active ingredient of inhibitor H is HTBPI, and the active ingredient of inhibitor HTBPI+BA1 is BA1 and HTBPI. In the inhibitor HTBPI+BA1, the molar ratio of BA1 and HTBPI is 1:2000. The preparation methods of these 3 liver cancer cell inhibitors are as follows:
[0059] 1.1 Preparation of Inhibitor H
[0060]HTBPI was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to prepare a 10 mmol / L stock solution, and stored in an aliquot at -20°C, and diluted with DMEM medium containing 10% FBS and 1% penicillin / streptomycin. The stock solution is used to obtain the HTBPI solution, which is the inhibitor H. In the HTBPI solution, the HTBPI content is 40 μmol / L (40000 nmol / L).
[0061] 1....
Embodiment 2
[0083] Embodiment 2, HTBPI anti-liver cancer activity
[0084]1. HTBPI inhibits the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes the apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma
[0085] The cell viability was measured by CCK-8 method, and the growth inhibitory effect of HTBPI on two typical human liver cancer cell lines (HepG2, Hep3B) was analyzed. HepG2 and Hep3B cells were planted in the logarithmic growth phase, and then treated with HTBPI 0, 2.5, 5, 10, and 20 μM for 24 hours, and the cell viability was measured by the CCK-8 method. The results showed that HTBPI-treated liver cancer Cell viability had a time-dependent downward trend ( Figure 7 ). The HepG2 and Hep3B treated with HTBPI for 24 hours were taken for monoclonal formation test, and the results showed that HTBPI treated HepG2 and Hep3B for 24 hours could significantly inhibit the cell proliferation of HepG2 and Hep3B ( Figure 8 , the blank group was treated with 0 μM HTBPI for 24 hours, and the HTBPI group was ...
Embodiment 3
[0095] Example 3. Inhibition of autophagy can further promote the apoptosis of HTBPI-induced liver cancer cells
[0096] To study the relationship between apoptosis and autophagy, it was found in this study that the autophagy inhibitor BA1 can further promote the apoptosis of HCC cells induced by HTBPI ( Figure 14 ). The specific method is as follows: take the control treated cells of HepG2 in Example 1, the HTBPI treated cells of HepG2 alone, the BA1 treated cells of HepG2 alone, the HTBPI and BA1 combined treated cells of HepG2, the controlled treated cells of Hep3B, the HTBPI treated cells of Hep3B alone , BA1 of Hep3B treated cells alone and HTBPI of Hep3B combined with BA1 and analyzed by Western blot.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com