Dual inhibitor targeting JAK/STAT and NF kappa B signal channels and application thereof
A dual inhibitor and signaling pathway technology, applied in medical preparations containing active ingredients, anti-inflammatory agents, non-central analgesics, etc., to achieve the effect of improving survival rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Example 1 Verification of the inhibitory effect of L971-0101 on JAK / STAT and NFκB signaling
[0050] Based on the screening of STAT3-driven luciferase reporter system, L971-0101 was obtained, and the firefly luciferase activity assay method and cell viability assay method (as above S1, S6 and S7 methods) were used to verify and evaluate the inhibition of L971-0101 on STAT3 signaling specificity.
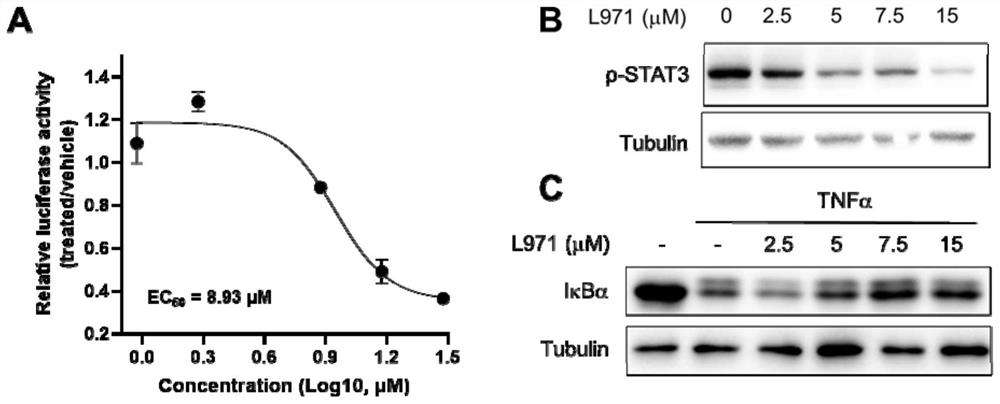
[0051] Such as figure 1 As shown in A, it was found that L971-0101 had a concentration-dependent effect on luciferase activity (EC50=8.93μM), and L971-0101 had a significant inhibitory effect on STAT3 signaling. The effect of L971-0101 on STAT3 in prostate cancer cell line DU145 was detected in vitro Phosphorylation and effects of TNFα-induced IκB degradation in the cervical cancer cell line Hela.
[0052] Such as figure 1 As shown in B, L971-0101 can dose-dependently inhibit the constitutive activation of STAT3 in the concentration range of 0.94 μM, 1.88 μM, 3.75 μM, 7.5 μ...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2 Verification of the effect of L971-0101 on inhibiting JAK / STAT and NFκB signaling in peritoneal macrophages
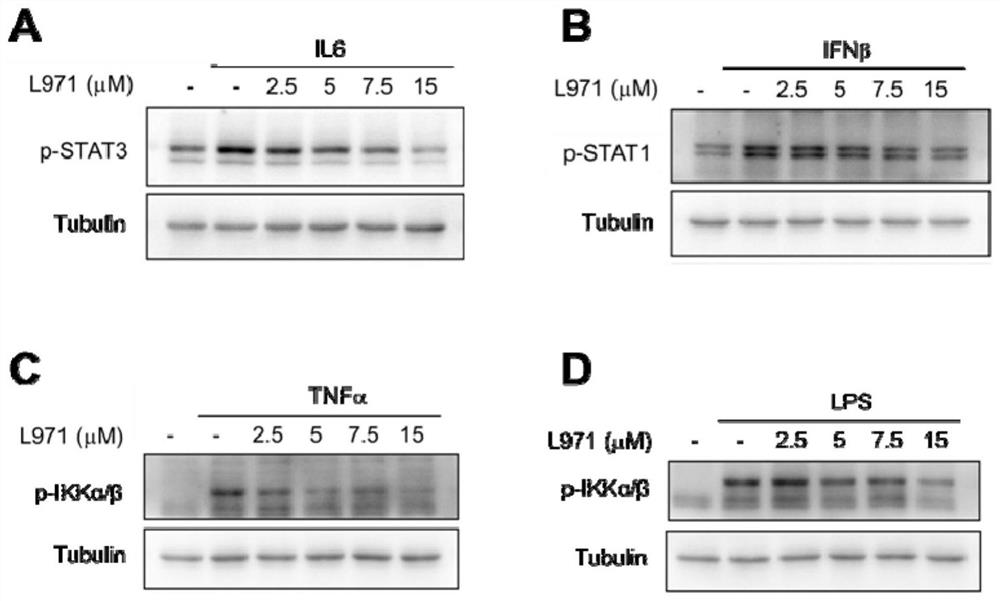
[0054] JAK / STAT and NFκB signaling are the regulatory centers that coordinate immune and inflammatory responses. In the classic JAK / STAT pathway, cytokines such as IL6 and interferon can induce the activation of STAT3 and STAT1 (as in methods S1, S2 and S3 above). Under IL6 stimulation, L971-0101 could dose-dependently inhibit the activation of STAT3 in mouse primary peritoneal macrophages in the concentration range of 2.5 μM, 5 μM, 7.5 μM, and 15 μM ( figure 2 A). L971-0101 also inhibited IFNβ-induced STAT1 phosphorylation in a dose-dependent manner in the concentration range of 2.5 μM, 5 μM, 7.5 μM, and 15 μM ( figure 2 B). It was further found that L971-0101 also inhibited the production of TNFα ( figure 2 C) and LPS ( figure 2 D) Induced phosphorylation of IKK.
Embodiment 3
[0055] Example 3 Verification that L971-0101 inhibits the downstream gene expression of JAK / STAT and NFκB signaling in peritoneal macrophages
[0056] Since LPS can sequentially activate JAK / STAT and NFκB signaling, the expression of their downstream genes was also detected (as in methods S1 and S4 above).
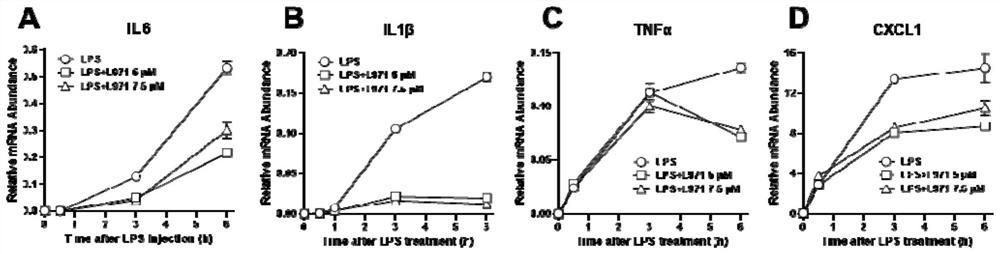
[0057] The results showed that 5 μM and 7.5 μM L971-0101 could inhibit the IL 6 induced by LPS stimulation at 3 h and 6 h ( image 3 A), IL 1β ( image 3 B) and CXCL1 ( image 3 D) expression, and inhibition of TNFα induced by 6h LPS stimulation ( image 3 C) Expression. The results showed that L971-0101 may play an anti-inflammatory role by inhibiting JAK / STAT and NFκB signaling and their downstream gene expression in peritoneal macrophages.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com